Lens¶
Lens Resource in DataOS is a logical modeling layer designed for accessing tabular data in data warehouses or lakehouses. It operates on top of physical tables, allowing the extension of these tables into logical tables by adding logical columns (measures) and relationships. It empowers analytical engineers, the key architects of business intelligence, with a model-first approach.
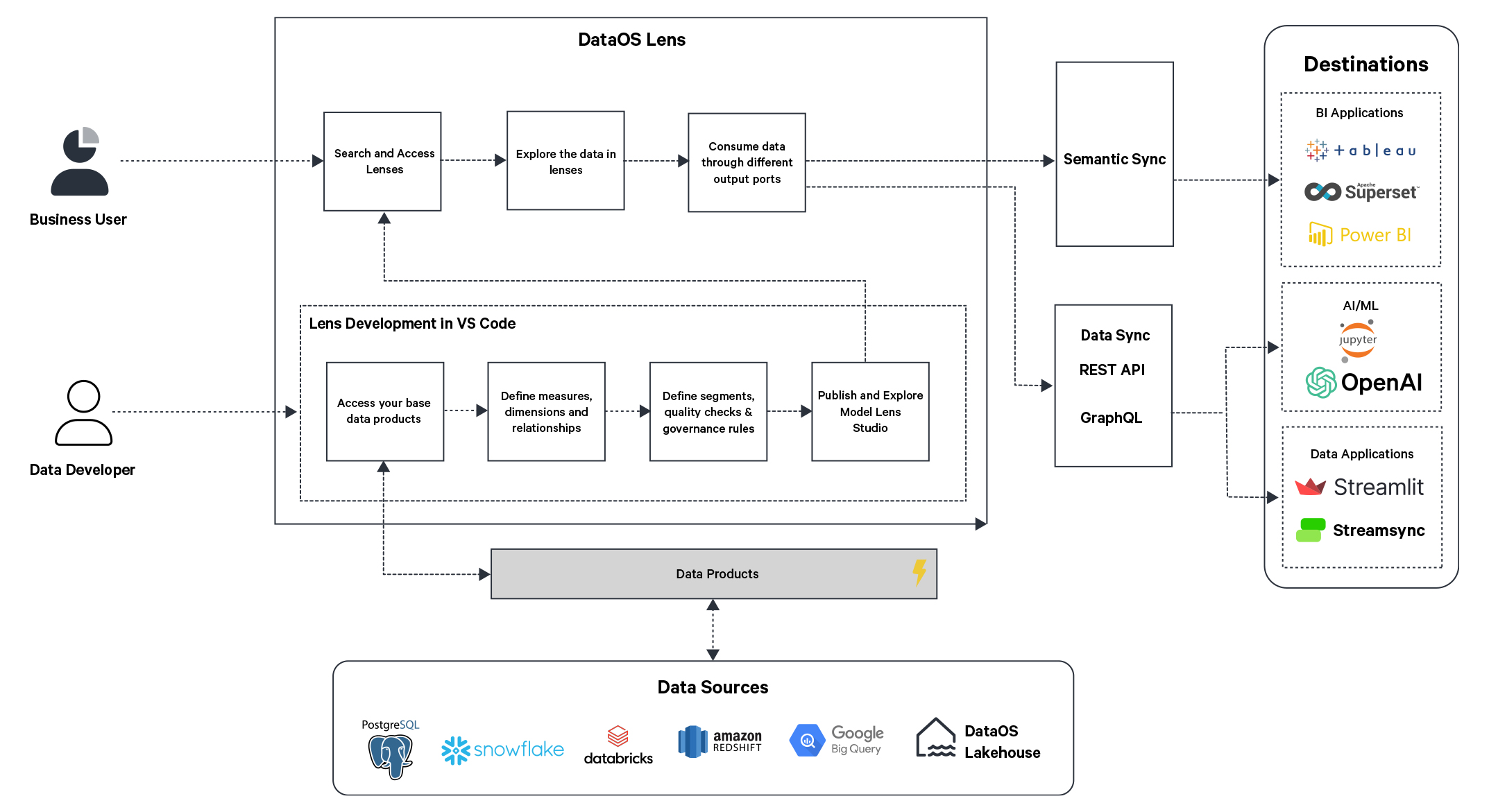
Lens within the Data Product Lifecycle
Lens operates in the consumption layer of the Data Product Life Cycle within DataOS. By leveraging Lens, Data Products can be created to inform decision-making, ensuring data is well-organized and aligned with business objectives. To consume it, Lens exposes APIs such as Postgres, REST APIs, and GraphQL.
Why Lens?
The data modeling layer serves as an interface that overlays the underlying data, consistently presenting business users with familiar and well-defined terms like product, customer, or revenue. This abstraction enables users to access and consume data in a way that aligns with their understanding, facilitating self-service analytics and reducing dependence on data engineers for ad-hoc data requests.
As a Resource within the DataOS ecosystem, Lens enhances Data Product consumption by delivering improvements in how Data Products are accessed and utilized. It streamlines the developer experience in consumption patterns, focusing specifically on refining the use and interaction with data products.
Key features of Lens¶
Lens is engineered to handle complex and large-scale data models with ease. Key features include:
-
Code modularity: Lens supports modular code structures, simplifying the maintenance of extensive models, particularly when dealing with entities, dimensions, and measures. This modularity enables efficient development and management, allowing teams to navigate large codebases with reduced complexity.
-
Segments: Segments are predefined filters that enable the definition of complex filtering logic in SQL. They allow you to create specific subsets of data, such as users from a particular city, which can be reused across different queries and reports. This feature helps streamline the data exploration process by simplifying the creation of reusable filters.
-
API support: Lens enhances interoperability by simplifying application development with support for Postgres API, REST API, and GraphQL.
-
Governance and access control: Lens ensures data governance through user group management and data policies, enabling precise control over who can access and interact with data models.
-
BI integration: Lens improves interoperability through robust integration with Superset, Tableau, and Power BI. This ensures that data models can be easily utilized across various BI platforms, enhancing the overall analytics experience.
-
Performance optimization through Flash: Designed to work with DataOS Lakehouse and Iceberg-format Depots, Flash improves query performance by leveraging in-memory execution. This optimization ensures that data teams can efficiently handle large-scale queries with enhanced speed and performance.
How to build semantic model?¶
To build a semantic model with Lens, there are three primary options depending on your data environment: using a single source, combining data from multiple sources, or enabling query acceleration for performance optimization. The following sections outline how to build and deploy semantic model based on each scenario.
Single source¶
When data resides in a single source such as AWS Redshift, BigQuery, PostgreSQL, or Snowflake, the semantic model is built directly on top of the source.
Multiple source¶
When working with distributed data systems, a unified semantic model is constructed using Minerva or Themis clusters. These clusters facilitate seamless integration across heterogeneous data sources.
Query acceleration¶
For high-performance analytical workloads, Flash provides an in-memory query acceleration layer that significantly improves query execution speed.
Exploration of semantic model¶
After creating a semantic model, the next step is to explore it by running queries. This section covers key concepts for querying Lens through various methods, all following the same general format. Multiple methods are available to interact with the Lens model or its data, enabling to ask questions and gain insights.
BI Integration¶
GraphQL APIs¶
GraphQL API enables Lens to deliver data over the HTTP protocol to GraphQL enabled data applications, e.g., most commonly, front-end applications. The following resources provide detailed instructions on how to interact with the Lens GraphQL API:
- To explore the Lens using the GraphQL API click here.
- To learn about the query format for GraphQL and explore more examples click here.
SQL APIs¶
Lens provides a PostgreSQL-compatible interface, enabling users to interact with the semantic model over SQL. The following resources offer detailed instructions on how to set up and use the SQL APIs with Lens:
- To explore how to interact with Lens using SQL APIs.
- To learn about the supported functions and operators within the SQL API.
REST APIs¶
Lens offers a REST API for querying data, retrieving metadata, and managing resources programmatically. To know step-by-step guidance on interacting with Lens through API calls, details of available endpoints, parameters, and request-response formats please refer to this link.
Python¶
Lens supports interaction through Python, allowing one to use libraries such as requests for making API calls and handling responses programmatically. This method is ideal for more complex queries and automation tasks. For detailed instructions on setting up and using Python with Lens, refer to the full Python guide here.
Semantic modeling¶
Semantic modeling is the process of organizing raw data into meaningful business definitions. It involves creating schemas, relationships, and aggregations to represent how data is stored, processed, and accessed. Navigate through the following documents to explore the concepts involved in creating a semantic model in Lens:
Configurations¶
Lens can be configured to connect to different sources using data source attributes and configurable attributes in the deployment.yml manifest files. For a comprehensive guide to configure supported properties, click here.
Best Practices¶
Click here to explore recommended guidelines and techniques to create efficient and scalable semantic models, along with a concise list of do’s and don’ts.
Troubleshooting¶
Click here to understand and resolve common errors while creating semantic model and deploying Lens.
Cataloging¶
Click here to learn about how the metadata of a semantic model or Lens Resource is cataloged and can easily be discovered.
Governance¶
Click here to learn how data governance in DataOS is structured across four different layers.
Observability¶
Click here to learn how to observe and monitor Lens Resource and semantic model.
Optimizing Lens semantic model¶
The Lens semantic layer provides several optimization techniques that can significantly enhance the performance of data queries. The following page explores best practices and strategies for fine-tuning your Lens model to maximize efficiency.