Pager¶
A Pager in DataOS is a Resource that enables data developers to specify criteria for identifying an incident within the incident stream and delivering it to a user-specified destination. It operates by evaluating pre-defined conditions against incoming incident data from the incident stream. Upon identifying a match, it triggers an alert and delivers it to the specified destination.
-
How to create a Pager?
Learn how to create and manage a Pager in DataOS.
-
How to configure the manifest file of Pager?
Discover how to configure the manifest file of Pager by adjusting its attributes.
-
How does a Pager work?
Understand the inner workings of a Pager within DataOS.
-
Pager recipes
Explore examples showcasing the usage of Pager in various scenarios.
Supported alerting channels¶
Pager Resource can send alerts to the following channels:
-
Microsoft Teams channel: Send alerts directly to Teams channels using webhook integration.
-
Email: Supports all major email providers including Gmail, Outlook, and others.
-
Any channel with webhook support: Integrate with Slack, custom applications, or other platforms that accept webhook payloads.
Users can configure Pager to send alerts to all supported channels at once, or to any individual channel, depending on the preference and requirements.
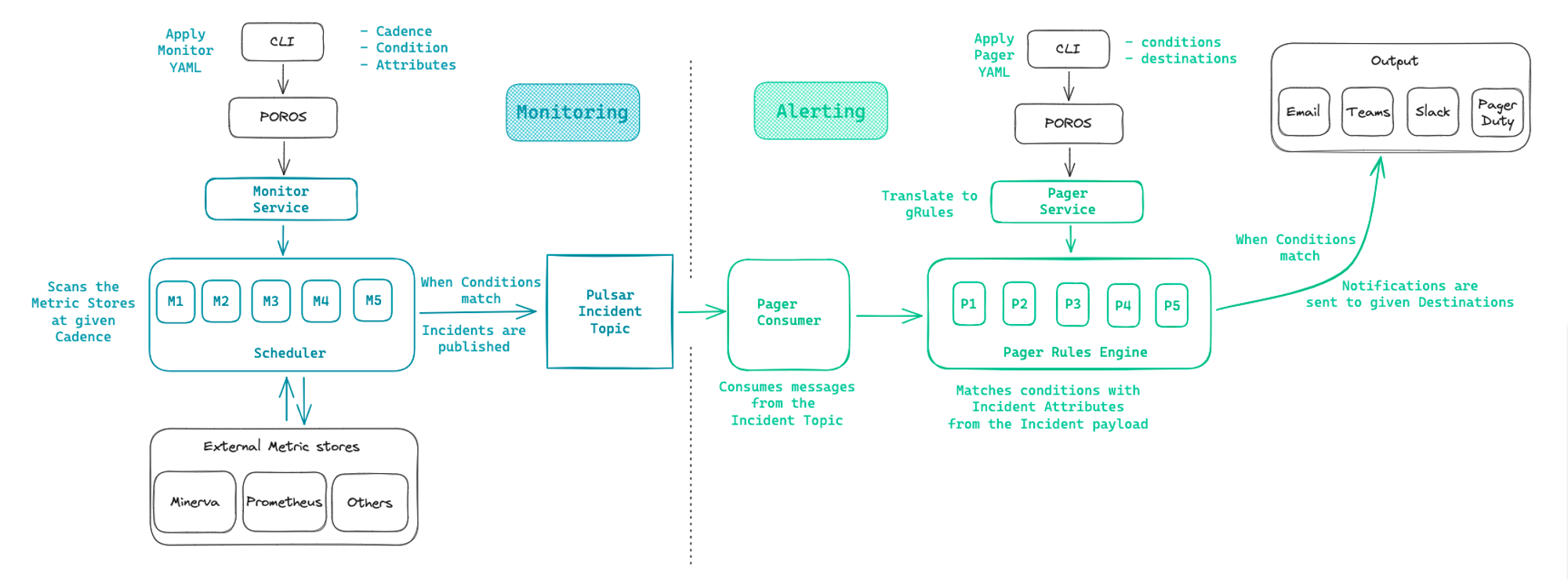
The Pager along with Monitor Resource comprise the backbone of the DataOS Observability and enable alerting mechanism in response to specified incident conditions.
How to create a Pager Resource?¶
To create a Pager Resource in DataOS, follow the step-by-step instructions provided here: First steps. This section covers the prerequisites, manifest file structure, and the commands required to create and apply a Pager Resource.
How does a Pager work?¶
A Pager within DataOS operates by continuously monitoring the incident stream for occurrences that match predefined criteria, known as conditions. Here's a breakdown of how a Pager functions:
-
Condition evaluation: The Pager evaluates incoming incident data against the conditions specified in its manifest file. These conditions typically include attributes like severity, type, name of the incident, etc.
-
Matching criteria: When an incident matches all specified conditions, the Pager identifies it as a trigger for an alert. This matching process ensures that only relevant incidents initiate alert notifications.
-
Alert triggering: Upon identifying a matching incident, the Pager triggers an alert, notifying designated recipients or systems about the occurrence. The alert can be sent to various destinations such as email, Microsoft Teams, or custom webhooks.
-
Destination delivery: Depending on the configuration, the alert is delivered to the specified destination. For example, if the Pager is configured to send alerts via email, it will generate an email containing details of the incident and send it to the designated email addresses.
How to delete a Pager?¶
To remove a specific Pager Resource-instance from the DataOS environment, you can use the delete command. There are three methods to delete a Pager:
Method 1: Delete by identifier
-
Copy the name of the Pager from the output table of the
getcommand.dataos-ctl get -t pager -w public -n pager-test INFO[0000] 🔍 get... INFO[0001] 🔍 get...complete NAME | VERSION | TYPE | WORKSPACE | STATUS | RUNTIME | OWNER -------------------|---------|-------|-----------|--------|---------|-------------- pager-test | v1alpha | pager | public | active | running | iamgroot -
Use the name as a string in the delete command.
Method 2: Delete by manifest file path
-
Copy the path of the manifest file containing Pager configuration.
-
Use the
deletecommand with the-fflag.
Method 3: Delete by workspace, Resource-type, and name
Specify the Workspace, Resource-type, and Pager name in the delete command.
After executing the delete command, you will receive a confirmation message indicating successful deletion of the Pager.
Configurations¶
The Pager manifest file serves as the blueprint for defining the structure and behavior of Pager Resources within DataOS. By configuring various attributes within the the Pager manifest file, data developers can customize the functionality of their Pagers to meet specific requirements. Below is an overview of the key attributes used to configure a the Pager-specific section: Attributes of a Pager manifest.
For details about the Resource meta section, refer to the Attributes of Resource meta section
Troubleshooting¶
When a Pager encounters errors, data developers can employ various tactics to diagnose and resolve issues effectively. Here are the recommended debugging techniques:
-
Get Pager details
-
Retrieve detailed information about the Pager to gain deeper insights into its configuration and execution status. This can be accomplished using the following command:
dataos-ctl get -t pager -w public -n pager-test -d # output: INFO[0000] 🔍 get... INFO[0000] 🔍 get...complete --- # pager-test:v1alpha:pager # pager:v1alpha:pager-test:public name: pager-test version: v1alpha type: pager tags: - workflow-failed-pager - dataos:type:resource - dataos:resource:pager - dataos:layer:user - dataos:workspace:public description: This is for triggring n8n wf. owner: iamgroot workspace: public pager: conditions: - valueJqFilter: .properties.name operator: equals value: monitor-incident-prom - valueJqFilter: .properties.incidentType operator: equals value: resource_consumption output: webHook: url: https://hwifiadda.app.n8n.cloud/webhook/e517984a-0a56-4890--b8e49e183b3d headers: content-type: application/json verb: post contentType: application/json templateType: liquid bodyTemplate: | { "context": "{{ equationContext }}" } generation: 1 uid: 001c339c-9c82-4733-be84-7472394c7d6c created: 2025-08-06T11:32:37Z status: aggregateStatus: active cloudKernelResources: - name: pager-test-tags-pager-xo54 namespace: public version: v1 kind: Secret resource: secrets dataplane: hub status: created webServiceResources: - id: pager-test_public service: pager type: pager self: /pagers/pager-test_public status: created builderState: stage: building numberOfWantedResources: "2" numberOfProcessedResources: "2" info: builder is finished with work for now runtimeState: status: running -
Review the output to identify any discrepancies or misconfigurations in the Pager that could be contributing to the error.
-
-
Check Pager Service Logs
- Navigate to the Operations App, and switch to its Core Kernel Tab, within the Pods section you will find the Pager API Service pod. By clicking on it you check out the Pod Details, Pod YAML, Pod Logs, and Pod Usage.
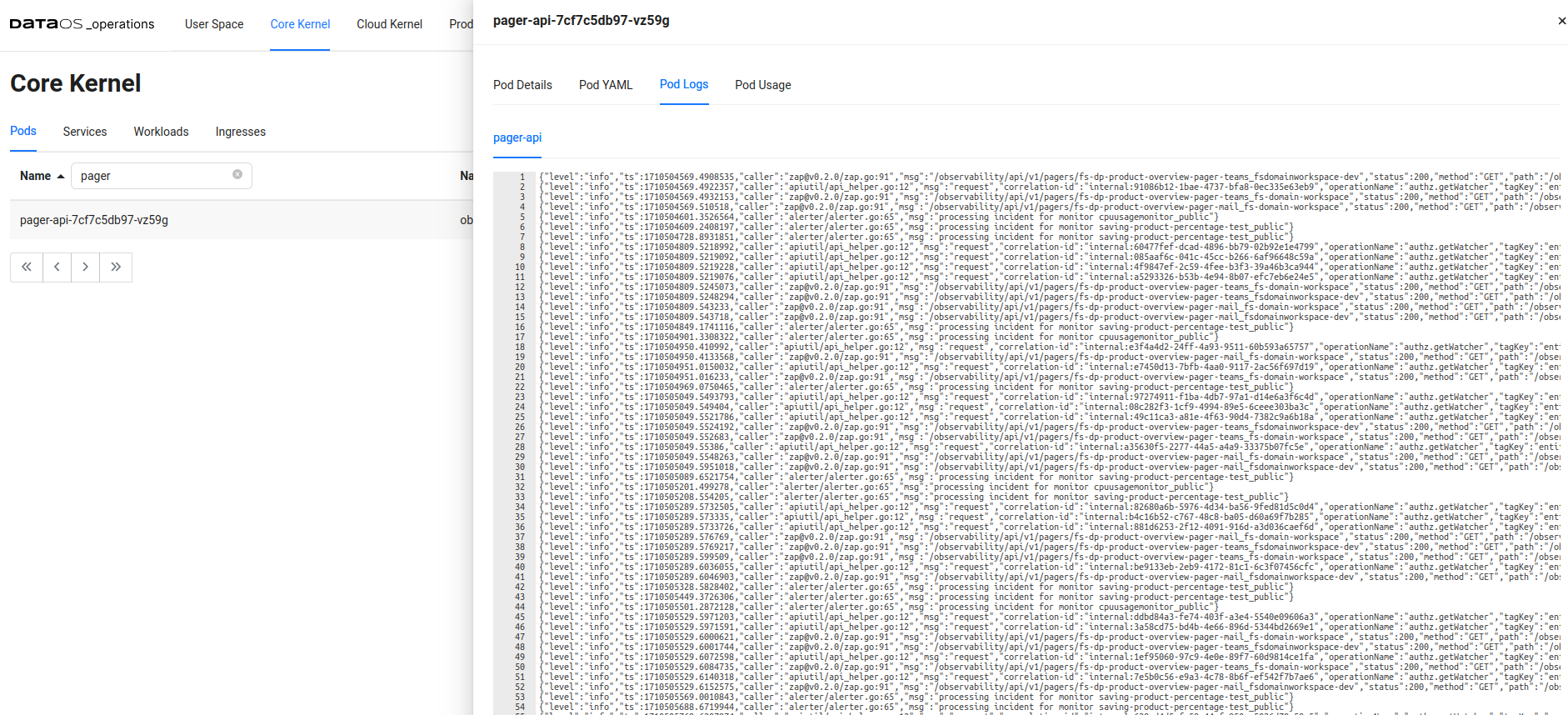
Pager Service pod logs - Analyze the logs for any error messages or exceptions that might provide insights into the cause of the issue.