Setting up Talos within DataOS¶
This section provides a guide and reference for setting up Talos within DataOS environment. It includes configuration steps, and required access permissions for execution.
Pre-requisite¶
-
Set up the Talos project folder in the following manner:
Or Download the following “Template” and initialize it with any Git-based source control services such as bitbucket, github etc. -
The following steps outline the process for initializing a directory with Bitbucket, assuming Git is installed on the local machine:
- Navigate to the root directory of the existing source code locally.
- Initialize the project by running the following commands in the terminal:
git init git add --all git commit -m "Initial Commit" Log into Bitbucket(or respective source control service) Server and create a new repository.- Locate the clone URL in the nav panel on the left (for example: https://username@your.bitbucket.domain:7999/yourproject/repo.git).
- Push your files to the repository by running the following commands in the terminal (change the URL accordingly):
git remote add origin https://username@your.bitbucket.domain:7999/yourproject/repo.git git push -u origin masterThe repository has been successfully created in Bitbucket Server.
-
Access Permissions in DataOS
If access is managed through use cases, following use cases are required to run Talos:
- Read Talos
- Manage Talos
If access is managed through role tags, following roles are required to run Talos:
roles:id:data-devroles:id:system-devroles:id:user
Use the following command to check assigned roles:
dataos-ctl user get # expected output INFO[0000] 😃 user get... INFO[0000] 😃 user get...complete NAME │ ID │ TYPE │ EMAIL │ TAGS ───────────────┼─────────────┼────────┼──────────────────────┼───────────────────────────────── Jhon Doe │ johndoe │ person │ jhon.doe@example.com │ roles:id:data-dev, │ │ │ │ roles:id:system-dev, │ │ │ │ roles:id:user, │ │ │ │ users:id:johndoeIf any required tags or use cases are missing, contact a DataOS Operator.
Steps¶
Connect to the data source¶
Open the repository in the preferred code editor. Navigate to the setup folder and open the config.yaml manifest file. This file contains details such as the Talos app name, description, version, authentication information, and source connection settings.
name: ${{superstore}}
description: ${{A talos-depot-snowflake app}} # description
version: "0.1.26-test" # The version of the Talos(string)
auth:
userGroups:
- name: datadev
description: data dev group
includes:
- users:id:iamgroot
- users:id:thisisthor
- name: default
description: Default group to accept everyone
includes: "*"
logLevel: ${{'DEBUG'}}
sources: # source details
- name: ${{snowflakedepot}} # source name
type: ${{depot}} # source type
Update the following attributes within the file to align with the required configurations:
- name: Set the Talos app name.
- description: Provide a description of the Talos application.
- version: Specify the application version.
- source name: Update the source system name(e.g. mysql, postgres, lens etc.).
- source type: Define the type of source system being used(lens, depot, flash etc.).
To know more information about each attribute, please refer to the Configuration Page.
Writing SQL templates¶
Open the apis folder within the setup directory and access the table.sql and table.yaml files. Update the SQL queries in table.sql and modify the urlPath, description, and source fields in table.yaml to accurately reflect the API's data access paths and configuration details.
urlPath: /table # output path
description: product list # description
source: ${{snowflakedepot}} # source name same as mentioned in the config.yaml
Ensure that both the queries and the YAML configuration are properly aligned with the API requirements.
Additionally, multiple SQL files and their corresponding manifest files can be added within the apis folder as needed. This ensures modularity and maintainability of query definitions.
To know more information about each attribute, please refer to the Configuration Page.Push the changes¶
Push the changes to the working source control service (here 'bitbucket') repository as shown below:
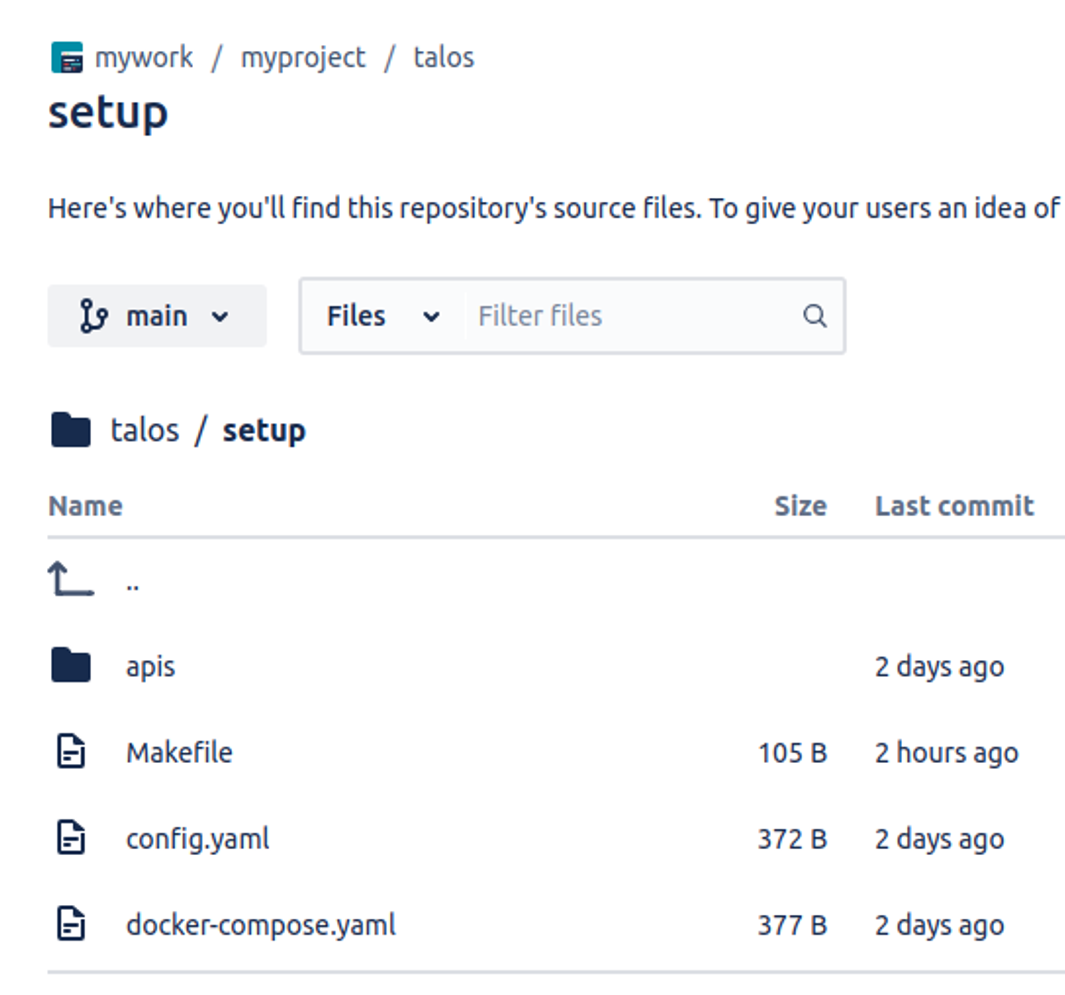
Create an Instance Secret¶
To run it as a Service, create an Instance Secret to store the Bitbucket credentials. This step ensures that the necessary authentication details are securely stored and accessible for the Service.
name: ${{bitrepo}}-r
version: v1
type: instance-secret
description: ${{"Bitbucket credentials"}}
layer: ${{user}}
instance-secret:
type: ${{key-value}}
acl: ${{r}}
data:
GITSYNC_USERNAME: ${{"iamgroot7340"}} # Bitbucket username
GITSYNC_PASSWORD: ${{"ATBBe2we5UPdGVthtEHnjkLDHL7443AC"}} # Bitbukcet app password
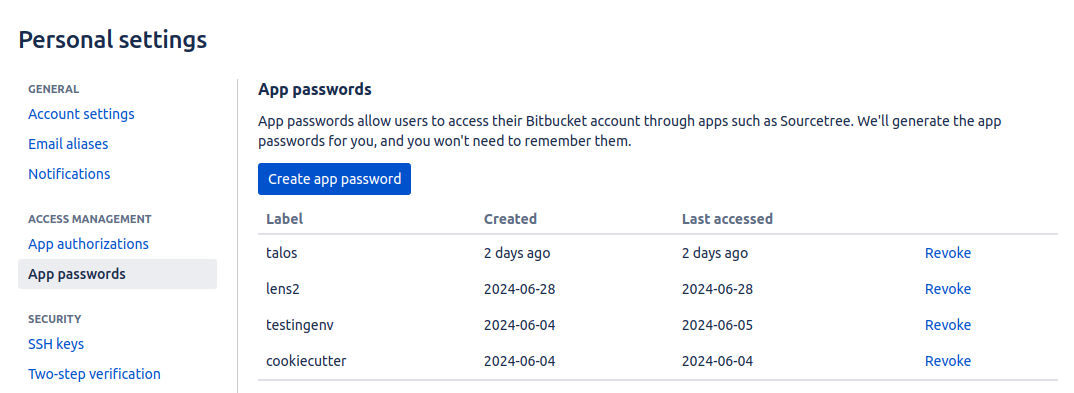
To create an app password in Bitbucket follow the below steps:
- Go to settings, then click on Personal Bitbucket settings.
-
Go to App passwords create one and paste the password into the Instance Secret manifest file.
Apply the Instance Secret manifest file by executing the below command:
For more information about Instance Secret, please refer to the Instance Secret Page.
Create a Talos Service manifest file¶
-
Now create a manifest file for the Service as shown below.
name: ${{talos-test}} # service name version: ${{v1}} # version type: service # resource type tags: # tags - ${{service}} - ${{dataos:type:resource}} - ${{dataos:resource:service}} - ${{dataos:layer:user}} description: ${{Talos Service}} workspace: ${{public}} service: # service specific section servicePort: 3000 ingress: enabled: true stripPath: true path: /talos/${{workspace}}:${{talos-test}} # service name noAuthentication: true replicas: ${{1}} logLevel: ${{DEBUG}} compute: runnable-default envs: TALOS_SCHEMA_PATH: ${{talos/setup}} TALOS_BASE_PATH: /talos/public:${{talos-test}} resources: requests: cpu: ${{100m}} memory: ${{128Mi}} limits: cpu: ${{500m}} memory: ${{512Mi}} stack: talos:2.0 dataosSecrets: - name: ${{bitrepo-r}} allKeys: true stackSpec: repo: url: ${{https://bitbucket.org/mywork15/talos/}} projectDirectory: ${{talos/setup}} syncFlags: - '--ref=main'To know more information about each attribute, please refer to the Configuration Page.
-
Apply the Service manifest by executing the below command:
-
To check if the service is running successfully, execute the following command.
The successful execution is displayed above and varies based on the sources, methods, ports, etc.dataos-ctl resource log -t service -n ${{service-name}} -w ${{workspace}} # Expected Output INFO[0000] 📃 log(public)... INFO[0001] 📃 log(public)...complete NODE NAME │ CONTAINER NAME │ ERROR ───────────────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────────┼──────── aaditest-service-zvs7-d-5dc48797c6-gs9fb │ aaditest-service-zvs7-main │ -------------------LOGS------------------- 2025-03-07 04:08:49.536 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: temp_directory = /etc/dataos/work/.worktrees/a76bec81137783ce29782bb6aa6de0856a076401/aadi-test/talos_cache.db.tmp 2025-03-07 04:08:49.536 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: threads = 1 2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: username = NULL 2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: arrow_large_buffer_size = false 2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: user = NULL 2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: wal_autocheckpoint = 16.0 MiB 2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: worker_threads = 1 2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: allocator_flush_threshold = 128.0 MiB 2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: duckdb_api = nodejs 2025-03-07 04:08:49.538 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: custom_user_agent = 2025-03-07 04:08:49.538 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: partitioned_write_flush_threshold = 524288 2025-03-07 04:08:49.538 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: enable_http_logging = false 2025-03-07 04:08:49.538 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: http_logging_output = 2025-03-07 04:08:49.538 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: binary_as_string = 2025-03-07 04:08:49.538 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: Calendar = gregorian 2025-03-07 04:08:49.539 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: TimeZone = UTC 2025-03-07 04:08:49.539 DEBUG [SERVE] Data source duckdb initialized 2025-03-07 04:08:49.539 DEBUG [SERVE] Initializing data source: pg 2025-03-07 04:08:49.539 DEBUG [CORE] Initializing profile: sivapostgresdepot using pg driver 2025-03-07 04:08:49.636 DEBUG [CORE] Profile sivapostgresdepot initialized 2025-03-07 04:08:49.636 DEBUG [CORE] Initializing profile: lens using pg driver 2025-03-07 04:08:49.789 DEBUG [CORE] Profile lens initialized 2025-03-07 04:08:49.789 DEBUG [SERVE] Data source pg initialized 2025-03-07 04:08:49.789 DEBUG [SERVE] Initializing data source: redshift 2025-03-07 04:08:49.789 DEBUG [SERVE] Data source redshift initialized 2025-03-07 04:08:49.790 DEBUG [SERVE] Initializing data source: snowflake 2025-03-07 04:08:49.790 DEBUG [SERVE] Data source snowflake initialized 2025-03-07 04:08:49.791 INFO [SERVE] Start to load and schedule prefetched data results from data sources to cache layer... 2025-03-07 04:08:49.796 DEBUG [SERVE] profile: sivapostgresdepot, allow: * 2025-03-07 04:08:49.796 DEBUG [SERVE] profile: lens, allow: * 2025-03-07 04:08:49.797 DEBUG [SERVE] profile: talos.cache, allow: * 2025-03-07 04:08:49.805 DEBUG [CORE] Authenticator: { "heimdallUrl": "https://dataos-training.dataos.app/heimdall", "ttl": 120, "userGroups": [ { "name": "default", "description": "auto-generated default group to include everyone", "includes": "*" } ] } 2025-03-07 04:08:49.810 INFO [CLI] 🚀 Server is listening at port 3000. -
The data can now be accessed through the API endpoint on platforms such as Postman, Swagger (OpenAPI Specification), and Google APIs Platform, as shown below (in Postman):
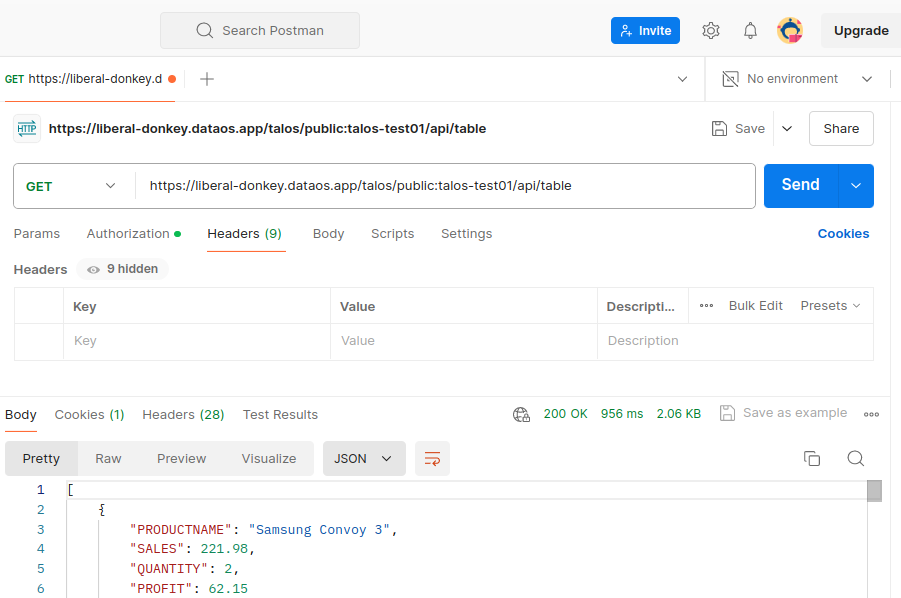
The endpoint may vary depending on the respective FQDN and repository path.
The endpoint can also be hit as “/doc/postman?apikey=xxxxxxxxxxxxx" in order to download the postman collection and import the .json collection into postman.
- Authenticate the API endpoints by passing the API Key on DataOS CLI, as query param as shown below.
Additional steps¶
Caching datasets¶
Talos supports dataset caching to improve API query performance and efficiency. Using the {% cache %} tag, query results can be retrieved directly from the cache layer storage, reducing redundant queries to the data source.Learn More.
API documentation¶
Talos enables automatic generation and serving of API documentation. To automate API documentation generation, refer to this section.
Data governance¶
Talos allows data access control based on user groups, enabling role-based data visibility and interaction restrictions. For details on configuring access controls, refer to this section.
Data masking¶
Talos supports data masking for API endpoints by defining user groups with specific segment and dimension restrictions. For more information on configuring data masking, refer to this section.
Handling error¶
If an error occurs during execution, Talos stops processing and returns an error code instead of query results. For details on error handling, refer to this section.
Monitoring metrics¶
Real-time API metrics can be monitored through the /metrics endpoint. To enable monitoring, refer to this section.
Adding validators¶
Validators enforce predefined rules and formats on API request input parameters before processing. This ensures data integrity, enhances security, and maintains consistent API behavior. For instructions on adding validators, refer to this section.