Monitor the CPU and Memory Usage of a Worker¶
When a Worker Resource is created, a corresponding pod is automatically provisioned in the backend. You can monitor the CPU and memory usage of this pod directly through the Metis UI.
To monitor the CPU and memory usage of a Worker on the Metis Catalog UI, follow the steps below:
-
Open the Metis Catalog.

Open the Metis Catalog (Metis UI) -
Search for the Worker by name.
Search for the Worker in Metis -
Click on the Worker that needs to be monitored and navigate to the ‘Runtime’ section.
Worker details in Metis -
Click on the pod name for which you want to monitor the CPU and memory usage, and navigate to the ‘Pod Usage’ section.
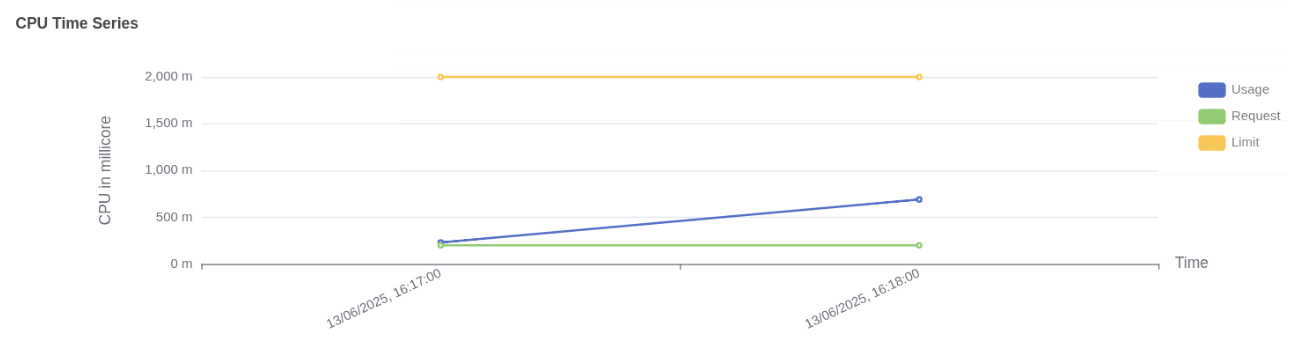
Pod CPU usage vs request and limit CPU usage:
- Usage (blue line) shows actual CPU consumed by the Worker pod, increasing steadily and reaching just above 600 millicores.
- Request (green line) is fixed at approximately 250 millicores, indicating the CPU guaranteed for the pod at scheduling time.
- Limit (yellow line) is flat at 2000 millicores, representing the maximum CPU the pod is allowed to use if resources are available.
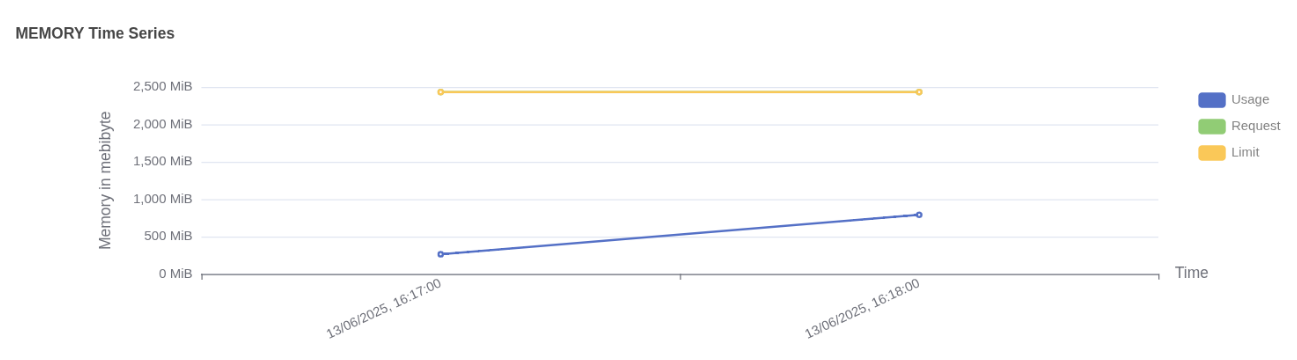
Pod memory usage vs limit Memory usage:
- Usage (blue line) shows actual memory consumed by the workflow pod, increasing over time and reaching just under 1000 MiB.
- Request (green line) is not visible in the graph, which indicates that memory was not explicitly requested or the request value is not available in this dataset.
- Limit (yellow line) remains constant at 2500 MiB, indicating the maximum memory the pod is allowed to consume.
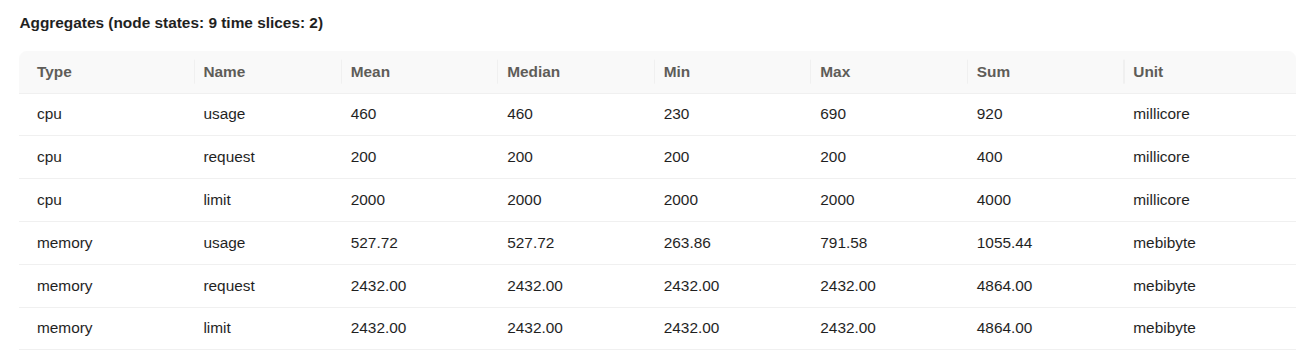
Aggregated CPU and memory statistics Details:
- Type: Indicates whether the metric refers to CPU or memory.
- Name: Describes the metric subtype
usage(actual consumption),request(minimum reserved), orlimit(maximum allowed). - Mean / Median / Min / Max: Statistical summaries over the measured time slices.
- Sum: Total usage across all time slices.
- Unit: CPU is in millicores (1000 millicores = 1 core); memory is in mebibytes (1 MiB = 1,048,576 bytes).
- CPU Usage: Average CPU usage was 460 millicores, peaking at 690 millicores. The pod used significantly more than its request, but stayed within the limit.
- CPU Request: Set at 200 millicores consistently, meaning the pod was guaranteed a small baseline of CPU.
- CPU Limit: Fixed at 2000 millicores (2 cores), providing ample room for the workload to scale under load.
- Memory Usage: Average memory usage was approximately 527.72 MiB, with a maximum usage of 791.58 MiB.
- Memory Request: Set at 2432 MiB, meaning this much memory was reserved and guaranteed to the pod.
- Memory Limit: Also set at 2432 MiB, indicating that the pod could not use more memory than requested.
The Worker was allowed to consume significantly more CPU than it requested, and it did so, but stayed under the defined limit. Memory usage remained far below both the request and limit. This suggests an opportunity to reduce memory allocation to free up resources for other workloads.
Operations App¶
When a Worker Resource is created, a corresponding pod is automatically provisioned in the backend. You can monitor the CPU and memory usage of this pod directly through the Operations app.
To monitor the CPU and memory usage of a Worker on the Operations app, follow the steps below:
-
Open the Operations app.

Open the Operations app -
Navigate to User Space → Resources → types, select the Worker as type, and search for the Worker by its name that needs to be monitored.
Operations > User Space > Resources -
Click on the Worker, navigate to the ‘Resource Runtime’ section.
Worker resource runtime in Operations -
Click on the pod name for which you want to monitor the CPU and memory usage, and navigate to the ‘Runtime Node Usage’ section.
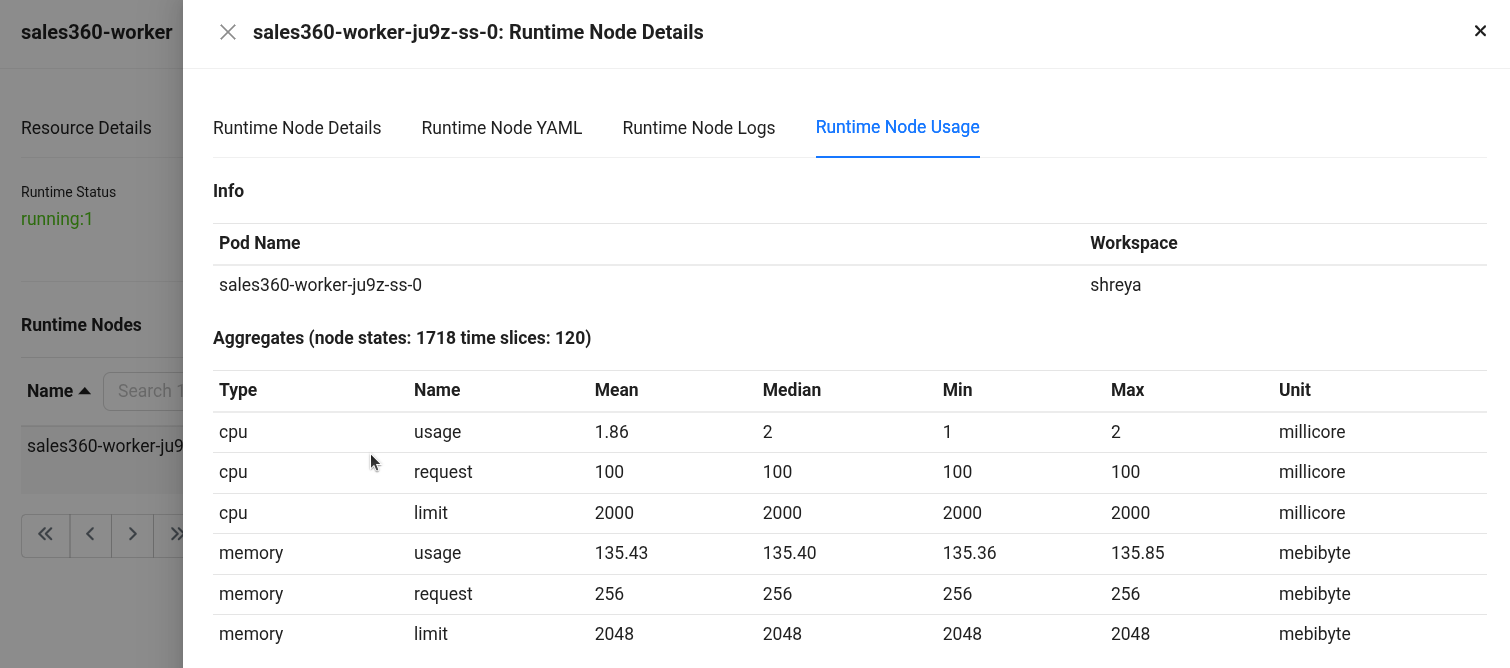
Runtime Node Usage details Details:
- Type: Indicates whether the metric is related to CPU or memory.
- Name: Specifies the metric subtype,
usage(actual consumption),request(guaranteed minimum), andlimit(maximum allocable resource). - Mean / Median / Min / Max: Statistical summaries of the metric over the evaluated time slices.
- Sum: Total value accumulated across all time slices.
- Unit: Measurement unit (millicore for CPU, mebibyte for memory).
- CPU Usage: Average CPU usage was ~1.86 millicores, peaking at 2 millicores (1 core = 1000 millicores). Millicores provide fine-grained control over how much CPU each pod or container should receive.
- CPU Request: The pods are configured to request 100 millicores of CPU each, consistently across time slices.
- CPU Limit: The pods are configured to limit 2000 millicores of CPU each, consistently across time slices.
- Memory Usage: Average memory consumption stands at ~135.43 MiB, with a peak at 135.85 MiB (1 MiB = 2²⁰ bytes = 1,048,576 bytes).
- Memory Request: Each pod has been allocated 256.00 MiB as a guaranteed memory reservation.
- Memory Limit: Each pod has been allocated 2048 MiB as a limited memory reservation.
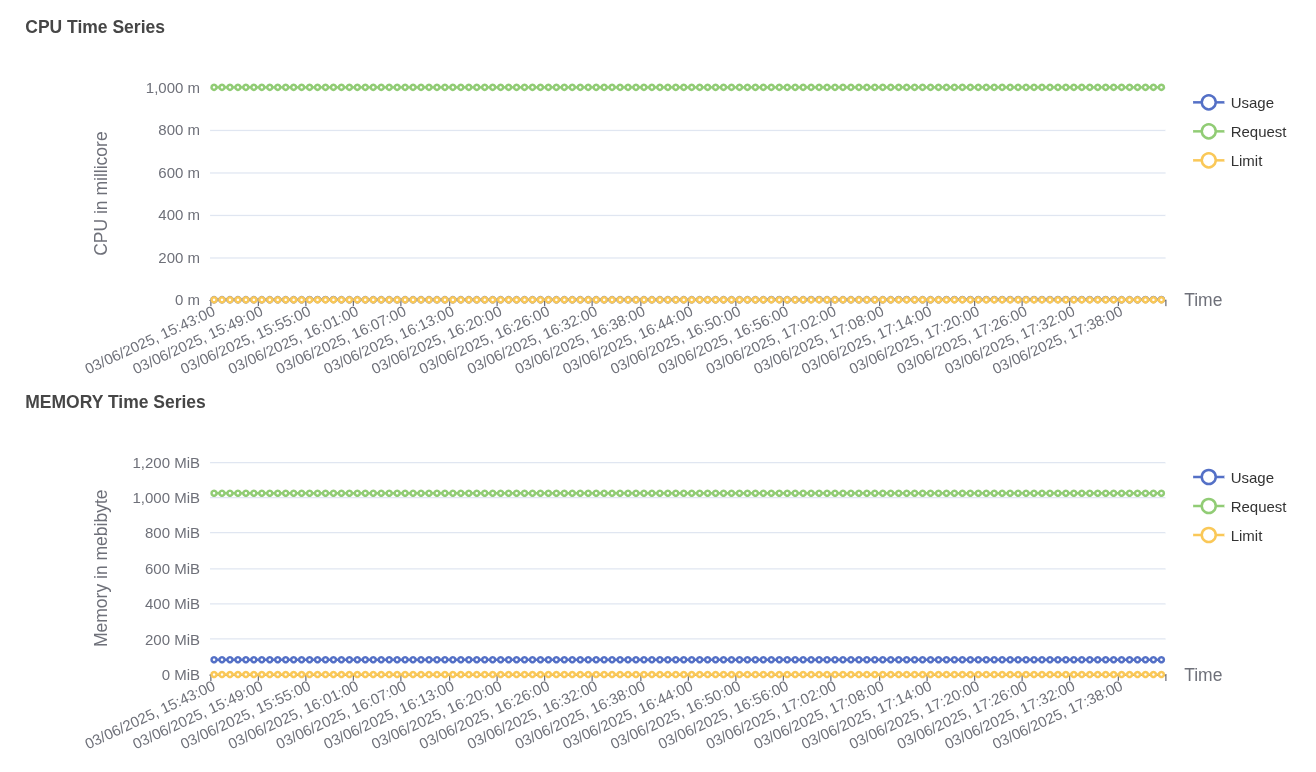
CPU usage over time in Operations CPU usage:
- Usage (blue line) shows intermittent spikes in CPU consumption, peaking close to 600 millicores. Between spikes, CPU usage drops near zero, indicating short bursts of activity followed by idle periods.
- Request (green line) is not plotted, suggesting no CPU request was explicitly configured or it’s not captured here.
- Limit (yellow line) remains constant at around 1200 millicores, representing the maximum CPU the pod can consume.
Memory usage:
- Usage (blue line) steadily increases, reaching up to 1900 MiB, then dips temporarily and stabilizes again around 1200–1400 MiB. This indicates a consistent memory footprint with some momentary drops.
- Request (green line) is missing, indicating it was either not set or not shown in this view.
- Limit (yellow line) is fixed at 2048 MiB, defining the upper bound for memory allocation.
Grafana¶
When a Worker Resource is created, a corresponding pod is automatically provisioned in the back-end. You can monitor the CPU and memory usage of this pod directly through the Grafana app.
To monitor the CPU and memory usage of a Service on the Grafana app, follow the steps below:
-
Execute the following command in DataOS CLI to get the pod name corresponding to the Service Resource.
Example usage:
dataos-ctl log -t worker -w research -n sales360-worker INFO[0000] 📃 log(research)... INFO[0000] 📃 log(research)...complete NODE NAME │ CONTAINER NAME │ ERROR ────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┼──────── sales360-worker-ju9z-ss-0 │ sales360-worker │ # ^ pod name -------------------LOGS------------------- 🚀 Lens2 (0.35.60-34) => DataOS:pro-alien.dataos.app DEBUG: 🇮🇳 Configured time-zones: [ "America/Toronto", "America/Vancouver", "UTC" ] DEBUG: authenticate pro-alien.dataos.app /heimdall/api/v1/authorize 200 {"allow":true,"result":{"id":"iamgroot","tags":["roles:id:data-dev","roles:id:operator","roles:id:system-dev","roles:id:user","users:id:iamgroot"]},"valid":true} DEBUG: source: { "type": "minerva", "dialect": "trino", "connection": "minerva://system", "meta": { "userId": "iamgroot", "catalog": "icebase", "cluster": "system", "host": "tcp.pro-alien.dataos.app", "port": "7432" } } -
Open the Grafana app.

Open the Grafana app -
Navigate to the Explore section and select ‘Thanos’ as a source and search for the metric
cpu_container_usage_total, and in the label filters select pod and paste the pod name which we have gotten from step 1, then click on ‘Run Query’.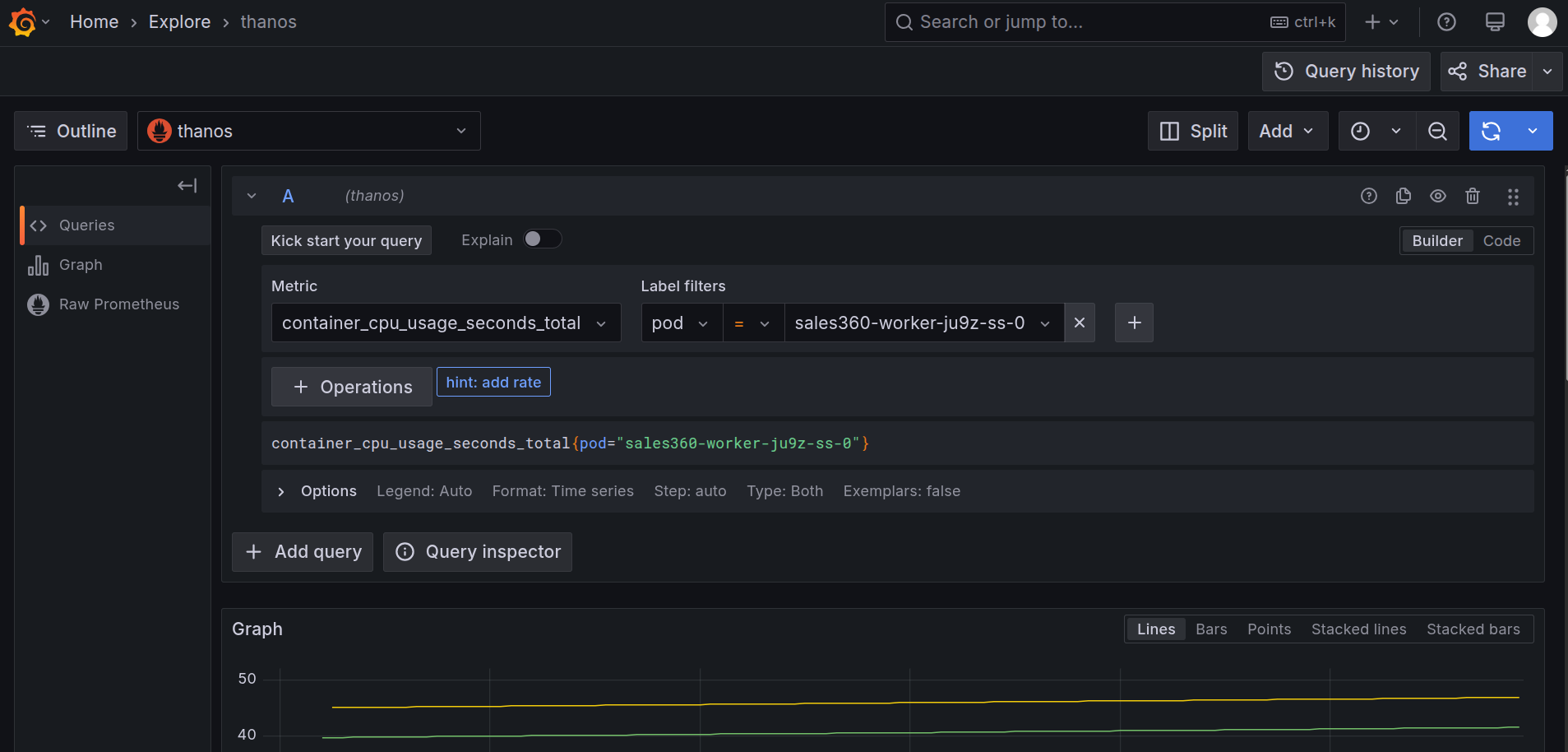
Grafana Explore: CPU usage query -
After clicking on the ‘Run Query’, you can find the usage of CPU by the Service.
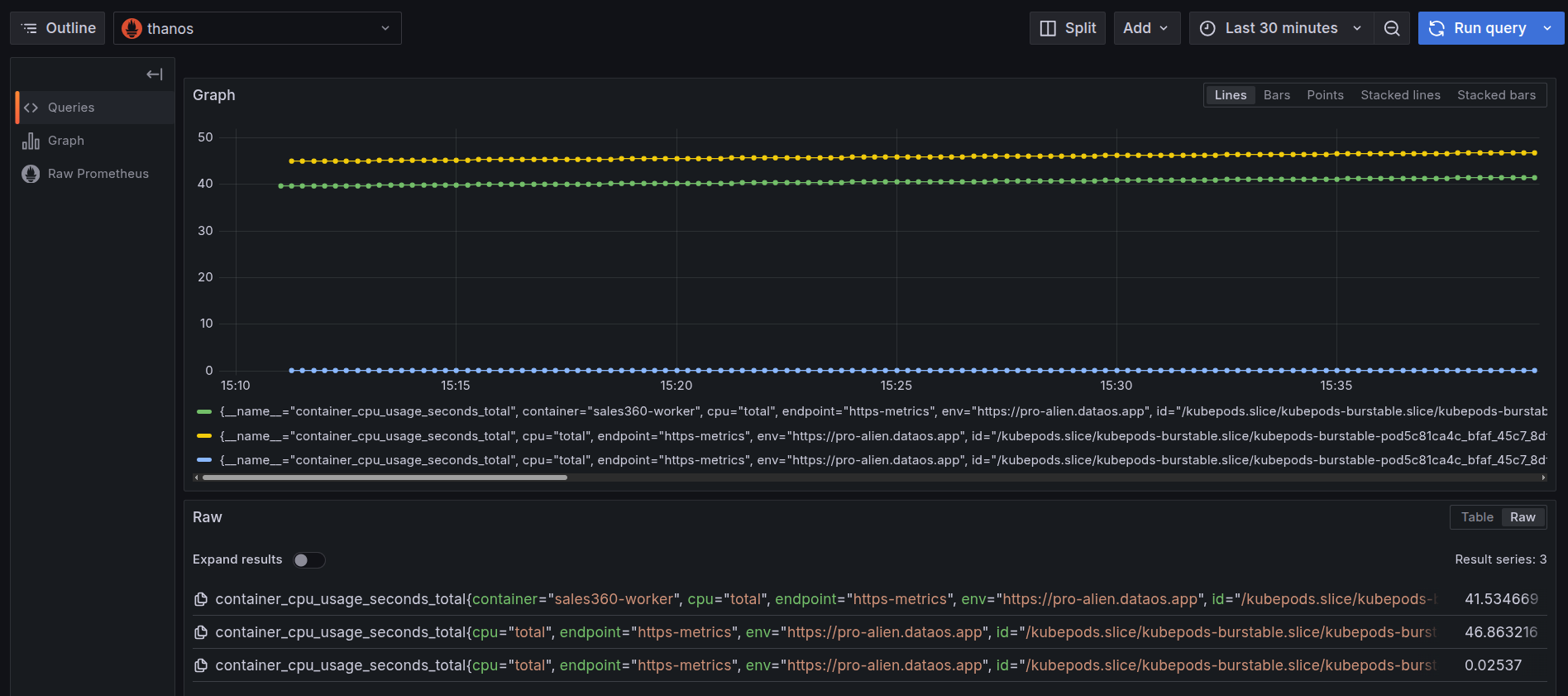
CPU usage by container over time This graph displays cumulative CPU usage (
container_cpu_usage_seconds_total) for each container inside a pod belonging to thesales360-workerWorker:- Green line: Represents the container named
sales360-worker, with cumulative CPU usage of 41.53 seconds, indicating this is the primary workload container. - Yellow line: Another container in the same pod with usage of 46.86 seconds, showing it consumed slightly more CPU over time.
- Blue line: A third container in the pod with usage of 0.025 seconds, reflecting very minimal CPU activity during the observed period.
Each line represents a different container inside the same pod, and the variation in CPU usage reflects the different computational responsibilities handled by each container.
- Green line: Represents the container named
-
To monitor the memory usage, select the
container_memory_working_set_bytesin the query explorer and select the pod name as the label filter of the corresponding Service, and run the query.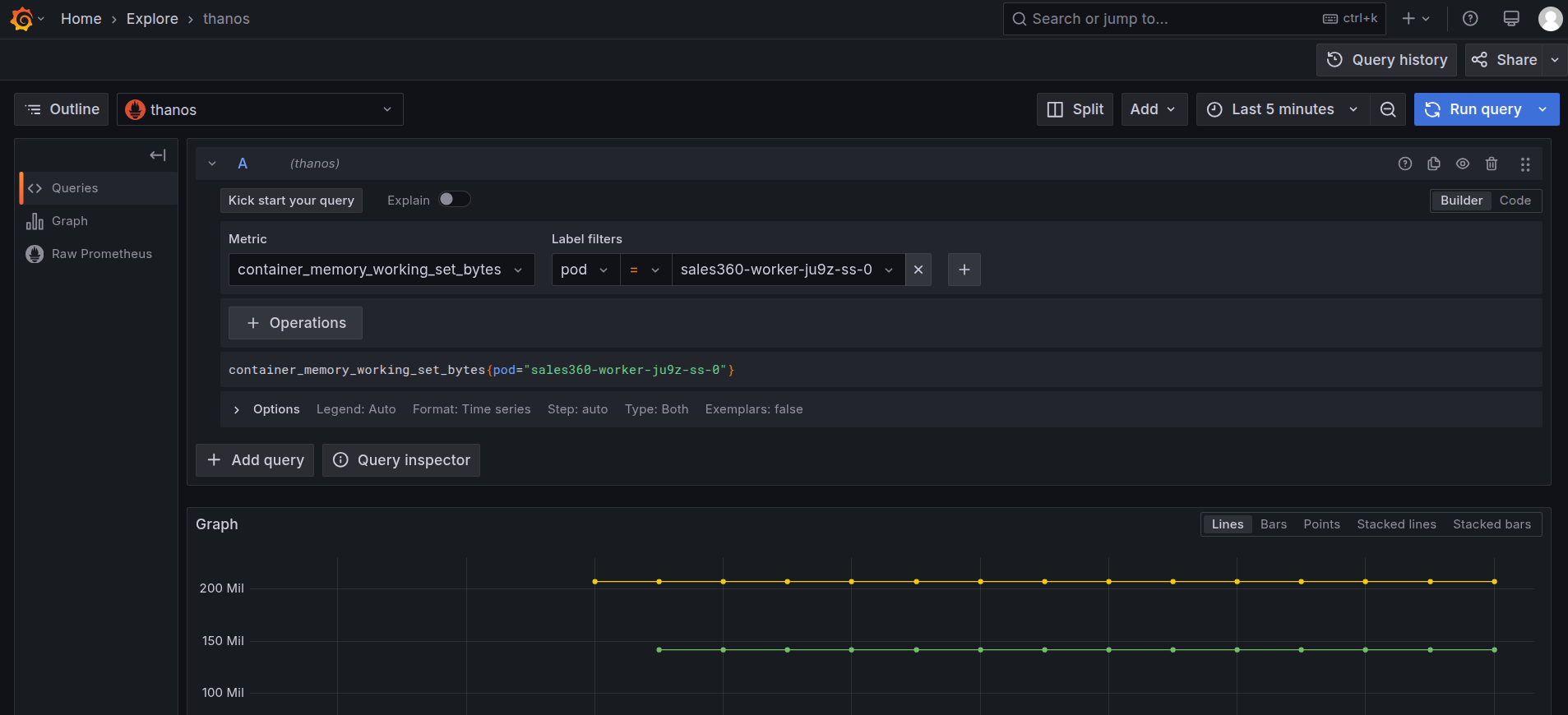
Grafana Explore: memory working set query -
On executing the query, you can see the memory used by the pod in the last thirty minutes.
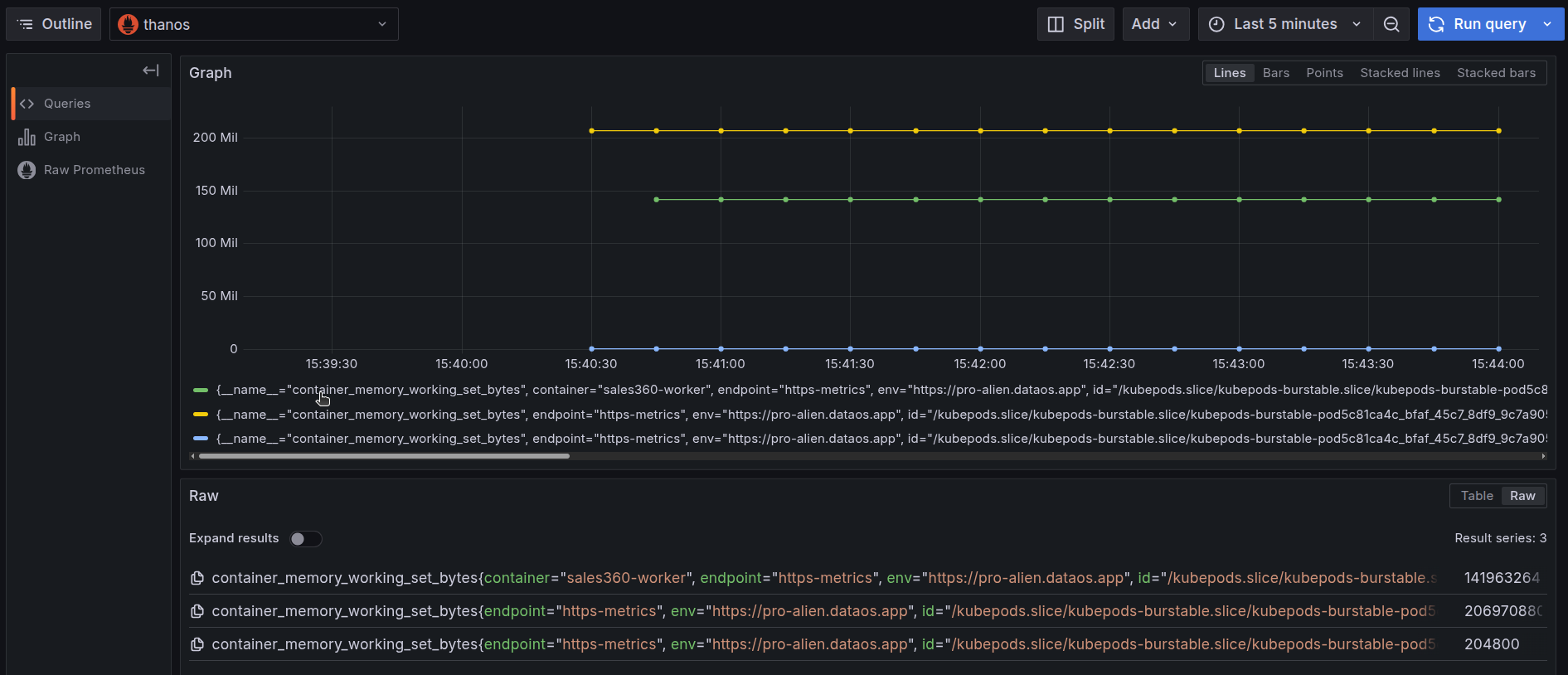
Memory usage by container over time This graph displays the cumulative CPU usage (in seconds) at the pod level for the
sales360-workerWorker. The distinct lines represent total CPU consumed by individual containers within the same pod, but together, they reflect the overall CPU footprint of the pod.The green and yellow lines accumulating around 46 seconds indicate that the pod performed sustained computational activity across multiple containers. Meanwhile, the blue line remains nearly flat, contributing negligible CPU usage, which reduces the pod’s total CPU footprint only marginally.
This distribution shows that the pod’s CPU demand is primarily driven by two containers, with the third playing a minimal runtime role. When monitoring pod-level efficiency, such patterns help in resource right-sizing and isolating CPU-intensive components.
-
You can further select the time range at which you want to see the CPU and memory usage.
Adjust the time range in Grafana
CPU alerts¶
To automatically track the CPU usage, users can configure a Monitor and a Pager to send alerts when the CPU usage exceeds certain limits. This enables teams to respond immediately to resource failures that may impact dependent components. Click here to view the steps to set up alerts for CPU usage.
Memory alerts¶
To automatically track the memory usage, users can configure a Monitor and a Pager to send alerts when the memory usage exceeds certain limits. This enables teams to respond immediately to resource failures that may impact dependent components. Click here to view the steps to set up alerts for memory usage.