Core Concepts of the Scanner Stack¶
The Scanner facilitates metadata extraction by utilizing Depots to connect to the metadata source. The core concepts include:
-
Metadata Extraction: Collects metadata from source systems, DataOS services, and components.
-
Scanner Job: A fundamental unit of work within a Workflow that performs metadata extraction.
-
Source: The metadata source from which the Scanner Stack extracts metadata.
-
Metadata Store: Extracted metadata is stored in MetisDB, a centralized PostgreSQL database.
-
Scheduled Workflow: Automates metadata extraction at predefined intervals.
-
Metadata Types: The Scanner Stack extracts various types of metadata, including:
-
General dataset/table information (e.g., names, owners, tags)
-
Detailed metadata (e.g., table schemas, column names, descriptions)
-
Data quality and profiling information
-
User and owner details
-
Data product metadata (e.g., inputs, outputs, SLOs, policies, lineage)
-
How the Scanner Stack Works¶
In DataOS, metadata extraction is orchestrated using two different types of DataOS resources: Workflow and Worker. The choice of orchestrator depends on the specific use case:
-
Workflow Resource: Used for batch workloads that perform metadata extraction at scheduled intervals.
-
Worker Resource: Used for long-running, continuous workloads that push metadata to MetisDB in real-time.
Metadata Extraction Process¶
The Scanner Stack follows an ETL-like process (Extract, Transform, Load):
-
Extract
-
The source system is defined in the Depot, which establishes the connection to the metadata source.
-
The Scanner Stack extracts metadata from the connected source.
-
-
Transform
- Metadata is standardized into a common format for consistency across DataOS.
-
Load
-
Transformed metadata is pushed to the Metis REST API server, which stores it in MetisDB(PostgreSQL).
-
Batch-based processing is handled via Workflow Resource, while continuous ingestion is performed via Worker Resource.
-
Usage of Extracted Metadata
- Metadata is utilized by various DataOS components for discoverability, governance, and observability.
- External applications running on DataOS can retrieve metadata via Metis Server APIs.
- In DataOS, all metadata entities are defined and consumed in JSON format.
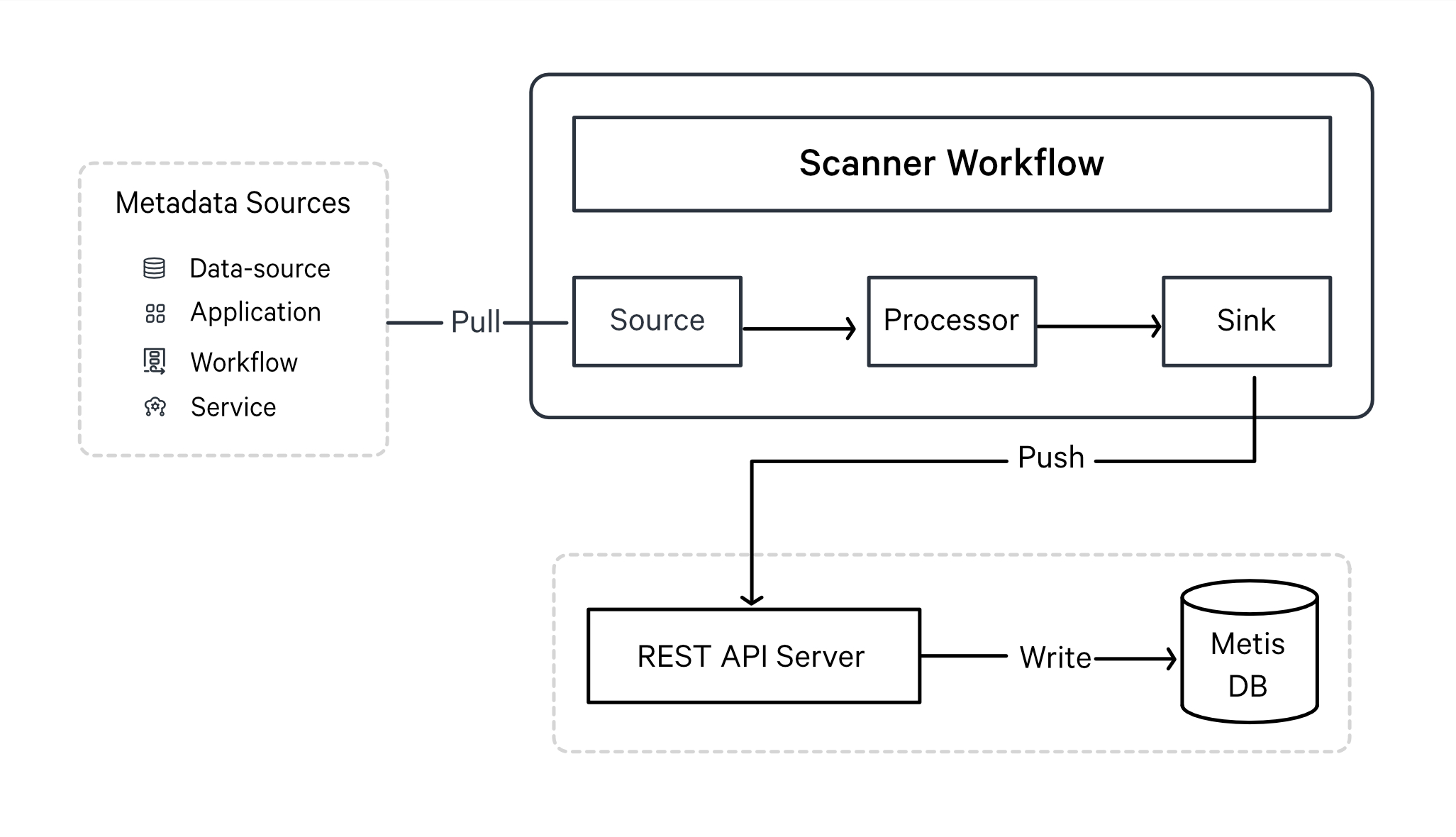
In addition to external applications, the Scanner Stack extracts metadata from DataOS applications and services. The Scanner job reads relevant metadata and pushes it to MetisDB through the Metis REST API server, making it accessible via Metis UI.
Scanner Job Integrations with DataOS Components¶
Collation Service
-
Scans and publishes metadata related to DataOS Resources such as Workflows, including execution history, execution states, and job metadata.
-
Collects historical metadata for pods, logs, and processing stacks like Flare and Bento, capturing job information and source-destination relationships.
Gateway Service
-
Retrieves metadata related to data profiling (statistical summaries of datasets) from the Soda.
-
Scans data quality metadata, capturing checks and their pass/fail status.
-
Extracts query usage insights, identifying frequently accessed datasets and relationships between datasets.
Heimdall
- Scans and retrieves user information within DataOS, including user descriptions and profile images, accessible via Metis UI.
Pulsar Service
- Listens to messages published by various services and stacks, ensuring real-time metadata updates.