Setting up Talos within DataOS¶
This section involves a step-by-step guide to set up Talos within DataOS enviroment using Service Resource.
Pre-requisite¶
Set up the Talos project folder or you can download the following template and initialize it with Bitbucket.
Following are the steps to initialize the directory with Bitbucket, Assuming you have Git installed on your local machine:
-
Locally, navigate to the root directory of your existing source.
-
Initialize the project by running the following commands in the terminal:
git init
git add --all
git commit -m "Initial Commit"
Log into Bitbucket Server and create a new repository.
-
Locate the clone URL in the nav panel on the left (for example: https://username@your.bitbucket.domain:7999 /yourproject/repo.git).
-
Push your files to the repository by running the following commands in the terminal (change the URL accordingly):
git remote add origin https://username@your.bitbucket.domain:7999/yourproject/repo.git
git push -u origin master
Done! Your repository is now available in Bitbucket Server.
Steps¶
Connect to the data source¶
Open the repository on your preferred code editor. Navigate to the setup folder and open the config.yaml manifest file which will contain the Talos app name, description, version, authentication details, and source connection information. Within this file, update the attributes for name, description, version, DataOS context, source name, and source type to ensure they accurately reflect your specific configurations and align with requirements.
name: ${{superstore}}
description: ${{A talos-depot-postgres app}} # description
version: 0.1.25 # talos image version
auth:
userGroups:
- name: datadev
description: data dev group
includes:
- users:id:iamgroot
- users:id:thisisthor
- name: default
description: Default group to accept everyone
includes: "*"
logLevel: ${{'DEBUG'}}
sources: # source details
- name: ${{snowflakedepot}} # source name
type: ${{depot}} # source type
To know more information about each attribute, please refer to this.
Connect to the DataOS environment¶
Open the docker-compose.yaml manifest file and update it by adding your DataOS username and API key. Enter your DataOS username in the DATAOS_RUN_AS_USER field and your DataOS API key in the DATAOS_RUN_AS_APIKEY field.
version: "2.2"
services:
talos:
image: rubiklabs/talos:0.1.6
ports:
- "3000:3000"
volumes:
- .:/etc/dataos/work
environment:
DATAOS_RUN_AS_USER: ${{iamgroot}}
DATAOS_RUN_AS_APIKEY: ${{dG9rZW5fYWRtaXR0ZGHHJ987uYXR1cmFsbHlfZW5hYmxpbmdfb3J5eC5lODg2MjIyZC05NDMwLTQ4MWEtYjU3MC01YTJiZWY5MjI5OGE=}}
DATAOS_FQDN: ${{liberal-donkey.dataos.app}}
tty: true
To know more about each attribute, please refer to this.
Writing SQL templates¶
Open the apis folder within the setup directory and access the table.sql and table.yaml files. Update the SQL queries in table.sql and modify the urlPath, description, and source fields in table.yaml to accurately reflect your API's data access paths and configuration details. Ensure that both the queries and the YAML configuration are properly aligned with your API requirements. Additionally, you may add multiple SQL files and their corresponding manifest files within the apis folder as needed.
urlPath: /table # output path
description: product list # description
source: ${{snowflakedepot}} # source name
To know more about each attribute, please refer to this.
Push the changes¶
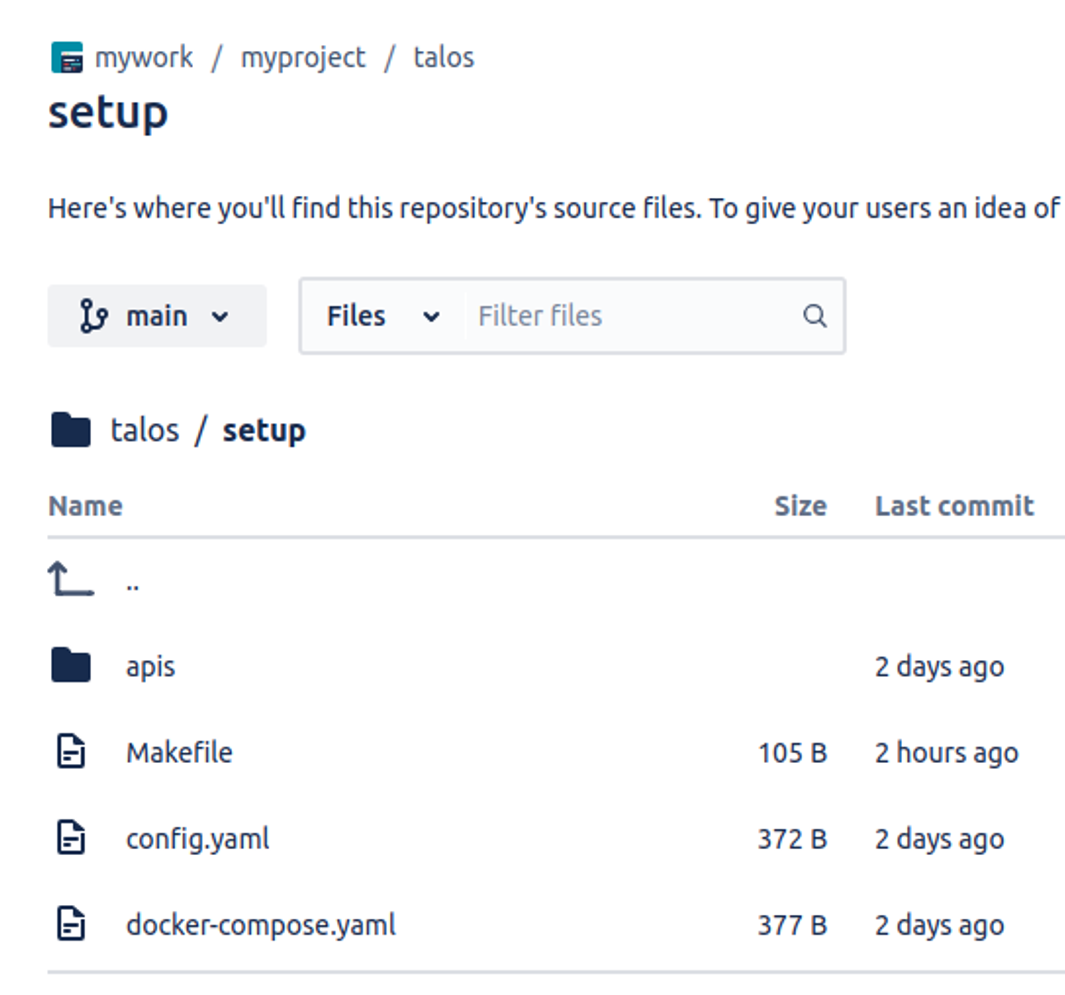
Push the changes to your working bitbucket repository as shown below:
Create an Instance Secret¶
To run it as a Service, create an Instance Secret to store your Bitbucket credentials. This step ensures that the necessary authentication details are securely stored and accessible for the Service.
name: ${{bitrepo}}-r
version: v1
type: instance-secret
description: ${{"Bitbucket credentials"}}
layer: ${{user}}
instance-secret:
type: ${{key-value}}
acl: ${{r}}
data:
GITSYNC_USERNAME: ${{"iamgroot7340"}}# Bitbucket username
GITSYNC_PASSWORD: ${{"ATBBe2we5UPdGVthtEHnjkLDHL7443AC"}}# Bitbukcet app password
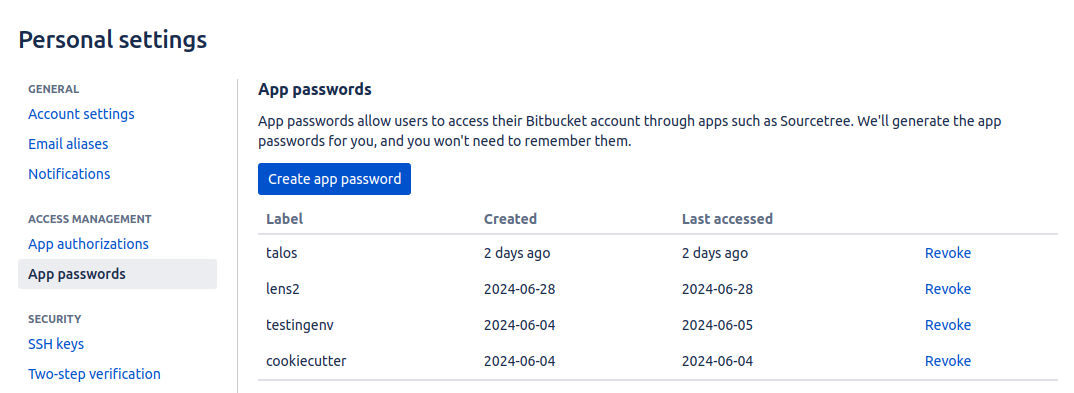
To create an app password in Bitbucket follow the below steps:
- Go to settings, then click on Personal Bitbucket settings.
-
Go to App passwords create one and paste the password into your Instance Secret manifest file.
Apply the Instance Secret manifest file by executing the below command:
To know more about Instance Secret, please refer to this.
Create a Talos Service manifest file¶
-
Now create a manifest file for the Service as shown below.
name: ${{talos-test}} # service name version: ${{v1}} # version type: service # resource type tags: # tags - ${{service}} - ${{dataos:type:resource}} - ${{dataos:resource:service}} - ${{dataos:layer:user}} description: ${{Talos Service}} workspace: ${{public}} service: # service specific section servicePort: 3000 ingress: enabled: true stripPath: true path: /talos/${{workspace}}:${{talos-test}} # service name noAuthentication: true replicas: ${{1}} logLevel: ${{DEBUG}} compute: runnable-default envs: TALOS_SCHEMA_PATH: ${{talos/setup}} TALOS_BASE_PATH: /talos/public:${{talos-test}} resources: requests: cpu: ${{100m}} memory: ${{128Mi}} limits: cpu: ${{500m}} memory: ${{512Mi}} stack: talos:2.0 dataosSecrets: - name: ${{bitrepo-r}} allKeys: true stackSpec: repo: url: ${{https://bitbucket.org/mywork15/talos/}} projectDirectory: ${{talos/setup}} syncFlags: - '--ref=main'To know more about each attribute, please refer to this.
-
Apply the Service manifest by executing the below command:
-
To check if the service is running successfully, execute the following command.
Successful execution will look like the following:
EBUG [CORE] config: TimeZone = Etc/UTC 2024-07-31 08:51:12.566 DEBUG [SERVE] Data source initialized 2024-07-31 08:51:12.567 DEBUG [SERVE] Initializing data source: pg 2024-07-31 08:51:12.567 DEBUG [SERVE] Data source pg initialized 2024-07-31 08:51:12.567 DEBUG [SERVE] Initializing data source: redshift 2024-07-31 08:51:12.567 DEBUG [SERVE] Data source redshift initialized 2024-07-31 08:51:12.568 DEBUG [SERVE] Initializing data source: snowflake 2024-07-31 08:51:12.568 DEBUG [CORE] Initializing profile: snowflake using snowflake driver 2024-07-31 08:51:12.681 DEBUG [CORE] Profile snowflake initialized 2024-07-31 08:51:12.681 DEBUG [SERVE] Data source snowflake initialized 2024-07-31 08:51:12.682 INFO [SERVE] Start to load and schedule prefetched data results from data sources to cache layer... 2024-07-31 08:51:12.689 DEBUG [SERVE] profile: snowflake, allow: * 2024-07-31 08:51:12.690 DEBUG [SERVE] profile: talos.cache, allow: * 2024-07-31 08:51:12.696 DEBUG [CORE] Authenticator: { "heimdallUrl": "https://liberal-donkey.dataos.app/heimdall", "userGroups": [ { "name": "default", "description": "auto-generated default group to include everyone", "includes": "*" } ] } 2024-07-31 08:51:12.702 INFO [CLI] 🚀 Server is listening at port 3000.
Good to go!¶
-
Now you can access the data on the API endpoint using Postman, as shown below:
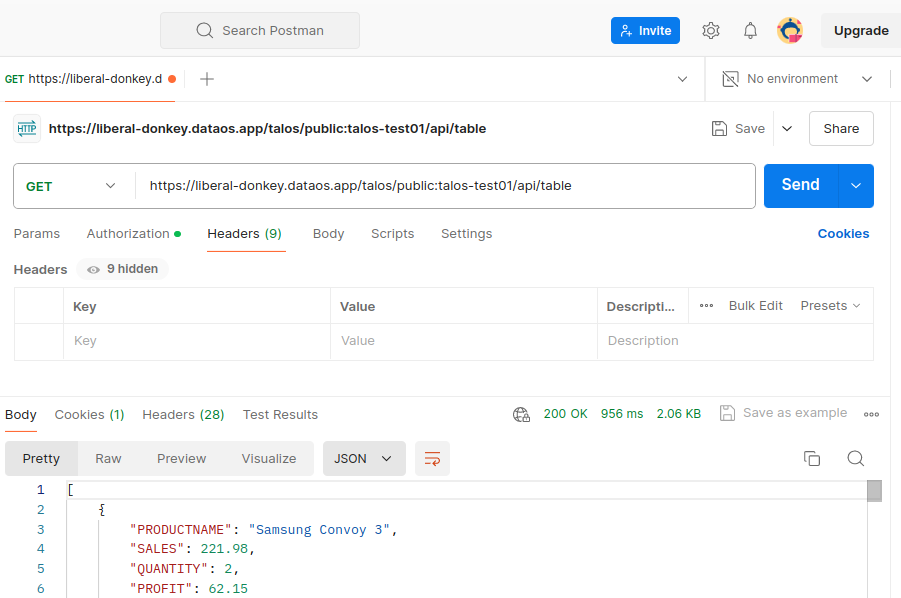
You can even hit the endpoint
/doc/postman?apikey='xxxxxxxxx'to download the postman collection and import the.jsoncollection into postman. -
Authenticate the API endpoints by passing the API Key on DataOS CLI, as query param as shown below.
Additional steps¶
Caching datasets¶
Talos allows you to cache the dataset to improve the performance and efficiency of your API queries. With the {% cache %} tag, you can query results directly from the cache layer storage, reducing the need for repeated queries to the data source. To explore how to use this feature effectively, please refer to this.
API documentation¶
Talos allows you to automatically generate and serve the API documentation. To automate API documentation generation, please refer to this.
Data governance¶
You can govern data access based on user groups, allowing you to control the level of data visibility and interaction according to each group's role. For more detailed information on how to configure access controls for user groups, please refer to this.
Data masking¶
With Talos, you can mask the data for the API endpoint by defining user groups on their segments and dimensions. To explore more about data masking in Talos, please refer to this.
Handling error¶
When the template encounters an error during execution, Talos halts further execution and sends an error code to the user, rather than returning query results. To learn more about error handling, please refer to this.
Monitoring metrics¶
You can monitor the real-time updates on API metrics through the /metrics endpoint. To enable monitoring feature, please refer to this.
Adding validators¶
Validators are tools used to ensure that the input parameters of API requests meet predefined criteria and formats before they are processed. Validators enforce rules on the data provided by users, helping to maintain data integrity, improve security, and ensure consistent behavior of the API. To add validators, please refer to this.