Use-Cases¶
A use-case consists of a combination of predicates (actions) and objects (entities upon which actions are performed), defining a specific set of permissions or actions granted to users. When you grant a Use-Case to a user, establishing a link between the subject and the use-case. This connection, in the back end, results in the creation of an access policy.
These Use-Cases can be broken down into smaller, more granular permissions, or bundled together. For instance, if a user has access to read lens, it's likely they should also have access to manage lenses, as managing encompasses the ability to create and update lenses, in addition to reading them. Each use-case may involve predicates such as delete, get, patch, and post, which collectively determine the actions a user can perform.
Assigning a use-case proves especially valuable in scenarios where granting access to the entire set of entities associated with a role is not desired. Instead, it enables a highly restricted set of permissions tailored to a specific task.
For instance, if a data analyst or user within your company needs to query a specific dataset within a collection, granting access to all datasets in that collection is not advisable. In such cases, assigning a use-case to that particular user appears more appropriate. By granting access to a specific dataset, you achieve a higher level of granularity in data access. Further refinement of data access can be achieved through authorization atoms.
The ‘Use-Cases’ tab in Bifrost lists all the possible actions needed to perform on various services and applications of DataOS as shown below.
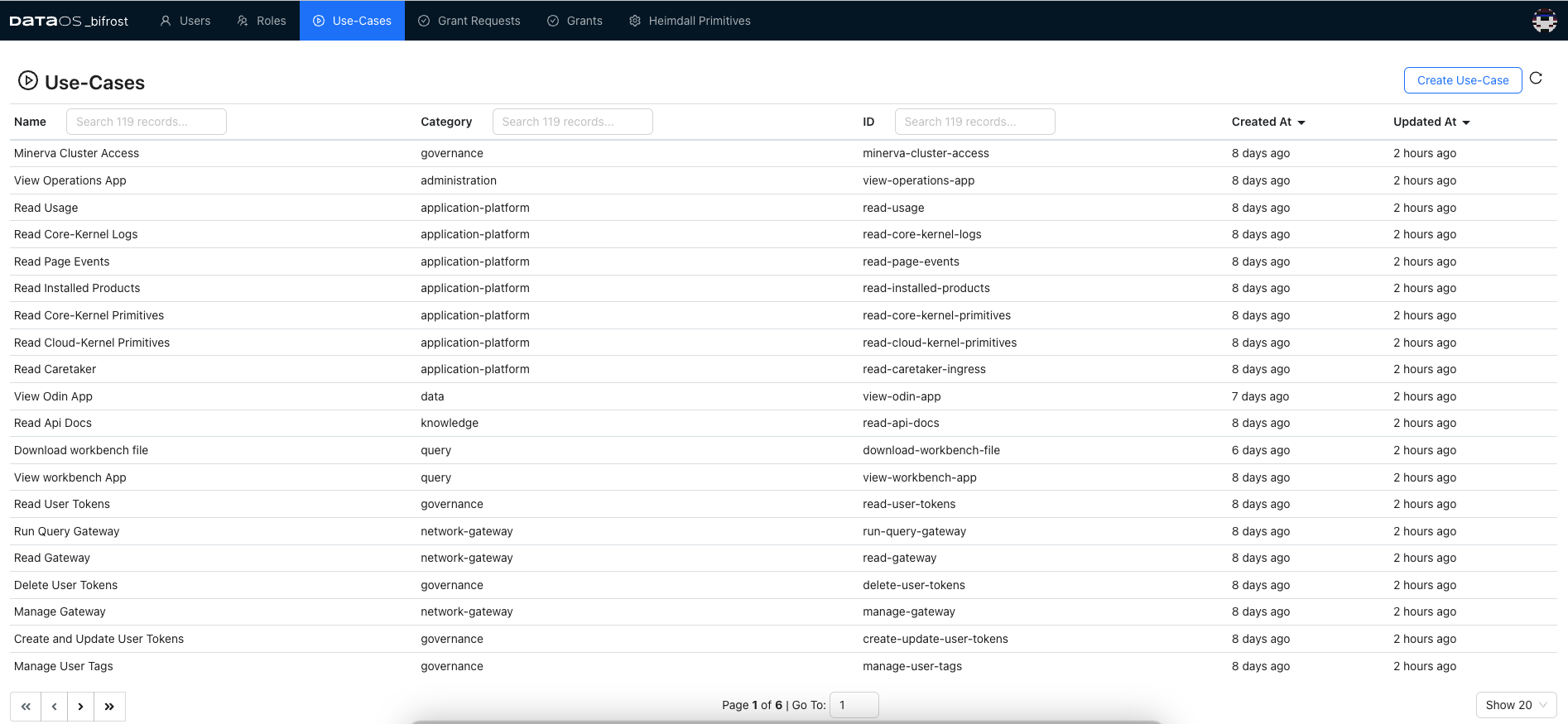
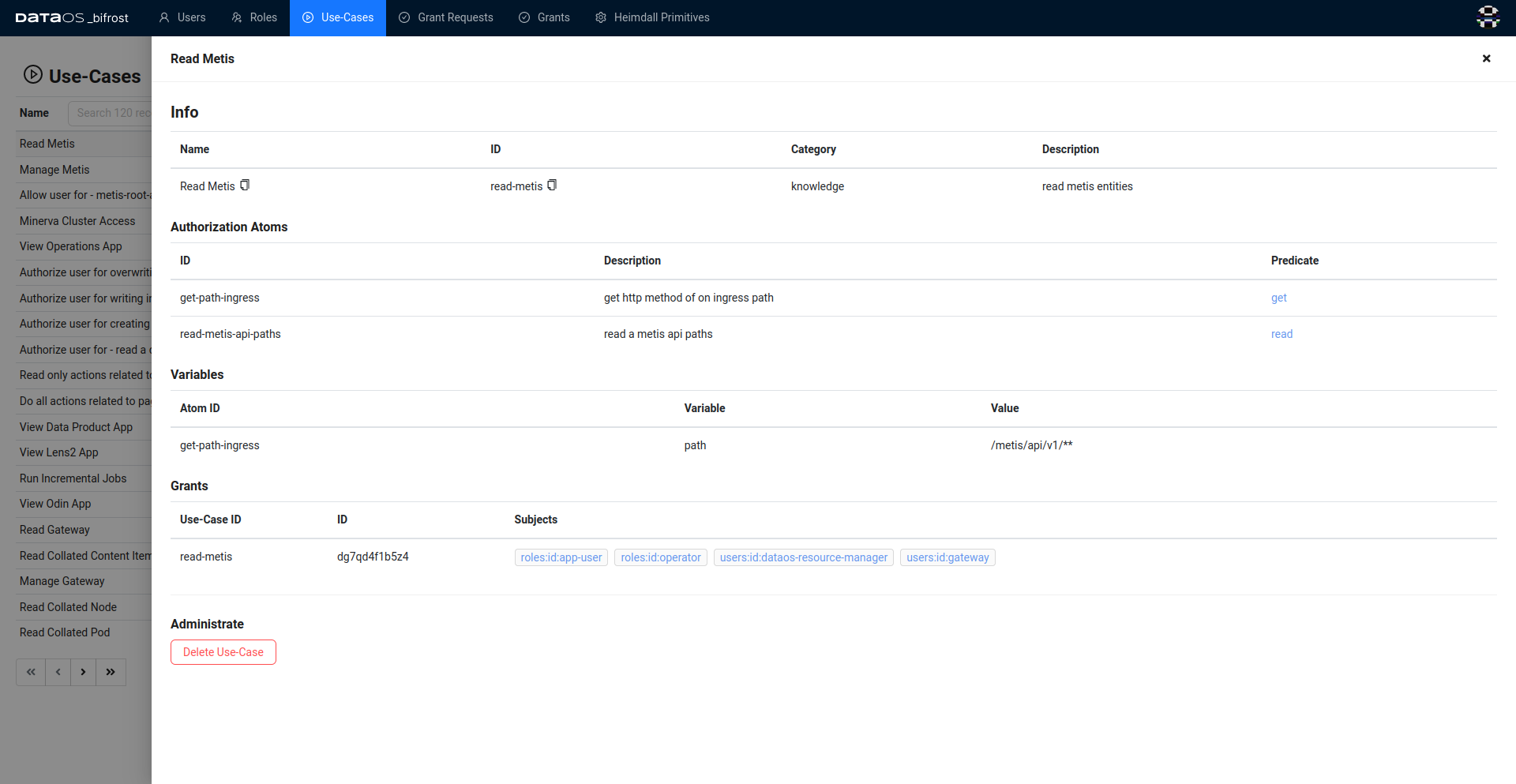
Upon selecting any listed use-case, a window appearing from the right has the details around the selected use-case such as Info, Authorization Atoms, Variables and Grant.
The Info section furnishes details such as the use-case's name, ID, and category, indicating its classification.
Clicking on a predicate reveals further details and the object, specifying where the action will take place. For instance, clicking on the "get" predicate unveils the object as an API path, typically defined as ${path}, offering flexibility in path updates without altering or even granting access to multiple API parts within a single use-case. Authorization atoms outline the permissions and actions available for a particular service or application.
To update the path value, navigate to the Variable section, where the actual path for the specific use-case is located.
Lastly, In the grant section, you'll find a subsection labeled "Subject" where you can determine who has been granted access to the use-case thus far.
How to grant a Use-Case to a role?¶
Granting a use-case to a role follows the same steps as granting a use-case to a user but instead of navigating to users, you'll go to roles and select any existing role. Let's demonstrate this process by adding a Use-Case named “Minerva Cluster Access" to the role:id:testrole
- Navigate to Roles and select the "test role".
- Navigate to the grants section. Click on the "Grant Use-Case" button.
- Enter "Minerva Cluster Access" in the search bar and select from the displayed options.
- Click on the Grant to add a Use-Case to the role.
A success message will be displayed confirming that the Use-Case has been successfully added to the role.
How to create a new Use-Case?¶
In addition to granting the current Use-Cases, you have the option to generate a new Use-Case by creating a YAML use-case artifact. This is particularly useful if you identify a combination of predicate and object that isn't already present but could be relevant to your organization. To create a new use-case follow the below steps:
-
Navigate to the Use-Cases tab in Bifrost
-
Click on create Use-Case
-
Enter the use-case manifest file
A sample Use-Case manifest is given below:
Sample Use-Case manifest
# Enter the Yaml Use-Case Artifact
id: write-depot-dataset
name: 'Write Depot - Dataset'
description: 'write depot and its datasets using specific dataset elements'
category: data
authorization_atoms:
- write-dataset
- write-depot-service-paths
- post-path-ingress
- put-path-ingress
values:
- authorization_atom_id: post-path-ingress
variable_values:
- path: /ds/api/v2**
- authorization_atom_id: put-path-ingress
variable_values:
- path: /ds/api/v2**
Note: When granting a new use-case, it is essential to specify whether full access is desired or if limited access should be granted.
For instance:
- To grant access to the entire depot, dataset, and tables, use the following address format:
- If access is to be restricted to specific tables, utilize the address format below:
- To grant access specifically on lakehouse, employ the address format demonstrated:
Alternatively, you can apply the following sample access policy manifest
Sample access policy manifest
name: access-policy-workspace
version: v1
type: policy
tags:
- data product
- dataos:workspace:curriculum
- curriculum
description: access policy to allow a user to work in a specific workspace
layer: user
policy:
access:
subjects:
tags:
- users:id:iamgroot
predicates:
- read
- create
- update
- delete
- create_in
- delete_in
- read_in
- update_in
objects:
tags:
- dataos:layer:user
- dataos:type:resource
- dataos:workspace:curriculum
- dataos:resource:database
- dataos:resource:cluster
- dataos:resource:service
- dataos:resource:workflow
- dataos:resource:worker
- dataos:resource:volume
- dataos:resource:secret
allow: true
How to edit a Use-Case?¶
To edit a Use-Case, you have two options. The first method is to delete the existing Use-Case and create a new one with the desired modifications. The second method involves editing the Use-Case that was generated during installation, as it's included in the installation file.
How to delete a Use-Case?¶
To delete a Use-Case:
- Navigate to the Use-Case section within Bifrost.
- Locate and select the specific use-case you wish to delete.
- Scroll down to the options and choose "Delete Use-Case."
List of Use-Cases¶
Here is the list of use-cases we currently support:
Info
This document may not cover every new use-case that gets added over time. For the most up-to-date and extended list of use-cases, please visit Use-Case tab of the Bifrost of your organization.
| Name | Category | Description |
|---|---|---|
| View Audience App | audience | View & browse through audience application. |
| Manage Analytics Events | analytics | Manage Analytics Events |
| Read Analytics Events | analytics | Read Analytics Events |
| View Operations App | administration | Browse all resources(cluster/workflow/service/depots etc.) in operations application. |
| Read Caretaker | application-platform | authorize user to read caretaker |
| Read Cloud-Kernel Primitives | application-platform | read cloud-kernel primitives; dataplanes, nodes |
| Read Collated Content Item | application-platform | read the collated content item. content items contain sensitive information. |
| Read Collated Node | application-platform | read the collated historical information of a node |
| Read Collated Pod | application-platform | read the collated historical information of a pod |
| Read Core-Kernel Logs | application-platform | read core-kernel logs from pods |
| Read Core-Kernel Primitives | application-platform | read core-kernel primitives; ingresses, services, workloads, pods |
| Read Installed Products | application-platform | read products that are installed on this instance |
| Read Page Events | application-platform | read page events that are installed |
| Read Usage | application-platform | read pod and container usage resource details |
| Peer and Exec Stream Service | application-platform | peer to a specific instance fqdn, then exec stream a pod |
| Peer and Log Stream Service | application-platform | peer to a specific instance fqdn, then log stream a pod |
| Peer and Stream Service | application-platform | peer to a specific instance fqdn, then tcp stream a target address |
| Allow user for metis root access | governance | allow user for metis root access |
| Authorize user for - read a dataset using themis | governance | authorize user for themis-read-dataset |
| Authorize user to manage data policy | governance | Authorize user to manage data policy |
| Authorize user to read data policy | governance | Authorize user to read data policy |
| Manage Governance Primitives | governance | manage governance primitives like roles, providers, atoms, use-cases, grants, policies |
| Manage Secrets | governance | Manage secrets in the heimdall vault |
| Manage User Tags | governance | create, update, and delete user tags |
| Manage User Tokens | governance | Manage users tokens |
| Manage Users | governance | Manage users |
| Minerva Cluster Access | governance | Fine grained access given to a user or a role on a specific cluster to query data using this cluster |
| Read All Secrets From Heimdall | governance | read All secrets in the heimdall vault |
| Read Governance Primitives | governance | read governance primitives like providers, atoms, use-cases, grants, policies |
| Read Specific Secret | governance | read a specific secret in the heimdall vault |
| Read User Tags | governance | read user tags |
| Read Users | governance | Read users |
| View Bifrost App | governance | View Bifrost App |
| Download workbench file | query | Download files from workbench. |
| View workbench App | query | View and query depots and sources through workbench application. |
| Manage Lens | contract | manage lens and contracts |
| Read Lens | contract | read lens and contracts |
| View Lens App | lens | Browse and query lenses in lense application. |
| Manage Lens2 Backend | lens | Manage Lens2 Backend |
| Read Lens2 Backend | lens | Read Lens2 Backend' |
| Save Lens Data | lens | Save lens data. |
| Get Products Details From Poros | product-management | Get Products |
| Manage Products in Poros | product-management | Get Products |
| Manage All Dataset | data | Manage All Dataset |
| Manage Specific Dataset | data | Manage Specific Dataset |
| Read All Dataset | data | Read All Dataset |
| Read Specific Dataset | data | Read Specific Dataset |
| View dph app | data | View dph application. |
| View Lens2 App | data | View & browse through lens2 application. |
| Run Query Gateway | network-gateway | run a query through the gateway |
| Manage Gateway | network-gateway | manage gateway entities |
| Read Api Docs | knowledge | Read Api Docs |
| Read Metis | knowledge | read metis entities |
| Run Incremental Jobs | knowledge | access to run incremental jobs |
| Manage Metis | knowledge | manage metis entities |
| Admin Grafana App | observability | Gives permission to create and edit graph in grafana |
| View Grafana App | observability | It will give access to view the graphs of grafana |
| Create Update and Delete Lakehouse in system layer workspaces | resource-management | Manage lakehouse in the system layer workspaces |
| Create Update and Delete Lens in System layer Workspaces | resource-management | Manage lens in the System layer Workspaces |
| Create Update and Delete Monitor Resources in user layer Workspaces | resource-management | Manage monitor in the user layer workspaces |
| Create Update and Delete Pager Resources in System layer Workspaces | resource-management | Manage pager Resource in the system layer workspaces |
| Create Update and Delete Pager Resources in user layer Workspaces | resource-management | Manage pager Resource in the user layer Workspaces |
| Manage All Depot | resource-management | Give permission to create, delete, update all depot |
| Manage Cluster in System Workspaces | resource-management | Manage cluster in the system layer workspaces |
| Manage Cluster in User Workspaces | resource-management | Manage cluster in the user layer workspaces |
| Manage Database in System Workspaces | resource-management | Manage database in the system layer workspaces |
| Manage Database in User Workspaces | resource-management | Manage database in the user layer workspaces |
| Manage Secret in System Workspaces | resource-management | Manage secret in the system layer workspaces |
| Manage Service in System Workspaces | resource-management | Manage service in the system layer workspaces |
| Manage Service in User Workspaces | resource-management | Manage service in the user layer workspaces |
| Manage System Workspaces | resource-management | create, delete system layer workspaces |
| Manage User Workspaces | resource-management | create, delete user layer workspaces |
| Manage Workflow in System Workspaces | resource-management | Manage workflow in the system layer workspaces |
| Manage Workflow in User Workspaces | resource-management | Manage workflow in the user layer workspaces |
| Manage Worker in System Workspaces | resource-management | Manage worker in the system layer workspaces |
| Manage Worker in User Workspaces | resource-management | Manage worker in the user layer workspaces |
| Manage all instance-level resources of DataOS in System Layer | resource-management | create, delete, update of all instance-level resources of DataOS in system layer |
| Manage All Instance-level Resources of DataOS in user layer | resource-management | create, delete, update of all Instance-level resources of DataOS in user layer |
| Read All Resources in System Workspaces | resource-management | read all resources in the system layer workspaces |
| Read All Resources in User Workspaces | resource-management | read all resources in the user layer workspaces |
| Read Collated Resource | resource-management | read the collated historical information of a resource |
| Read Instance Collated Resource | resource-management | read the collated historical information of an instance resource |
| Read Schemas | resource-management | read schemas |
| Read Stack related Secrets | resource-management | allows retrieval of a stack image pull secret |
| Read Workspaces | resource-management | read workspaces |
| Un-sanitize Resources | resource-management | un-sanitize resources during read operations, this makes secrets and sensitive fields visible |
| Read Talos | Talos | Read Talos |
| Manage Profile in Home App | profile | Manage Profile in Home App |
| Manage User Tokens in Home App | profile | Create and delete user tokens in home app |
| View home App | profile | View home app |