Build a Streamlit App on DataOS¶
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to create a simple streamlit application, dockerize it, and then run it on top of DataOS using Container stack.
Create a Streamlit Application¶
First, we need to create a simple Streamlit application. Streamlit is a popular Python library that allows you to create interactive web applications quickly and easily.
For this example, we will create a simple application that allows you to enter your name and then displays a personalized message.
# app.py
import streamlit as st
def main():
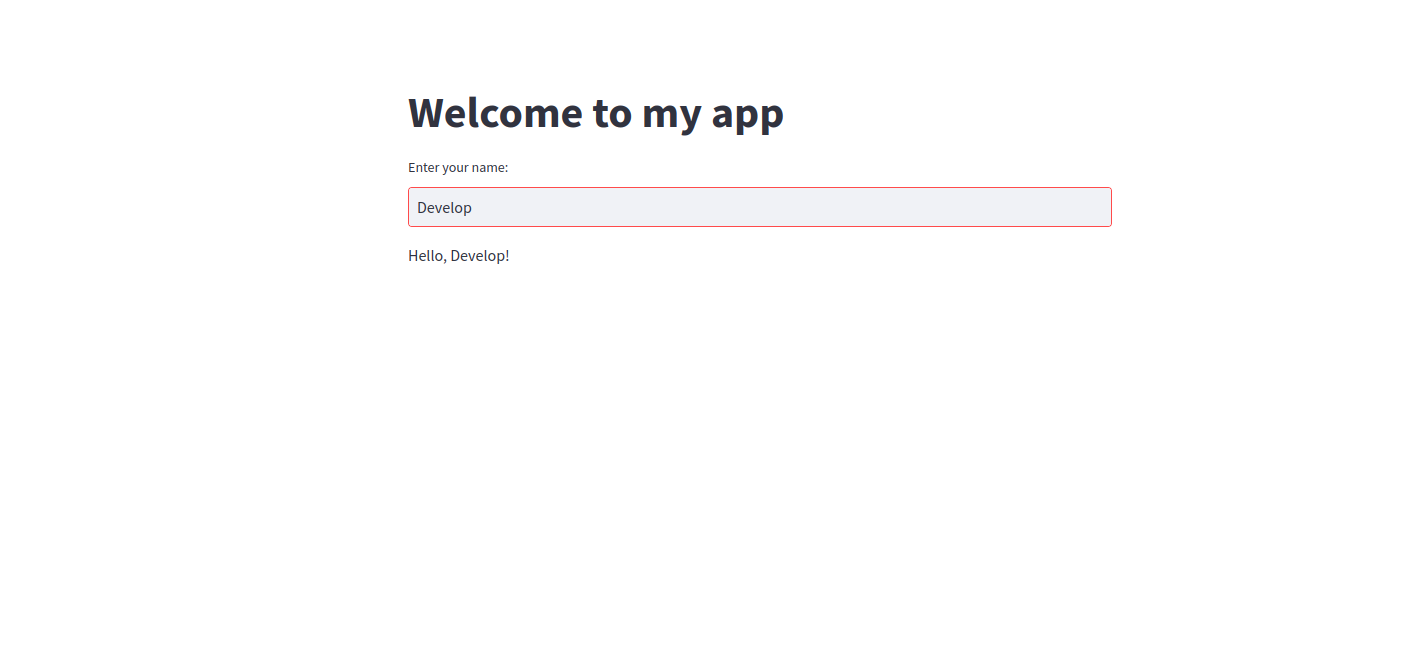
st.title("Welcome to my app")
name = st.text_input("Enter your name:")
if name:
st.write(f"Hello, {name}!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
You can run this application locally by running streamlit run app.py in the command line. The application will launch in your default web browser.
Create a Docker Image¶
Build a Docker Image¶
Next, we need to create a Docker image for our application. Docker is a containerization platform that allows you to package your application and its dependencies into a single image that can be run in any environment.
To create a Docker image, we need to create a Dockerfile that defines the build process.
# Dockerfile
FROM python:3.10-slim
RUN pip install streamlit
WORKDIR /app
COPY app.py .
CMD ["streamlit", "run", "app.py"]
This Dockerfile starts with a lightweight Python 3.10 base image, installs Streamlit, sets the working directory to /app, copies the app.py file into the container, and defines the command to run the application.
To build the Docker image, run the following command in the same directory as your Dockerfile:
This command builds a Docker image named my-app using the Dockerfile in the current directory.
Push the Docker Image to Container Registry¶
Now that we have a Docker image for our application, we need to push it to a container registry. For this example, we will use Docker Hub, but you can use any container registry that you prefer.
First, you need to create a Docker Hub account and repository.
Next, log in to Docker Hub using the docker login command.
Replace your-username with your Docker Hub username, and input the password to login.
Tag the Docker Image¶
To push an image to Docker Hub, your image needs to be tagged. In case it’s not tagged, you can use the below command.
Finally, push the Docker image to Docker Hub using the following command:
Create a manifest file¶
This command builds a Docker image named my-app using the Dockerfile in the current directory.
version: v1 # Version
type: service # Type of Resource
service: # Service Specific Section
compute: runnable-default # Compute is Runnable-default (since its a service)
replicas: 1 # Number of Service Replicas
servicePort: 8080 # Service Port
ingress: # Ingress Section
enabled: true
noAuthentication: true
path: /stream # URL Path on which you wanna expose the application on
stripPath: true
stack: container # Here stack is Container
envs: # Environment Variables
LOG_LEVEL: info # Log Level
stackSpec: # Container Stack-specific Section
image: your-username/my-app:new # Image Repository and Tag
command:
- streamlit
arguments:
- run
- app.py
Apply the YAML file¶
Apply the YAML file using the apply command, as follows:
Navigate over to the Web Browser¶
You can see the streamlit UI, on the web browser at the following address
https://<dataos-context>/<path>