Cluster management¶
This topic provides an overview of Clusters in DataOS, their role in optimizing data engineering and analytics tasks, and how they utilize computational resources through query engines like Themis and Minerva. It covers creating Clusters with supported query engine types for efficient data processing and resource management.
Scenario¶
Imagine that your team runs complex queries, perform analytics on Snowflake data, so you need a Cluster that references the Snowflake Depot. The cluster should scale efficiently. Using DataOS Clusters, you choose between Themis (elastic, scalable) and Minerva (static, predictable). You decide on Themis for its flexibility, configure a manifest file, and apply it via the DataOS CLI.
Once active, your team starts querying directly from the Workbench. Themis dynamically scales with your workload, ensuring fast, efficient queries and resource optimization. Mission accomplished!
Quick concepts¶
In DataOS, a Cluster is a Resource that combines the necessary computational resources and configurations for various data engineering and analytics tasks. It utilizes the Compute Resource for processing power.
In a Cluster, multiple provisioned machines work together to handle and execute queries efficiently. These machines collaborate through a query engine, which distributes tasks among them, optimizing performance and resource usage.
Types of query engines supported by a Cluster¶
DataOS supports two types of query engines, each designed to manage and process incoming queries by coordinating the workload across the machines within the Cluster. This collaboration enables the system to manage large datasets and complex queries with improved speed and reliability, leveraging the combined processing power of all machines in the Cluster.
Themis¶
Themis is an elastic, distributed SQL query engine optimized for fast querying across large datasets. It dynamically adjusts resources based on workload demands, making it ideal for high-concurrency and scalable enterprise environments. Themis supports a wider range of data sources and offers advanced security features, making it suitable for dynamic, large-scale applications.
Minerva¶
Minerva is a static, high-performance query engine designed for analytical and exploratory workloads. It allows seamless querying across various data sources using a unified SQL interface. Minerva Clusters handle memory, I/O, CPU, and long-running queries efficiently, making it ideal for predictable data analysis on large datasets.
Prerequisites¶
To begin creating a Cluster, ensure the following prerequisites are met:
-
You must have the specific tags or use cases assigned to create a Cluster.
-
Ensure the Depot, which you are going to target is active.
-
Decide on which query engine is suitable for your use case.
-
Make sure you have already configured the Compute Resource.
Creating a Themis Cluster¶
Follow the steps given below.
-
Configure a manifest file containing the following code and update the details accordingly.
# Resource meta section (1) name: themiscluster version: v1 type: cluster description: We are using this cluster to check the monitor and pager stuff with the help of themis cluster. tags: - cluster - themis # Cluster-specific section (2) cluster: compute: query-default type: themis # Themis-specific section (3) themis: depots: - address: dataos://lakehouseAttribute Description nameThe name of the resource. In this case, it is themiscluster, representing the name of the cluster resource.versionSpecifies the version of the resource. Here it is v1, indicating that this is the first version of the cluster.typeDefines the type of resource. The value clusterindicates that this is a cluster resource.descriptionProvides a brief description of the cluster, stating it is used for monitoring and pager tasks with the help of the Themis cluster. tagsA list of tags used for categorization. The tags clusterandthemisclassify the resource as both a cluster and related to Themis.computeDefines the compute environment for the cluster. Here, query-defaultindicates the default configuration for processing queries.typeSpecifies the type of the cluster. The value themisindicates that the cluster is using Themis query engine.depotsA list of depots (storage locations) associated with the cluster. addressSpecifies the location of the depot. In this case, it points to dataos://lakehouse. -
Apply the Cluster manifest by executing the following command in the terminal.
-
Verify the Cluster by executing the
dataos-ctl get -t cluster -w public -rcommand in the terminal. -
After the successful creation of the Cluster, you can find the Cluster on Workbench.
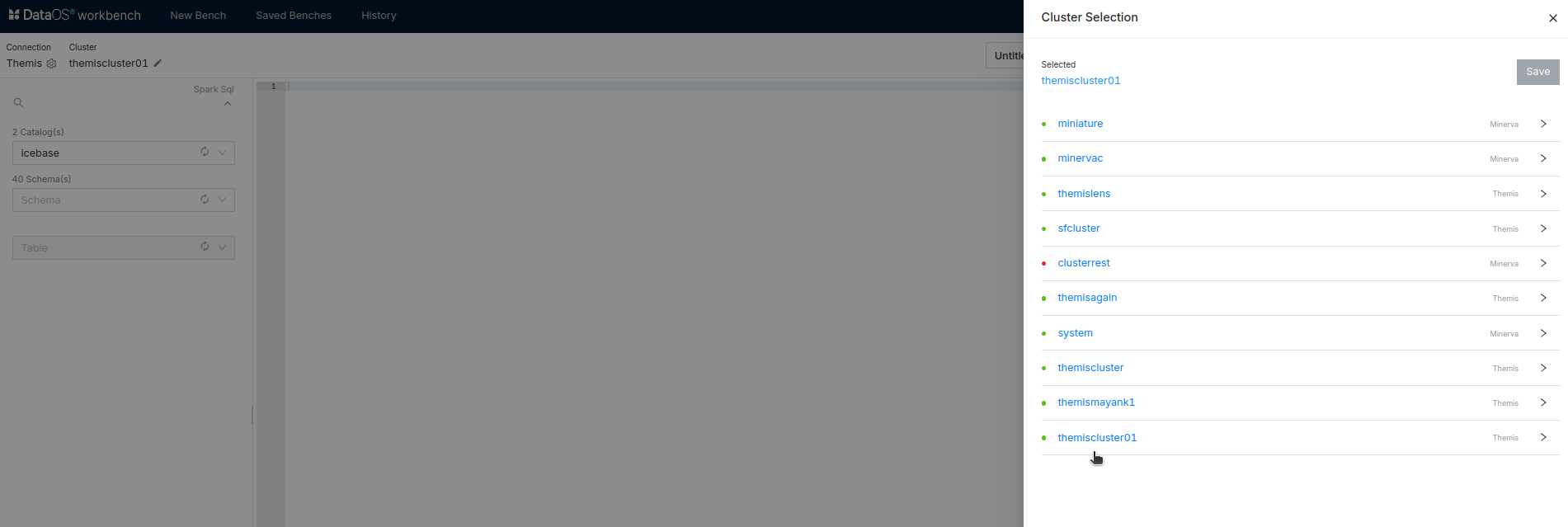
-
Similarly, you can add as many as Depots in a Cluster.
Creating a Minerva Cluster¶
-
Configure a manifest file containing the following code.
# Resource meta section name: minervatest version: v1 type: cluster description: testing tags: - cluster # Cluster-specific section cluster: compute: query-default type: minerva # Minerva-specific section minerva: replicas: 1 resources: limits: cpu: 2000m memory: 4Gi requests: cpu: 2000m memory: 4Gi depots: - address: dataos://lakehouseAttribute Description nameThe name of the Resource. In this case, it is minervatest, representing the name of the cluster resource.versionSpecifies the version of the resource. Here it is v1, indicating that this is the first version of the cluster.typeDefines the type of resource. The value clusterindicates that this is a cluster resource.descriptionProvides a brief description of the cluster, stating that it is being used for testing purposes. tagsA list of tags used for categorization. The tag clusterclassifies the resource as a cluster.computeDefines the compute environment for the cluster. Here, query-defaultindicates the default configuration for processing queries.typeSpecifies the type of the cluster. The value minervaindicates that the cluster is using Minerva-specific technology.replicasDefines the number of replicas for the cluster. Here, 1replica is specified, indicating a single instance of the cluster.resourcesSpecifies the resource requests and limits for the cluster. It includes CPU and memory configurations for both limits and requests. limitsDefines the maximum resources the cluster can consume. Here, the CPU limit is 2000m(2 CPUs) and memory limit is4Gi.requestsDefines the resources requested by the cluster. It includes 2000m(2 CPUs) of CPU and4Giof memory, matching the resource limits.debugDefines the logging configuration for the cluster. The logLevelis set toINFOfor general logs, and thetrinoLogLevelis set toERRORfor Trino logs.depotsA list of depots (storage locations) associated with the cluster. addressSpecifies the location of the depot. In this case, it points to dataos://lakehouse, indicating a depot in the DataOS. -
Apply the Cluster manifest using the following command in the terminal.
-
Verify the Cluster by executing the
dataos-ctl get -t cluster -w public -rcommand in the terminal. -
After the successful creation of the Cluster, you can find the Cluster on Workbench.
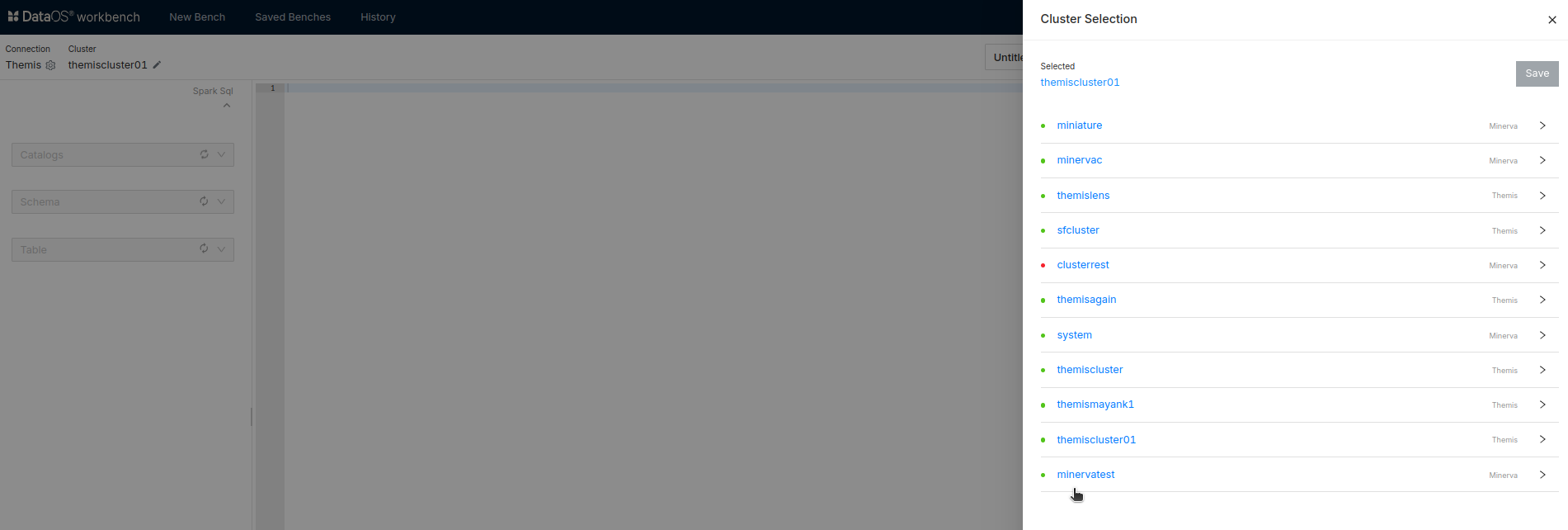
-
Similarly, you can add as many Depots as you need in a Cluster.