Integrate semantic model with Power BI Desktop¶
The following document outlines the process for integrating semantic model with Power BI Desktop.
The semantic model can be integrated with Power BI using the following ways:
-
Using Data Product Hub(Recommended - GUI based): Download
.pbipfile through an intuitive graphical interface. -
Using cURL command (Command-Line based): Download
.pbipPower BI connection via cURL command.
Using Data Product Hub¶
Prerequisites¶
-
Operating System: Power BI Desktop is only available for Windows operating systems.
-
Power BI Desktop version: Use Power BI Desktop version
2.132.908.0or later (version released after August 2024). -
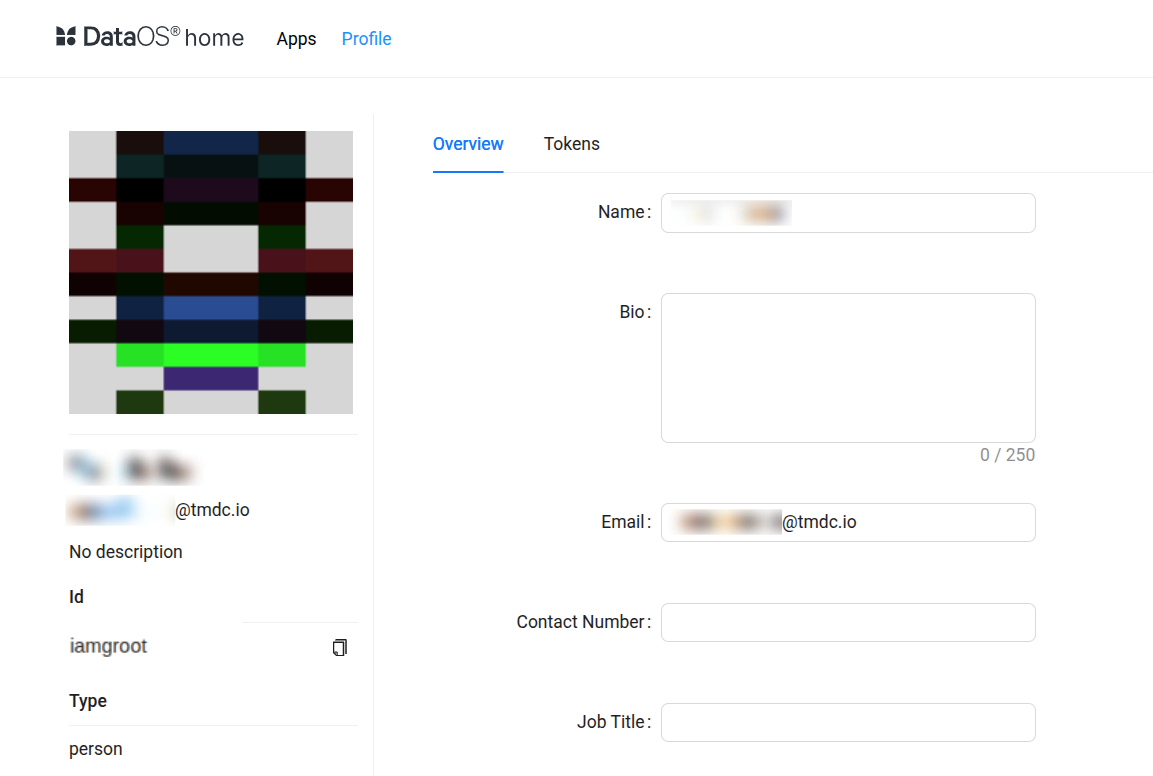
DataOS Id(username): Go to the Data Product Hub page > Click the Profile icon (bottom-left) > Select your Name/Email > On the Profile page, copy the 'Id'. It will be used as your DataOS username.
-
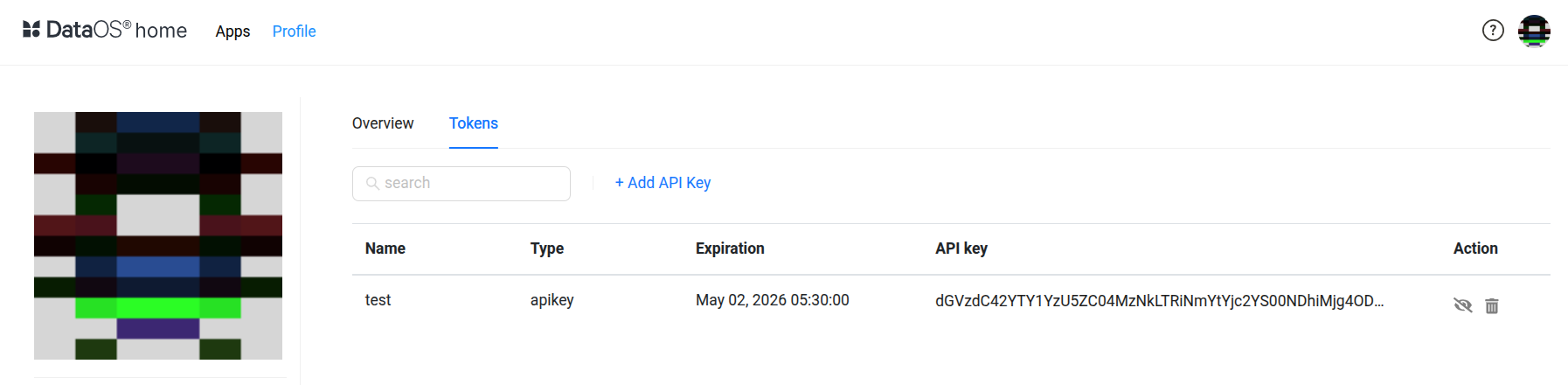
DataOS API Key(password): Obtain your key from Data Product Hub Page > Profile Icon (bottom-left) > Name/Email > Tokens Tab.
-
If no API key is listed, click
+Add API Key, provide a name for the token, and set an expiration duration (e.g., 24h or a specific date). -
Once the key appears, click the eye icon to reveal it, then click the API key to copy.
-
Note
This API key is used as your password when authenticating in Power BI.
Follow the steps below to integrate the semantic model with Power BI using Data Product Hub:
Step 1: Navigate to the Data Product Hub¶
Access the Home Page of DataOS. Click on Data Product Hub to explore the various Data Products available within the platform.
.png)
Step 2: Browse and select a Data Product¶
Browse the list of Data Products and select a specific Data Product to initiate integration with Power BI. For instance 'Product Affinity'.
.png)
Step 3: Access integration options¶
Navigate to the Access options > BI Sync > Excel and Power BI. Click the Download .pbip file button to download the ZIP folder.
.png)
Step 4: Download and open the ZIP file¶
Access the downloaded ZIP file on the local system and extract its contents to the specified directory. The extracted folder contains three files. Make sure they remain in the same directory to maintain semantic model synchronization.
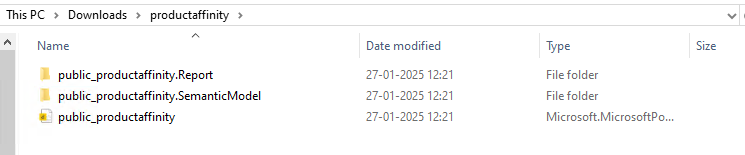
The folder contains the main components of a Power BI project for syncing the semantic model (here productaffinity). Here is the brief description of each:
-
public_productaffinity.Report: This folder contains
definition.pbirfile related to the report definition in Power BI. It stores the report metadata such as the version and dataset reference in JSON format. -
public_productaffinity.SemanticModel: This folder contains files that define the underlying data model for Power BI project. The semantic model plays a crucial role in managing how Power BI interacts with data, setting up relationships, and measures.
-
definition.bism: Contains the overall definition of a semantic model and core settings. This file also specifies the supported semantic model definition formats through the 'version' property.
-
model.bim: The
model.bimis a JSON file that defines the semantic model using Tabular Model Scripting Language (TMSL). It describes objects like measures, tables, and data sources for creating a Power BI dataset.
-
-
public_productaffinity.pbip: The
.pbipfile contains a pointer to a report folder, opening a.pbipopens the targeted report and model.
Step 5: Enter credentials¶
Open the public_productaffinity file in Power BI Desktop. A popup will appear prompting you to enter your DataOS Id as the username and API key as password.
Note
Instructions for retrieving these credentials were covered in the prerequisites section.
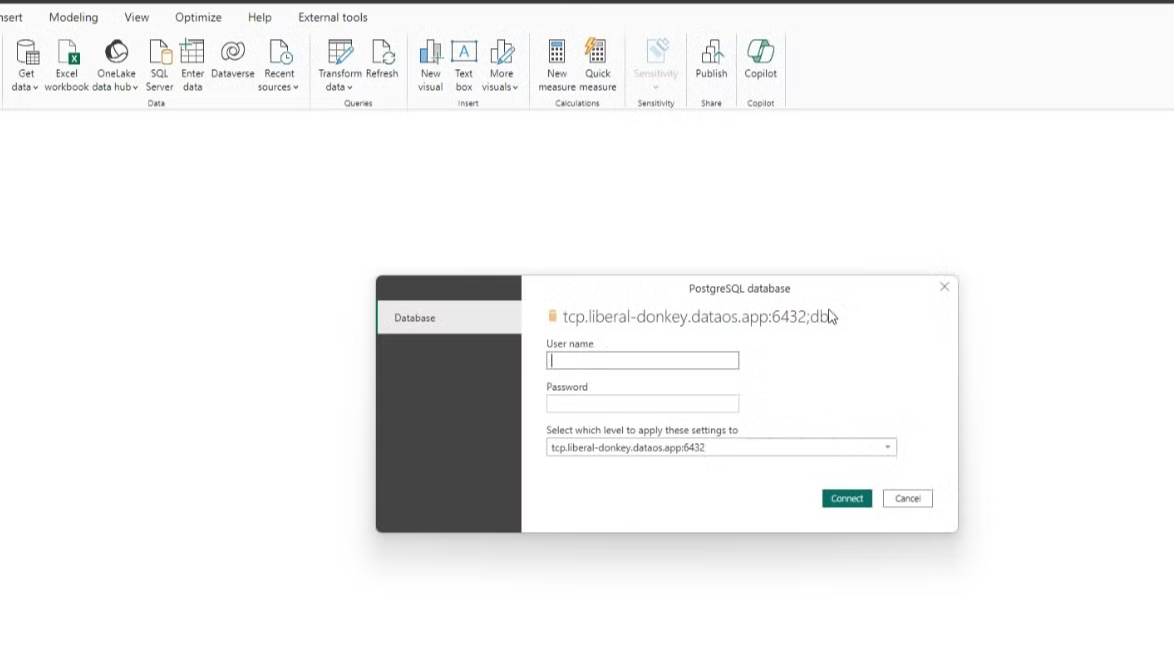
After entering your credentials, click 'Connect'. A confirmation popup will appear; click 'OK' to proceed.
Step 6: View data in Power BI¶
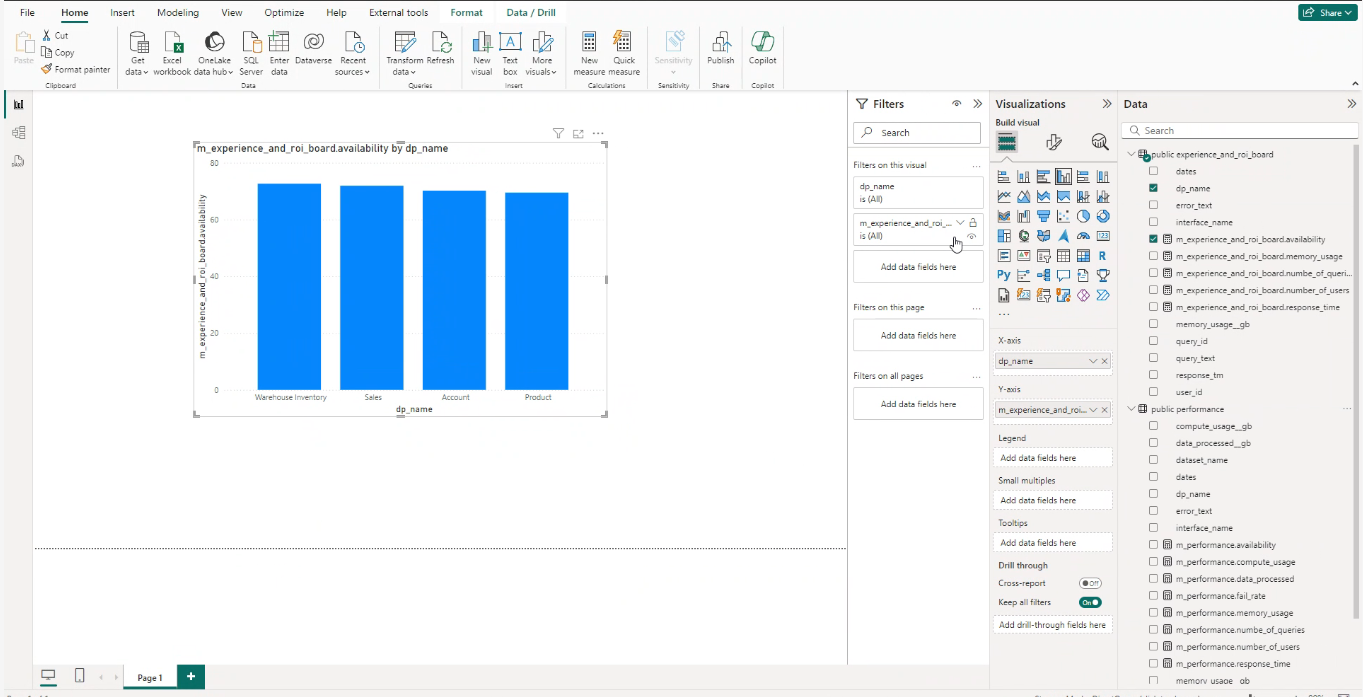
Once connected, users can explore tables and views containing dimensions and measures to build and customize dashboards.
Using cURL command¶
Prerequisites¶
-
cURL: Ensure you have
curlinstalled on your system. Windows users may need to usecurl.exe. -
Power BI version: Use
2.132.908.0or later. -
Lens API endpoint: The API endpoint provided by Lens to sync semantic model, enabling integration with Power BI.
-
Power BI Desktop: Ensure you have the Power BI Desktop app installed.
-
DataOS Id (used as the username): Retrieve your DataOS Id by running the following command in the terminal:
# command dataos-ctl user get #expected output NAME │ ID │ TYPE │ EMAIL │ TAGS ──────────────────┼────────────────┼────────┼─────────────────────────┼───────────────────────────────── Iamgroot │ iamgroot │ person │ iamgroot@tmdc.io │ `roles:id:data-dev`, │ │ │ │ `roles:id:system-dev`, │ │ │ │ `roles:id:user`, │ │ │ │ `users:id:iamgroot`
Note
Use the value under 'ID' column (e.g., iamgroot) as your username when prompted in Power BI.
-
DataOS API key: Make sure you have your DataOS API key ready — it will be used as the password when prompted. You can generate it using the command below.
If no API key is listed, execute the following command to create one:
cURL command¶
Prepare the cURL command:
curl --location --request POST '${{URL}}' --header 'apikey: ${{APIKEY}}' --output ${{FILE_NAME}}.zip
Parameters:
-
URL: This is the API endpoint for syncing semantic model with Power BI. It contains DATAOS FQDN, name and workspace of Lens (semantic model).
-
DATAOS_FQDN: Replace
with the current Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) where the Lens is deployed. For example, liberal-donkey.dataos.appis the FQDN andliberal donkeyis the context name. -
WORKSPACE_NAME: Replace
with the actual workspace where Lens has been deployed. For example, public,sandbox,curriculum. -
LENS_NAME: The name of the semantic model. For example
productaffinity.
-
-
Headers:
- apikey: User's API key for the current context in Lens.
The DataOS API key for the user can be obtained by executing the command below.
-
Output: Replace
${{File_name}}placeholder with the file name to save the file for examplefile. Afile.ziparchive is downloaded, containing the main components of a Power BI project. The name of the zip file can be specified during the curl command execution, and it will be saved accordingly.
The file.zip includes essential components for syncing a semantic model with Power BI, organized into folders such as .Report and .SemanticModel.
-
public_productaffinity.Report: This folder contains
definition.pbirfile related to the report definition in Power BI. It stores the report metadata such as the version and dataset reference in JSON format. -
public_productaffinity.SemanticModel: This folder contains files that define the underlying data model for Power BI project. The semantic model plays a crucial role in managing how Power BI interacts with data, setting up relationships, hierarchies, and measures.
-
definition.bism: Contains the overall definition of a semantic model and core settings. This file also specifies the supported semantic model definition formats through the 'version' property.
-
model.bim: The model.bim file is a JSON file that contains the Tabular Model Scripting Language (TMSL) definition of a Power BI semantic model. It's used to create a database from scratch by defining objects such as measures, tables, and connection sources.
-
-
public_productaffinity.pbip: The
.pbipfile contains a pointer to a report folder, opening a.pbipopens the targeted report and model.
Steps¶
To begin syncing the semantic model, the following steps should be followed:
Step 1 Run the curl command: For example, if the productaffinity semantic model is in the public workspace in the liberal-donkey.dataos.app FQDN, the cURL command would be:
curl --location --request POST 'https://tcp.liberal-donkey.dataos.app/lens2/sync/api/v1/power-bi/public:productaffinity' --header 'apikey: abcdefgh==' --output file.zip
Step 2 Download the zip file: Once the command is executed, a zip file will be downloaded to the specified directory. The downloaded file should be unzipped. Three folders will be found inside, all of which are necessary for semantic synchronization with Power BI.

Step 3 Open the Power BI file: Open the public_productaffinity file in Power BI Desktop. Once opened, a prompt will appear asking for your credentials. Enter your DataOS Id as the username and your API key as the password to proceed.
Step 4 Connect to DataOS: Click the 'Connect' button. When the popup appears, click OK to continue.
Step 5 Access tables with dimensions and measures: Upon successful connection, tables and views will be accessible, displaying dimensions and measures.
Connecting Power BI to the DataOS Lakehouse¶
This section involves steps to connect Power BI to physically modeled data in the DataOS Lakehouse using the DataOS REST API connector and the Presto ODBC Driver.
Using the DataOS REST API connector¶
Follow the steps below to connect Power BI to the DataOS Lakehouse using the DataOS REST API connector:
-
Install the custom connector locally. Refer to the installation guide here.
-
After setup, DataOS appears as a data source in Power BI Desktop. Connect and start visualizing tables from the catalog.
-
Queries are routed to the Minerva cluster, which retrieves data from the Lakehouse, allowing BI developers to define custom logic and calculations in Power BI.
Using the Presto ODBC Driver¶
Refer to this guide to connect Power BI to the DataOS Lakehouse using the Presto ODBC Driver.
Supported data types¶
| Category | Data Types | Support Status |
|---|---|---|
| Dimension | time, string, number, boolean |
Supported |
| Measure | max, min, number, sum, count, boolean, string, time, avg, count_distinct |
Supported |
| Measure | count_distinct_approx |
Not Supported |
| Rolling Window | - | Not Supported (Power BI doesn’t support) |
Important considerations¶
- In Power BI, measures typically have an 'm_' prefix to indicate they represent a measure. For example, a measure calculating total revenue might be named
m_total_revenue. - The connection is live, meaning any changes to the underlying data will be reflected in Power BI.
- When schema changes occur, such as CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete) on dimensions, measures, or other elements of the semantic model, a re-sync is required. To prevent losing previously created reports after the re-sync, download the
.pbipfolder from the Data Product Hub, extract the contents, and replace the existing.SemanticModelfolder with the new.SemanticModel.
Best practices¶
Adhering to best practices ensures that you effectively utilize the Data Product Hub and maintain compatibility with the latest features and updates. Following these guidelines will help optimize workflow, enhance performance, and prevent potential issues.
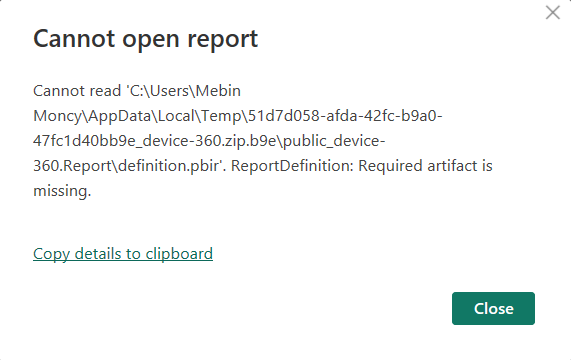
File handling¶
Ensure that .pbip folders are fully extracted before opening them. Failure to do so may result in missing file errors, as shown below:
Data retrieval and field selection considerations¶
It is important to select fields from tables that are directly related or logically joined, as the system does not automatically identify relationships between tables through transitive joins. Selecting fields from unrelated tables may result in incorrect or incomplete results.
Troubleshooting¶
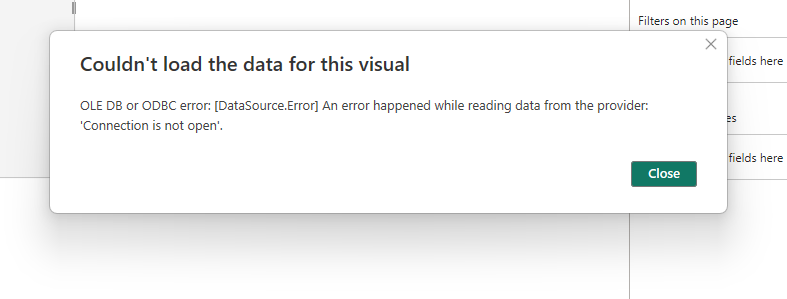
Connection reset¶
If you encounter a 'connection reset' error during Power BI sync as shown below:
- Go to the Home tab in Power BI Desktop.
- Click the Refresh button in the Queries section.
This should resolve the error and restore the sync.
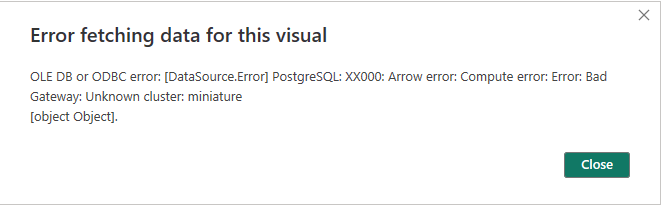
Unknown cluster¶
Whenever you encounter the error 'unknown cluster:
Limitations¶
- Power BI fails to handle special characters (e.g., &, %, #) when generating queries through the synced semantic model, causing errors in visualizations. Thus, it is best practice to address or remove special characters directly in the data.
- Power BI's Direct Query mode does not support creating custom dimensions and measures or querying the rolling window measure due to the lack of date hierarchy.
- DAX functions and Import query mode are not supported.
Governance of semantic model in Power BI¶
Data masking, restrictions, and permissions established by the publisher are automatically enforced for all report viewers, ensuring consistent data security and compliance. The behavior of these data policies, such as masking, may vary based on the use of Power BI Desktop or other interfaces.
When the Lens semantic model is activated via BI Sync on Power BI, authentication and authorization are handled using the DataOS Id and API key. This ensures that columns redacted by Lens data policies are restricted based on the user's group permissions.
For example, if a user named iamgroot, belonging to the 'Analyst' group, is restricted from viewing the 'Annual Salary' column, this column will not appear in either the Data Product exploration page or in Power BI after synchronization. Power BI requires the DataOS user Id and API key for authentication, ensuring that users can access the full model except for columns restricted by their data policies.
This approach ensures that users only see the data they are authorized to view, maintaining security and compliance.
FAQs¶
-
What are the version compatibility requirements for Power BI Desktop integration?
Power BI Desktop version 2.132.908.0 (released in August 2024) or later must be used for .pbip support without requiring preview settings. Additionally, Microsoft Power BI is primarily designed to run on Windows operating systems.
-
How do you get started with the Power BI Desktop?
To begin using Power BI Desktop:
-
Download the Power BI ZIP folder from Data Product Hub and extract it.
-
Open the
.pbipfile from the extracted folder using the Power BI Desktop application. -
When prompted, provide your DataOS Id as the username and API token as password to connect to the data source.
-
After successful authentication, you can start querying the semantic model and building reports.
-
-
How does governance work in Power BI Desktop?
Access Management (User Permissions)
Power BI Desktop users must provide their DataOS credentials (DataOS Id as the username and API token as password) when connecting to data sources. Upon successful authentication, they can begin developing reports within the Desktop environment.
Data Governance (Row-Level, Column-Level Policies)
Data policies such as redaction and access control are enforced based on the identity of the user who registered the data source. These policies govern access at both the row and column levels.
-
What different data types are supported?
Supported Data Types
Category Data Type Support Status Dimension Time, String, Number, Boolean Supported Measure Max, Min, Number, Sum, Count, Boolean, String, Time, Avg, Count_distinct Supported Measure Count_distinct_approx Not Supported Rolling Window - Not Supported (Power BI does not support) Limitations
Due to limitations in Power BI’s DirectQuery mode, rolling window measures cannot be queried. This is because DirectQuery does not support date hierarchies, making it impossible to offer time-based granularity required for rolling window logic.
Point to note
When creating cross-table queries, always select fields from logically related tables. Transitive joins are not auto-recognized by Power BI, and querying unrelated tables can yield incorrect results.
-
How does model update work?
If there are any schema changes in the semantic model, the model must be re-synced with Power BI. Re-downloading the Power BI project folder and opening the
.pbipfile without proper steps can cause previously created reports to be lost.To safely update the model without losing existing reports:
-
Download the new semantic model from Data Product Hub.
-
Replace only the model.bim file in your current Power BI project’s SemanticModel folder with the updated model.bim from the newly downloaded folder.
-
-
How does Power BI sync work when syncing model-first data products?
-
The Power BI Developer downloads the project folder containing the semantic model and
.pbipfile. -
The
.pbipfile is launched in Power BI Desktop. -
Authentication is performed using DataOS credentials (User Id and API Token) via DirectQuery on port 6432.
-
Queries triggered in Power BI are routed through the Postern service to the PgSQL API layer.
-
The API forwards the request to Lens, which translates it into native SQL and queries the data source.
-
The response flows back to Power BI Desktop for visual creation.
-
-
What connection mode does Power BI use to connect to DataOS when working with a model-first data product?
Power BI connects to DataOS using DirectQuery mode via the Postern service. When a visual is created, Power BI directly queries the underlying data source, and visual refresh time depends on source performance.
-
Where does the computation happen for the Power BI semantic model sync?
Computation occurs in two layers:
-
Within DataOS: Lens translates semantic model queries into native SQL.
-
Within Data Source: Actual data retrieval and computation are performed.
-
-
What data sources are supported to sync model-first data products to Power BI?
All data sources compatible with Lens can be synced to Power BI.
-
Is custom measure and dimension creation supported for model-first data products in Power BI?
No. All measures and dimensions must be defined in Lens. Power BI does not support custom calculation creation when using model-first products. For flexible use cases, integration with the Lakehouse is recommended. More info.
-
Is a separate connection required in Power BI for each model-first Data Product?
Yes. Each model-first Data Product in DataOS requires a separate connection configuration in Power BI.
-
What are the known limitations when syncing model-first data products to Power BI?
-
Direct Publishing: Not supported. Manual download and update are required for model changes.
-
On-Premises Gateway Dependency:
-
Required to connect PostgreSQL-based semantic models.
-
Must configure gateway with Npgsql driver.
-
-
Special Characters: Limited support in Power BI. Such characters must be handled in raw data or during semantic modeling.
-
-
How can percentage formatting be enforced in Power BI visuals?
Power BI allows format enforcement through its UI.
-
For Columns: Select the column, go to Column Tools → Formatting → Set to 'Percentage'.
-
For Measures: Select the measure, go to Measure Tools → Formatting → Choose 'Percentage'.
-
-
How is dashboard data freshness maintained in Power BI using DirectQuery?
DirectQuery ensures real-time querying from the data source, requiring no scheduled refresh. However, to ensure uninterrupted access, source-level monitoring of pipelines or jobs should be configured.