Talos for Redshift¶
Pre-requisites¶
To access the data using API from redshift, User need the following:
-
Access Permissions in DataOS: To execute a Talos Service in DataOS, verify that following role tags are assigned to the respective user:
roles:id:data-devroles:id:system-devroles:id:user
Use the following command to check assigned roles:
If any required tags are missing, contact a DataOS Operator or submit a Grant Request for role assignment.
Alternatively, if access is managed through use cases, ensure the following use cases are assigned:
- Manage Talos
- Read Talos
To validate assigned use cases, refer to the Bifrost Application's Use Cases section.
-
Pre-created Redshift Depot: Ensure that a Redshift Depot is already created with valid read access. To check the Depot go to the Metis UI of the DataOS or use the following command:
dataos-ctl get -t depot -a #expected output INFO[0000] 🔍 get... INFO[0000] 🔍 get...complete | NAME | VERSION | TYPE | WORKSPACE | STATUS | RUNTIME | OWNER | | ---------------- | ------- | ----- | --------- | ------ | ------- | ---------- | | redshiftdepot | v2alpha | depot | | active | | usertest |Template for creating redshift Depot is shown below:
name: ${{depot-name}} version: v2alpha type: depot tags: - ${{dropzone}} - ${{redshift}} owner: ${{owner-name}} layer: user depot: type: redshift description: ${{description}} # optional external: ${{true}} secrets: - name: ${{instance-secret-name}}-r allkeys: true - name: ${{instance-secret-name}}-rw allkeys: true
Steps¶
Connect to the data source¶
Create a repository, open the repository with a code editor (VS Code), and create a config.yaml manifest file and copy the below code. Update the name, description, version, dataos context, Depot name, and Depot type.
name: adventureworks
description: A talos app
version: 0.1.26
logLevel: DEBUG
auth:
userGroups:
- name: reader
description: This is a reader's group
includes:
- roles:id:data-dev
- roles:id:data-guru
excludes:
- users:id:iamgroot
- name: default
description: Default group to accept everyone
includes: "*"
metrics:
type: summary
percentiles: [ 0.5, 0.75, 0.95, 0.98, 0.99, 0.999 ]
rateLimit:
enabled: true
options:
interval:
min: 1
max: 100
delayAfter: 4
cors:
enabled: true
options:
origin: 'https://google.com'
allowMethods: 'GET'
cachePath: tmp
sources:
- name: redshiftdepot
type: depot
Similarly, for other types of Depot, the config.yaml file remains unchanged. The source name should be updated to reflect the actual Depot name. For this guide, the Tickit database set up on an AWS Redshift Depot is used as a reference.
Writing SQL templates¶
Create a folder named apis inside the same repository, then create categorypopularity.sql and categorypopularity.yaml files as shown below:
SQL Query (categorypopularity.sql)
SELECT category.catname, SUM(qtysold) AS total_tickets
FROM category
JOIN event ON category.catid = event.catid
JOIN sales ON event.eventid = sales.eventid
GROUP BY category.catname;
Manifest file Configuration (categorypopularity.yaml)
urlPath: /categories/popularity
description: Retrieve popularity metrics for event categories including total tickets sold per category.
source: redshiftdepot
To know more information about each attribute, please refer to the Configuration Page.
Push the changes¶
Push the changes to the working source control service (here ‘bitbucket’) repository as shown below:
Create a Talos Service manifest file¶
- Now create a manifest file for the Service as shown below.
name: ${{talos-test}} # service name
version: ${{v1}} # version
type: service # resource type
tags: # tags
- ${{service}}
- ${{dataos:type:resource}}
- ${{dataos:resource:service}}
- ${{dataos:layer:user}}
description: ${{Talos Service}}
workspace: ${{public}}
service: # service specific section
servicePort: 3000
ingress:
enabled: true
stripPath: true
path: /talos/${{workspace}}:${{talos-test}} # service name
noAuthentication: true
replicas: ${{1}}
logLevel: ${{DEBUG}}
compute: runnable-default
envs:
TALOS_SCHEMA_PATH: ${{talos/setup}}
TALOS_BASE_PATH: /talos/public:${{talos-test}}
resources:
requests:
cpu: ${{100m}}
memory: ${{128Mi}}
limits:
cpu: ${{500m}}
memory: ${{512Mi}}
stack: talos:2.0
dataosSecrets:
- name: ${{bitrepo-r}}
allKeys: true
stackSpec:
repo:
url: ${{https://bitbucket.org/mywork15/talos/}}
projectDirectory: ${{talos/setup}}
syncFlags:
- '--ref=main'
To know more information about each attribute, please refer to the Talos Configuration Service.
-
Apply the Service manifest by executing the below command:
-
To check if the service is running successfully, execute the following command.
Expected Output for service logs:
INFO[0000] 📃 log(public)... INFO[0001] 📃 log(public)...complete NODE NAME │ CONTAINER NAME │ ERROR ───────────────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────────┼──────── aaditest-service-zvs7-d-5dc48797c6-gs9fb │ aaditest-service-zvs7-main │ -------------------LOGS------------------- 2025-03-07 04:08:49.536 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: temp_directory = /etc/dataos/work/.worktrees/a76bec81137783ce29782bb6aa6de0856a076401/aadi-test/talos_cache.db.tmp 2025-03-07 04:08:49.536 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: threads = 1 2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: username = NULL 2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: arrow_large_buffer_size = false 2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: user = NULL 2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: wal_autocheckpoint = 16.0 MiB 2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: worker_threads = 1 2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: allocator_flush_threshold = 128.0 MiB 2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: duckdb_api = nodejs 2025-03-07 04:08:49.538 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: custom_user_agent = 2025-03-07 04:08:49.538 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: partitioned_write_flush_threshold = 524288 2025-03-07 04:08:49.538 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: enable_http_logging = false 2025-03-07 04:08:49.538 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: http_logging_output = 2025-03-07 04:08:49.538 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: binary_as_string = 2025-03-07 04:08:49.538 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: Calendar = gregorian 2025-03-07 04:08:49.539 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: TimeZone = UTC 2025-03-07 04:08:49.539 DEBUG [SERVE] Data source duckdb initialized 2025-03-07 04:08:49.539 DEBUG [SERVE] Initializing data source: pg 2025-03-07 04:08:49.539 DEBUG [CORE] Initializing profile: sivapostgresdepot using pg driver 2025-03-07 04:08:49.636 DEBUG [CORE] Profile sivapostgresdepot initialized 2025-03-07 04:08:49.636 DEBUG [CORE] Initializing profile: lens using pg driver 2025-03-07 04:08:49.789 DEBUG [CORE] Profile lens initialized 2025-03-07 04:08:49.789 DEBUG [SERVE] Data source pg initialized 2025-03-07 04:08:49.789 DEBUG [SERVE] Initializing data source: redshift 2025-03-07 04:08:49.789 DEBUG [SERVE] Data source redshift initialized 2025-03-07 04:08:49.790 DEBUG [SERVE] Initializing data source: snowflake 2025-03-07 04:08:49.790 DEBUG [SERVE] Data source snowflake initialized 2025-03-07 04:08:49.791 INFO [SERVE] Start to load and schedule prefetched data results from data sources to cache layer... 2025-03-07 04:08:49.796 DEBUG [SERVE] profile: sivapostgresdepot, allow: * 2025-03-07 04:08:49.796 DEBUG [SERVE] profile: lens, allow: * 2025-03-07 04:08:49.797 DEBUG [SERVE] profile: talos.cache, allow: * 2025-03-07 04:08:49.805 DEBUG [CORE] Authenticator: { "heimdallUrl": "https://dataos-training.dataos.app/heimdall", "ttl": 120, "userGroups": [ { "name": "default", "description": "auto-generated default group to include everyone", "includes": "*" } ] } 2025-03-07 04:08:49.810 INFO [CLI] 🚀 Server is listening at port 3000. -
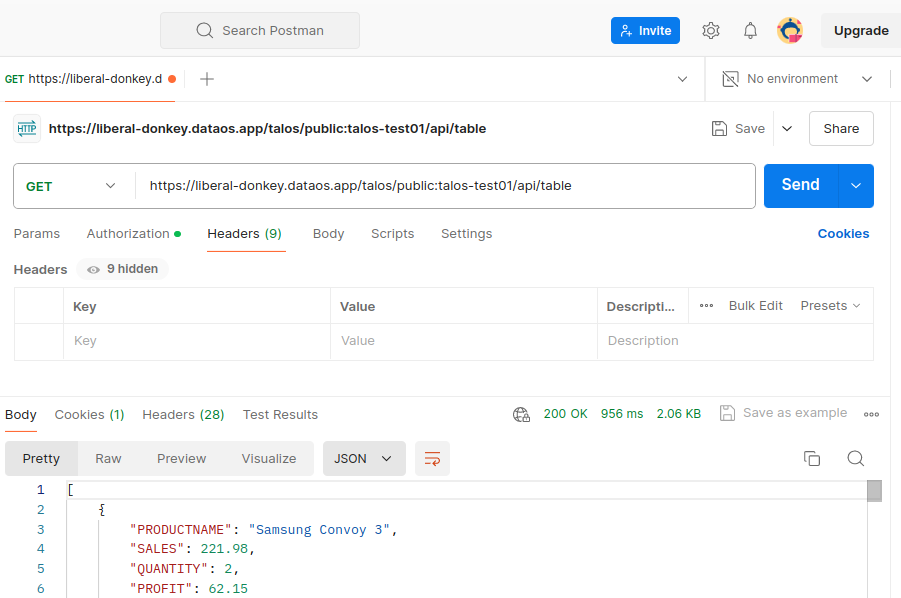
The data can now be accessed through the API endpoint on platforms such as Postman, Swagger (OpenAPI Specification), and Google APIs Platform, as shown below (in Postman):
The endpoint can also be hit as /doc/postman?apikey='xxxxxxxxx' in order to download the postman collection and import the .json collection into postman.
- Authenticate the API endpoints by passing the API Key on DataOS CLI, as query param as shown below.
Example for Redshif sample data(Tickit database)¶
The following examples illustrate different queries that can be generated by modifying the configurations in the apis folder:
-
Event details API
Manifest Configuration (
eventdetails.yaml):urlPath: /events/:id description: Retrieve detailed information for a specific event. request : - fieldName: id fieldIn: path source: redshiftSQL Query (
eventdetails.sql) -
Create all events API
Manifest Configuration (
events.yaml)urlPath: /events description: Retrieve details of all events including event ID, name, venue, category, and start time. source: redshift cache: - cacheTableName: 'event_cache' sql: 'SELECT * FROM event' source: redshiftSQL Query (
events.sql) -
Create sales by event API
Manifest Configuration (
getsalesbyevent.yaml)urlPath: /events/:id/sales description: Retrieve sales details for a specific event including ticket quantity sold, price paid, and sale time. request : - fieldName: id fieldIn: path source: redshiftSQL Query (
getsalesbyevent.sql) -
Create user purchase history API
Manifest Configuration (
getuserpurchasehistory.yaml)urlPath: /users/:bid/purchases description: Retrieve all purchases made by a specific user. request : - fieldName: bid fieldIn: path source: redshift cache: - cacheTableName: 'sales_cache' sql: 'SELECT * FROM sales' source: redshiftSQL Query (
getuserpurchasehistory.sql) -
Create venue performance API
Manifest Configuration (
venueperformance.yaml)urlPath: /venues/:id/performance description: Retrieve performance metrics for a specific venue including number of events hosted and total tickets sold. request : - fieldName: id fieldIn: path source: redshiftSQL Query (
venueperformance.sql)