Lens Query¶
The Lens can be queried by the end-user using Lens Queries which are essentially abstracted SQL queries. The query API exposes the Lens, enabling the end-user to query it. Upon defining and deploying a data model, you can start querying the model. Users with limited SQL proficiency can explore the model using Lens Explorer - a low code, intuitive, drag-and-drop data exploration utility.
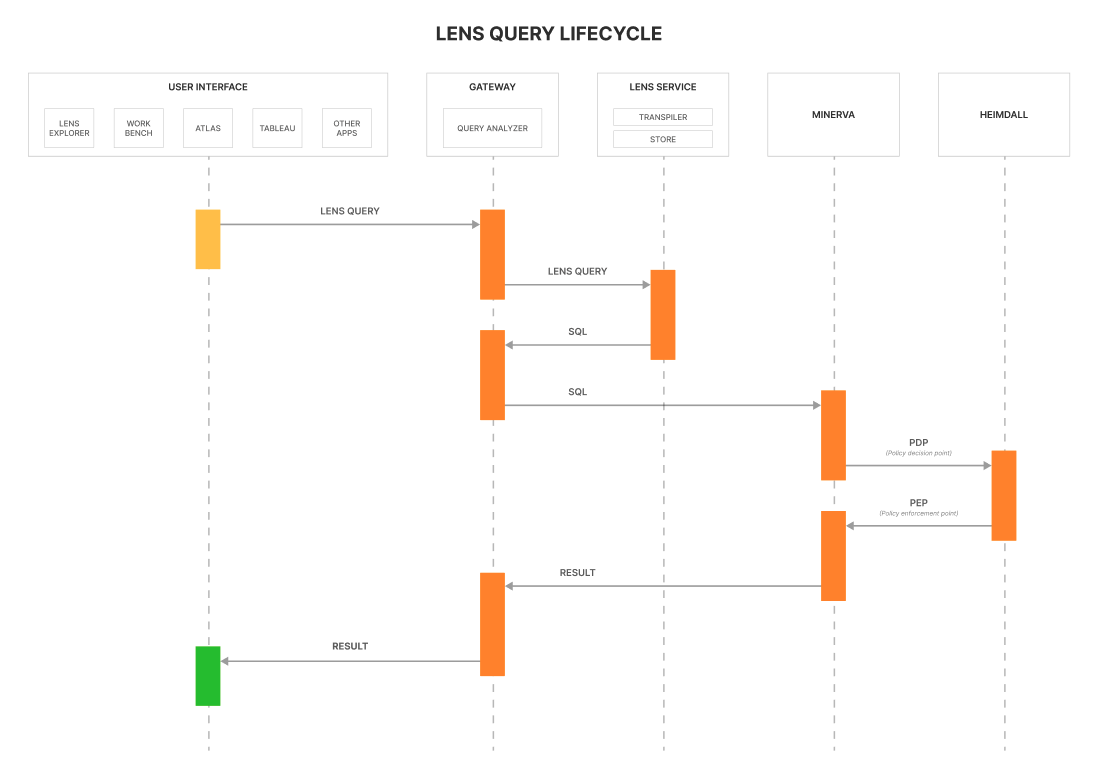
How does a Lens Query gets executed?¶
Currently, one can access the Lens service via Gateway. Queries from various interfaces like Lens Explorer, Workbench, Atlas, Tableau, Power BI, etc., land on Gateway. Gateway analyses each incoming query and decides whether to invoke Lens Service or not. If the service has to be used, Gateway will send the query text to Lens Service, and the transpiler within the Lens Service will return the expanded SQL query to the Gateway. After receiving the expanded SQL query, Gateway sends it to Minerva for execution. Minerva, with the help of Heimdall, implements policies and returns the governed result to the Gateway.
Lens Query Grammar¶
Lens Query Language (LQL) is a low code SQL (Structured Query Language) that’s powered with SQL capabilities. With the help of LQL, you can query a Lens from the workbenchor BI tools such as Atlas, Power BI, Tableau etc.
In addition to specifying the Lens to query, the lens grammar primarily consists of straightforward abstract SQL functions.
Clauses¶
| LQL Clause | Description |
|---|---|
SELECT |
Just like in SQL, you can select the entity.dimensions or entity.measures that will appear in the resulting view. |
WHERE |
Use where to filter your results based on measures and dimensions. |
DATE |
Name of the date dimension, used to evaluate range and granularity. |
RANGE |
To filter date dimensions to a specified range. |
GRANULARITY |
Date dimensions are grouped according to the level of granularity set. You can add the following granularity -second, minute, hour, day, week, month, year |
GROUP BY |
Group rows on the basis of selected dimensions. It’s just like your SQL group by clause, you can only group by dimensions. |
ORDER BY |
Behaves like SQL order by clause; you can order your resultant rows either on the basis of dimension or measures. |
LIMIT |
To limit the number of rows count returned. |
OFFSET |
The offset rows are skipped before the rows after offset is returned. |
Keywords to Specify Range¶
To aptly define the range, you can use any of the following keywords -
last [0-9] days|week|year|month|quarternext [0-9] days|week|year|month|quartertodayyesterdaythis days|week|year|month|quarterlast days|week|year|month|quarter
Lens Query Example¶
Below is an example of a Lens query that extracts quantities sold and revenue generated in Beach, Fort, and Somerset cities.
LENS (
SELECT
'order.totalOrders',
'orderLine.totalQuantities'
FROM retail
WHERE
'retailer.city' IN ("Beach", "Fort", "Somerset")
AND (
"orderLine.quantities" < 12
AND "orderLine.quantities" > 15
OR "orderLine.quantities" > 1600
)
DATE 'order.order_datetime'
RANGE ('last quarter')
GRANULARITY ('week')
TIMEZONE ('Asia/Kolkata')
GROUP BY 'retailer.state'
ORDER BY 'order.totalOrders' DESC
LIMIT 100
OFFSET 10
# If you do not pass value for Params, it will take a default value
PARAMS(key = January)
)
Utilities¶
List all Lenses¶
Using List Lenses you can list all the lenses.
List all entities within a Lens¶
Using Select "*" you can list all the entities within a lens.
List row-level details of an entity¶
Using entity_name.* you can list row-level details for a specific entity. It’s functionally similar to ‘select *’.
List row_count for an entity¶
With entity_name.# you can list the row count for a specific entity. Functionality is similar to ‘count(*)’.
Apply ORDER BY, LIMIT, and OFFSET¶
You can add the ORDER BY, LIMIT, and OFFSET in the Lens Query. It will apply ORDER BY on selected measure and selected dimensions.
SELECT
*
FROM
LENS (
SELECT
"order_placed.recency",
"order_placed.frequency",
"order_placed.monetary",
"order_placed.activity_uuid",
"order_placed.entity_id",
"order_placed.order_id"
FROM
c360
ORDER BY
'order_placed.recency' ASC,
'order_placed.frequency' DESC
LIMIT
50
OFFSET
50
)
Lens Query Language (LQL) Errors and Solutions¶
When you run a Lens query on Workbench, Notebook or any other interface like BI tools, you might come across errors concerning syntax or case sensitivity in date filters. These issues can prevent the Lens query from functioning properly. Refer to the following document for the common errors and their solutions.