Quick Guide for Flare Workflow¶
DataOS uses Flare Workflows to carry out large-scale data transformation, ingestion, syndication, and even a combination of these tasks.
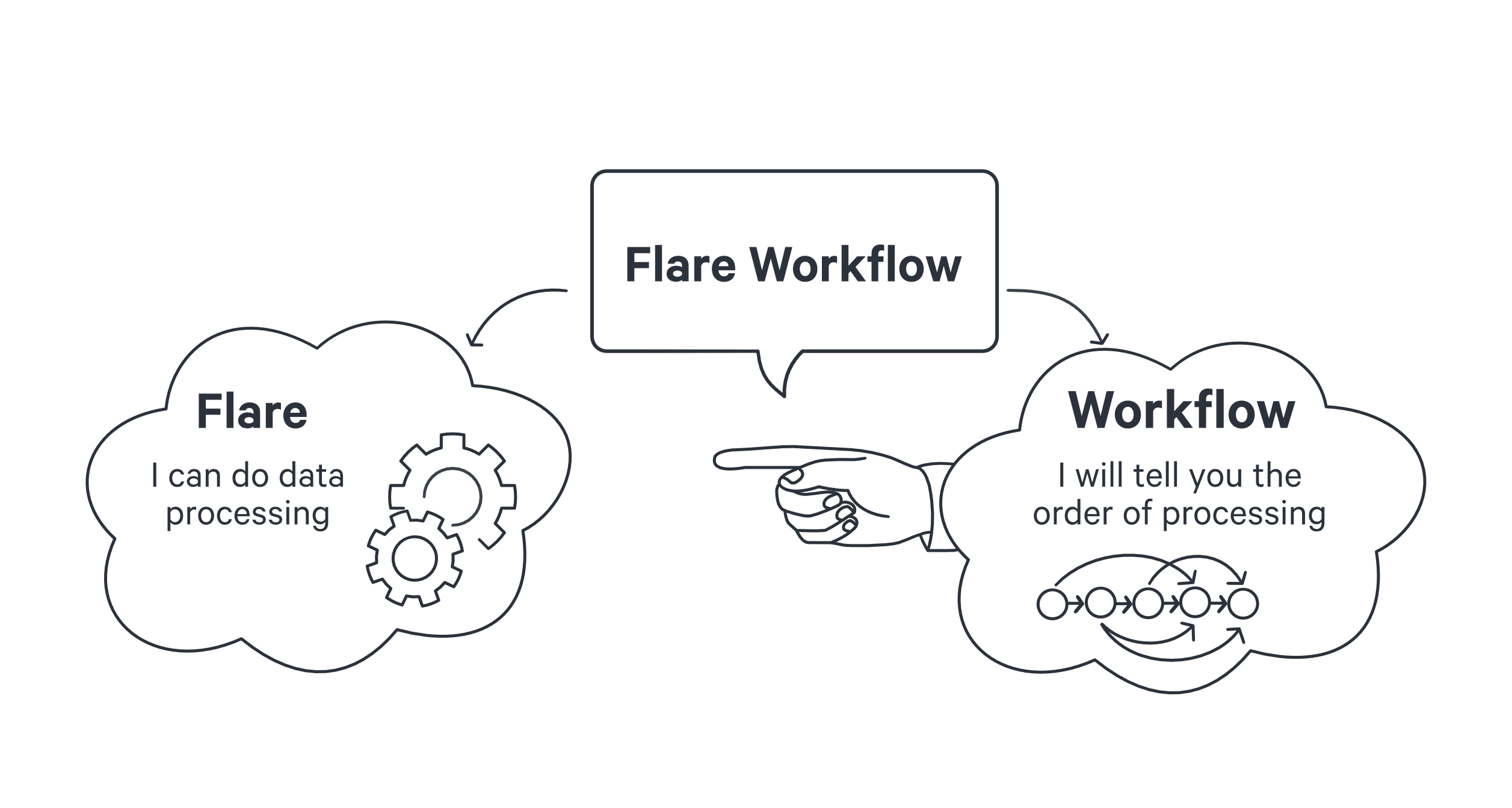
Flare is a declarative stack designed to process large-scale data Workflows using sequential manifest configurations. In contrast, a Workflow is a primitive, or Resource, within DataOS that executes a defined sequence of jobs in a specific order. Each Workflow is represented as a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) of jobs. For additional information on Workflows, refer to the Workflow Resource documentation.
Deep Diving into a Flare Job¶
A job defines a transformation task based on a specific scenario or use case. Each job requires a supporting stack to execute the task and is fully dependent on the successful completion of its preceding job. For example, a Flare Job represents a data processing workload—such as ingestion, transformation, profiling, or syndication—executed on the Flare stack.
In the manifest configuration, a Flare Job defined within a DAG consists of three main sections:
- Input: Specifies the data source.
- Output: Specifies the data destination.
- Steps: Defines the data transformation logic.
In order to grasp the intricacies of creating a Flare Job and the process of testing and deploying it, we shall explore a specific example of Data Ingestion. The data ingestion process will involve acquiring batch data in CSV format from an external source, applying various transformations on top of it, and ultimately storing the data within DataOS internal storage, Lakehouse.
However, before delving into the technical aspects of this task, it is vital to verify certain prerequisites for smooth execution.
Prerequisites¶
Required Permissions¶
Before executing a Flare Workflow, the necessary permission tags must be in place. To run a Flare Workflow using the CLI, the following tags are required:
roles:id:data-devroles:id:system-dev
A
Forbidden Errorwill be returned if the required permissions are not assigned.
The following command can be used to verify the assigned permission tags. Authentication to the DataOS CLI must be completed prior to executing the command.
dataos-ctl user get
#expected Output
INFO[0000] 😃 user get...
INFO[0000] 😃 user get...complete
NAME | ID | TYPE | EMAIL | TAGS
---------------|-------------|--------|----------------------|---------------------------------
IamGroot | iamgroot | person | iamgroot@tmdc.io | roles:id:data-dev,
| | | | roles:id:system-dev,
| | | | roles:id:user,
| | | | users:id:iamgroot
Note: If the required permission tags are not assigned, contact an administrator within the organization who holds Operator-level permissions. The administrator is responsible for assigning the necessary tags to enable Workflow execution.
Check the required Depot¶
To execute a Flare Workflow, Depots must be configured to interface with both source and sink systems for data read and write operations. To retrieve a list of Depots created by all DataOS users, execute the following command in the CLI:
dataos-ctl resource get -t depot -a
# Expected Output
INFO[0000] 🔍 get...
INFO[0000] 🔍 get...complete
NAME | VERSION | TYPE | WORKSPACE | STATUS | RUNTIME | OWNER
-----------------|---------|-------|-----------|---------|-----------|--------------------------
lakehouse01 | v2alpha | depot | | active | running:1 | dataos-resource-manager
redshiftdepot | v2alpha | depot | | active | | user03
retail | v2alpha | depot | | active | running:1 | user02
snowflake01 | v2alpha | depot | | active | | dataos-resource-manager
thirdparty01 | v2alpha | depot | | active | running:1 | user02
If a suitable Depot already exists, proceed to the next step of creating a Flare Job. Metis may be used to explore datasets across various Depots. If the required Depot is not present in the list, a manifest configuration file can be created for the appropriate source Depot and applied using the CLI. Following template display the manifest configuration for a Snowflake Depot:
name: ${{snowflake-depot}}
version: v2alpha
type: depot
tags:
- ${{tag1}}
- ${{tag2}}
layer: user
depot:
type: snowflake
description: ${{snowflake-depot-description}}
snowflake:
warehouse: ${{warehouse-name}}
url: ${{snowflake-url}}
database: ${{database-name}}
account: ${{account}}
external: true
secrets:
- name: ${{snowflake-instance-secret-name}}-r
allkeys: true
- name: ${{snowflake-instance-secret-name}}-rw
allkeys: true
For detailed instructions on creating a Depot on different sources, refer to the Create Depot documentation.
Crating the Flare Job¶
To define a workflow for executing a Flare job, configuration parameters must be specified as key-value pairs within a manifest configuration file. Prior to constructing the manifest file, the Uniform Data Locator (UDL) values for both the input and output Depots must be identified.
For this scenario:
-
Input
-
dataset:dataos://thirdparty01:none/city -
format:CSV -
Output
-
dataset:dataos://lakehouse01:retailsample
This configuration requires integration with two Depots—thirdparty01 and lakehouse01—to enable data ingestion from the source and data persistence to the sink. These Depots serve as endpoints for reading and writing operations, respectively.
name: ${{cnt-city-demo-001}} # Name of the Workflow
version: v1 # Version of the Workflow
type: workflow # Type of Workflow
tags: # Tags for classification
- ${{tag}}
- ${{tag}}
description: The job ingests city data from dropzone into raw zone # Description of the workflow
workflow: # Workflow block
title: Connect City # Title of the workflow
dag: # DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph)
- name: ${{wf-sample-job-001}} # Job identifier
title: ${{City Dimension Ingester}} # Job title
description: The job ingests city data from dropzone into raw zone # Job description
spec: # Job specifications
tags: # Additional classification tags
- Connect
- City
stack: flare:7.0 # Runtime stack to use
compute: runnable-default # Compute resource profile
stackSpec: # Stack-specific configuration
job:
explain: true # Enable explain plan for transformations
logLevel: INFO # Log level
inputs: # Input dataset specifications
- name: city_connect # Input alias
dataset: dataos://thirdparty01:none/city # Source dataset path
format: csv # Input file format
schemaPath: dataos://thirdparty01:none/schemas/avsc/city.avsc # Avro schema location
outputs: # Output dataset specifications
- name: cities # Output alias
dataset: dataos://lakehouse01:retailsample/city?acl=rw # Output dataset path
format: Iceberg # Output format
description: City data ingested from external csv # Output description
options: # Write options
saveMode: append # Save mode for writing (append)
sort: # Sorting configuration for partitions
mode: partition
columns:
- name: version # Partition column
order: desc # Sorting order
iceberg: # Iceberg-specific settings
properties: # Additional Iceberg properties
write.format.default: parquet # Default file format
write.metadata.compression-codec: gzip # Metadata compression
partitionSpec: # Iceberg partitioning
- type: identity
column: version # Partition by version column
steps: # Steps for data transformation
- sequence: # Step sequence
- name: cities # Step name
doc: Pick all columns from cities and add version as yyyyMMddHHmm formatted timestamp. # Step description
sql: | # SQL transformation logic
SELECT
*,
date_format (now(), 'yyyyMMddHHmm') AS version,
now() AS ts_city
FROM
city_connect
Save the manifest file and copy its path. Path could be either relative or absolute.
To know more about the various Flare Stack manifest file configurations, click here.
Applying the Flare Workflow¶
Apply the Workflow manifest by executing the below command:
dataos-ctl resource apply -f <file-path>
# Example
dataos-ctl resource apply -f /home/Desktop/city_flare.yaml
# Expected Output
INFO[0000] 🛠 apply...
INFO[0000] 🔧 applying(public) cnt-city-demo-001:v1beta1:workflow...
INFO[0002] 🔧 applying(public) cnt-city-demo-001:v1beta1:workflow...created
INFO[0002] 🛠 apply...complete
If a workspace is not explicitly defined, the resource is applied to the public workspace by default.
Best Practice
It is recommended that workflows be created within a specific workspace aligned to the client's context, such as by environment (e.g., dev) or domain (e.g., marketing).
To apply a resource within a specific workspace, use the following syntax:
If the specified workspace does not exist, create it using the following command:
Workflow Runtime Information¶
To obtain runtime status for a specific workflow, execute the following command:
dataos-ctl get runtime -w <workspace-name> -t workflow -n <workflow-name>
# Example:
dataos-ctl get runtime -w public -t workflow -n cnt-city-demo-001
Alternative Method:
Workflow runtime details can also be retrieved by passing workflow metadata as a string. Extract the segment from the NAME to WORKSPACE column in the get command output and use the -i flag.
dataos-ctl -i " cnt-city-demo-001 | v1 | workflow | public" get runtime
# Expected Output
INFO[0000] 🔍 workflow...
INFO[0001] 🔍 workflow...complete
NAME | VERSION | TYPE | WORKSPACE | TITLE | OWNER
--------------------|---------|----------|-----------|--------------|-------------
cnt-city-demo-001 | v1 | workflow | public | Connect City | tmdc
JOB NAME | STACK | JOB TITLE | JOB DEPENDENCIES
-----------|------------|-------------------------|-------------------
city-001 | flare:7.0 | City Dimension Ingester |
system | dataos_cli | System Runnable Steps |
RUNTIME | PROGRESS | STARTED | FINISHED
----------|----------|---------------------------|----------------------------
failed | 6/6 | 2022-06-24T17:11:55+05:30 | 2022-06-24T17:13:23+05:30
NODE NAME | JOB NAME | POD NAME | TYPE | CONTAINERS | PHASE
--------------------------------------|----------|-----------------------------------|--------------|-------------------------|------------
city-001-bubble-failure-rnnbl | city-001 | cnt-city-demo-001-c5dq-2803083439 | pod-workflow | wait,main | failed
city-001-c5dq-0624114155-driver | city-001 | city-001-c5dq-0624114155-driver | pod-flare | spark-kubernetes-driver | failed
city-001-execute | city-001 | cnt-city-demo-001-c5dq-3254930726 | pod-workflow | main | failed
city-001-failure-rnnbl | city-001 | cnt-city-demo-001-c5dq-3875756933 | pod-workflow | wait,main | succeeded
city-001-start-rnnbl | city-001 | cnt-city-demo-001-c5dq-843482008 | pod-workflow | wait,main | succeeded
cnt-city-demo-001-run-failure-rnnbl | system | cnt-city-demo-001-c5dq-620000540 | pod-workflow | wait,main | succeeded
cnt-city-demo-001-start-rnnbl | system | cnt-city-demo-001-c5dq-169925113 | pod-workflow | wait,main | succeeded
To view live updates of workflow progress, append the -r flag:
Press Ctrl + C to exit the runtime stream.
Additional Link¶
-
Flare Stack Manifest Configurations – Configuration settings for reading, writing, and transforming data.
-
Flare Functions List – List of supported functions for Flare-based data processing.
-
Flare Optimizations – Techniques for tuning and optimizing Flare stack jobs.
-
Case Scenario – Examples of real-world data processing using the Flare stack.