Data APIs on Lens with Talos¶
This document provides step-by-step instructions for setting up Data APIs on Lens using Talos within DataOS. This document will enable users to:
- Create a config file for Talos API definition for Lens.
- Add SQL query and manifest files for API paths.
- Push the code to a hosted code repository.
- Configure an Instance Secret to securely manage code repository access.
- Define and deploy a Talos Service to set up a Data API on deployed Lens.
Prerequisites¶
- Ensure Lens is deployed in DataOS. Refer to the Lens documentation for setup instructions.
Steps¶
Step 1: Initialize a Git repository¶
- Create a new project directory.
- Initialize a Git repository within the directory.
Step 2: Prepare the configuration file¶
- In the project directory, open a code editor (e.g., Visual Studio Code).
- Create a file named
config.yamland add the following configuration:name: cross_sell_api # Replace the name with your API name description: A Data API on top of Lens using Talos. # API description version: 0.1.26 # API Version auth: userGroups: # User Groups - name: datadev description: Data dev group includes: - users:id:thor - users:id:iamgroot - name: default description: Default group to include everyone includes: "*" logLevel: 'DEBUG' # Log Level sources: - name: lens # Source name type: lens # Source Type lensName: 'public:cross-sell-affinity' # Lens Name format '<workspace>:<lens-name>' - Adjust the values for
name,description,version,heimdallUrl,userGroupsandlensNameto suit your environment. Refer to the Talos config.yaml attribute documentation for detailed descriptions.
Step 3: Add SQL query and manifest files¶
-
Inside the project directory, create a folder named
apis. -
Within the
apisfolder:-
Create the
product_affinity.sqlcontaining the SQL query: -
Create a corresponding
product_affinity.yamlmanifest file defining the API path:
-
-
Each
.sqlfile should have a matching.yamlmanifest file to ensure correct API path mappings.
Step 4: Caching the data (optional)¶
-
To cache the data, add the cache attribute inside the
product_affinity.yamlfile as shown below. -
Similarly, update the
product_affinity.sqlfile as shown in the example below.To know more about the caching in Talos, please refer to this.{% cache %} with random_cat as(select customer_id, CASE WHEN random() < 0.2 THEN 'Wines' WHEN random() < 0.4 THEN 'Meats' WHEN random() < 0.6 THEN 'Fish' WHEN random() < 0.8 THEN 'Sweet Products' ELSE 'Fruits' END AS product_category from affinity_cache) SELECT cp1.product_category AS category_1, cp2.product_category AS category_2, COUNT(DISTINCT cp1.customer_id)*4/10.0 AS product_affinity_score FROM random_cat cp1 INNER JOIN random_cat cp2 ON cp1.customer_id = cp2.customer_id AND cp1.product_category <> cp2.product_category group by 1,2 {% endcache %}
Step 5: Push the code to the repository¶
After following the above steps, push the code to the code repository. The repository structure will resemble the following:
Step 6: Configure Instance Secret¶
Info
For setups using a public code repository, this step can be skipped entirely.
In cases where the code is stored in a private code repository, Instance Secrets become necessary to securely store and access repository credentials. This enables Talos Service to sync with the repository without exposing sensitive information in the configuration files.
-
If you are using Bitbucket, to securely store Bitbucket credentials so that the Talos Service could securely access them, create an Instance Secret manifest file named
secret.ymlwith the following content:name: bitbucket-r version: v1 type: instance-secret description: "Bitbucket credentials" layer: user instance-secret: type: key-value acl: r data: GITSYNC_USERNAME: "iamgroot7340" # Replace with actual Bitbucket username GITSYNC_PASSWORD: "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuv" # Replace with Bitbucket app password -
To generate an app password in Bitbucket:
- Navigate to Settings > Personal Bitbucket settings > App passwords.
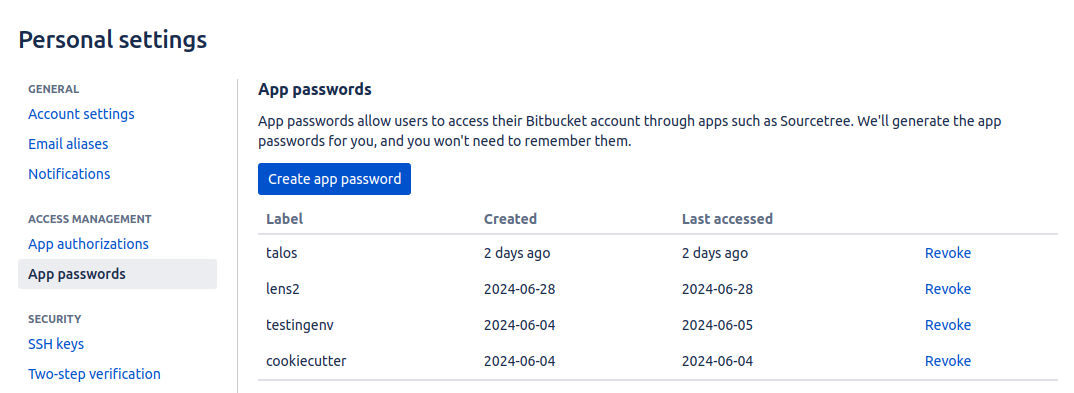
- Create a new app password and include it in
secret.yaml.
- Navigate to Settings > Personal Bitbucket settings > App passwords.
-
Apply the
secret.yamlfile to DataOS:
The process remains the same for other hosted code repository such as GitHub, and AWS Codecommit with slight variations in the data section of Instance Secret manifest file. For more details, refer to the following link.
Step 7: Define the Talos Service manifest¶
-
In the project directory, create
service.yamlto configure the Talos Service, specifying details likeservicePort,path, andresources:name: cross-sell-api version: v1 type: service tags: - service - dataos:type:resource - dataos:resource:service - dataos:layer:user description: Talos Service workspace: public service: servicePort: 3000 ingress: enabled: true stripPath: true path: /talos/public:cross-sell-api noAuthentication: false replicas: 1 logLevel: DEBUG compute: runnable-default envs: TALOS_SCHEMA_PATH: talos/setup/consumption_ports/project-directory # Path to the project directory TALOS_BASE_PATH: /talos/public:cross-sell-api # Base Path (Format /talos/<workspace>:<api-name>) resources: requests: cpu: 100m memory: 128Mi limits: cpu: 500m memory: 512Mi stack: talos:1.0 dataosSecrets: # For public code repository you can commented out the entire `dataosSecrets` attribute - name: bitbucket-cred # Replace with Instance Secret name allKeys: true stackSpec: repo: url: https://bitbucket.org/mywork/talos # Repository URL projectDirectory: talos/setup/consumption_ports/project-directory # Project directory path syncFlags: # Branch - --ref=main -
Refer to the Talos Service configuration documentation for attribute descriptions.
Step 8: Deploy the Talos Service¶
-
Run the following command to apply the
service.yamlfile: -
Verify the deployment by checking service logs:
Logs will display successful initialization messages, confirming the service is running.
Successful execution will look like the following:
```bash
INFO[0000] 📃 log(public)...
INFO[0001] 📃 log(public)...complete
NODE NAME │ CONTAINER NAME │ ERROR
───────────────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────────┼────────
aaditest-service-zvs7-d-5dc48797c6-gs9fb │ aaditest-service-zvs7-main │
-------------------LOGS-------------------
2025-03-07 04:08:49.536 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: temp_directory = /etc/dataos/work/.worktrees/a76bec81137783ce29782bb6aa6de0856a076401/aadi-test/talos_cache.db.tmp
2025-03-07 04:08:49.536 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: threads = 1
2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: username = NULL
2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: arrow_large_buffer_size = false
2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: user = NULL
2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: wal_autocheckpoint = 16.0 MiB
2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: worker_threads = 1
2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: allocator_flush_threshold = 128.0 MiB
2025-03-07 04:08:49.537 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: duckdb_api = nodejs
2025-03-07 04:08:49.538 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: custom_user_agent =
2025-03-07 04:08:49.538 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: partitioned_write_flush_threshold = 524288
2025-03-07 04:08:49.538 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: enable_http_logging = false
2025-03-07 04:08:49.538 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: http_logging_output =
2025-03-07 04:08:49.538 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: binary_as_string =
2025-03-07 04:08:49.538 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: Calendar = gregorian
2025-03-07 04:08:49.539 DEBUG [CORE] Duckdb config: TimeZone = UTC
2025-03-07 04:08:49.539 DEBUG [SERVE] Data source duckdb initialized
2025-03-07 04:08:49.539 DEBUG [SERVE] Initializing data source: pg
2025-03-07 04:08:49.539 DEBUG [CORE] Initializing profile: sivapostgresdepot using pg driver
2025-03-07 04:08:49.636 DEBUG [CORE] Profile sivapostgresdepot initialized
2025-03-07 04:08:49.636 DEBUG [CORE] Initializing profile: lens using pg driver
2025-03-07 04:08:49.789 DEBUG [CORE] Profile lens initialized
2025-03-07 04:08:49.789 DEBUG [SERVE] Data source pg initialized
2025-03-07 04:08:49.789 DEBUG [SERVE] Initializing data source: redshift
2025-03-07 04:08:49.789 DEBUG [SERVE] Data source redshift initialized
2025-03-07 04:08:49.790 DEBUG [SERVE] Initializing data source: snowflake
2025-03-07 04:08:49.790 DEBUG [SERVE] Data source snowflake initialized
2025-03-07 04:08:49.791 INFO [SERVE] Start to load and schedule prefetched data results from data sources to cache layer...
2025-03-07 04:08:49.796 DEBUG [SERVE] profile: sivapostgresdepot, allow: *
2025-03-07 04:08:49.796 DEBUG [SERVE] profile: lens, allow: *
2025-03-07 04:08:49.797 DEBUG [SERVE] profile: talos.cache, allow: *
2025-03-07 04:08:49.805 DEBUG [CORE] Authenticator: {
"heimdallUrl": "https://dataos-training.dataos.app/heimdall",
"ttl": 120,
"userGroups": [
{
"name": "default",
"description": "auto-generated default group to include everyone",
"includes": "*"
}
]
}
2025-03-07 04:08:49.810 INFO [CLI] 🚀 Server is listening at port 3000.
```
Testing the API¶
- Use Postman to test the API endpoint.
- Download the Postman collection by hitting the endpoint
/doc/postman?apikey='xxxxxxxxx'and importing the.jsonfile into Postman. Provide theDATAOS_USER_APIKEYfor Authorization in Bearer Token Auth Type.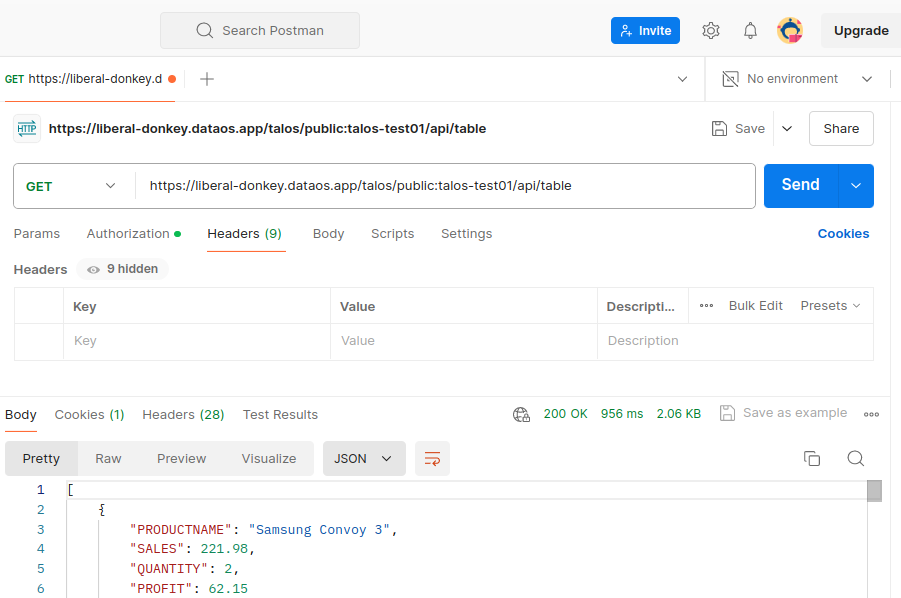
-
To test the endpoint via CLI, use
curlwith the API key as a query parameter: