Integration with API¶
Overview
The Integration feature for your Data Product, allows developer teams to programmatically access system data—specific metrics, filtered datasets, or targeted subsets—directly through APIs. This is ideal for applications requiring automation, data embedding, or on-demand querying.
📘 Scenario¶
While exploring the semantic model in the Studio feature, a developer needs to retrieve the total number of customers by country to power an internal analytics dashboard. They select the appropriate measure and dimension to analyze customer distribution across regions. Once the data is reviewed in Studio on Data Product Hub, the developer decides to integrate it programmatically into their application to support automated and dynamic reporting.
Integration options¶
For teams needing to fetch data programmatically, the 'Integration' tab provides options:
Let’s assume you need to fetch the 'total number of customers by country'. Rather than building REST endpoints, you can efficiently query the data using a curl command, GraphQL, or Postgres, depending on your preference. These methods allow you to retrieve data from a given endpoint and present it in a user-friendly format within your application.
First, select the following dimensions and measures:
total_customerscountry
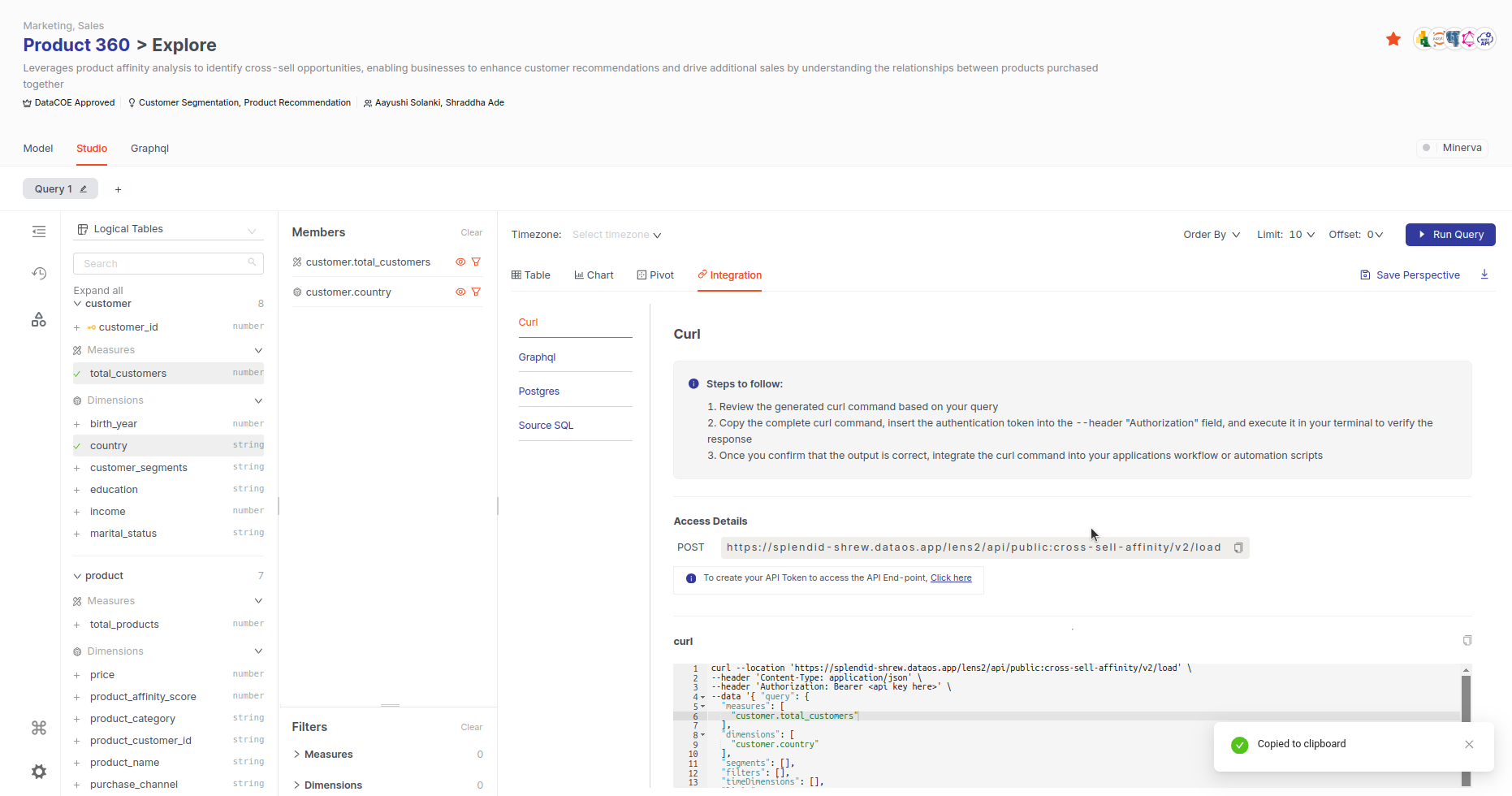
Using Curl¶
To access your data over HTTP using curl, follow these steps:
-
Copy the
curlCommandGo to the 'Integration' section and choose 'Curl' option. Copy the provided Curl command and paste it into your terminal.
-
Replace Placeholder You will notice a placeholder for
<api_key>in the command. Replace it with your actual API key. This will allow you to fetch the required data for integration into your application.
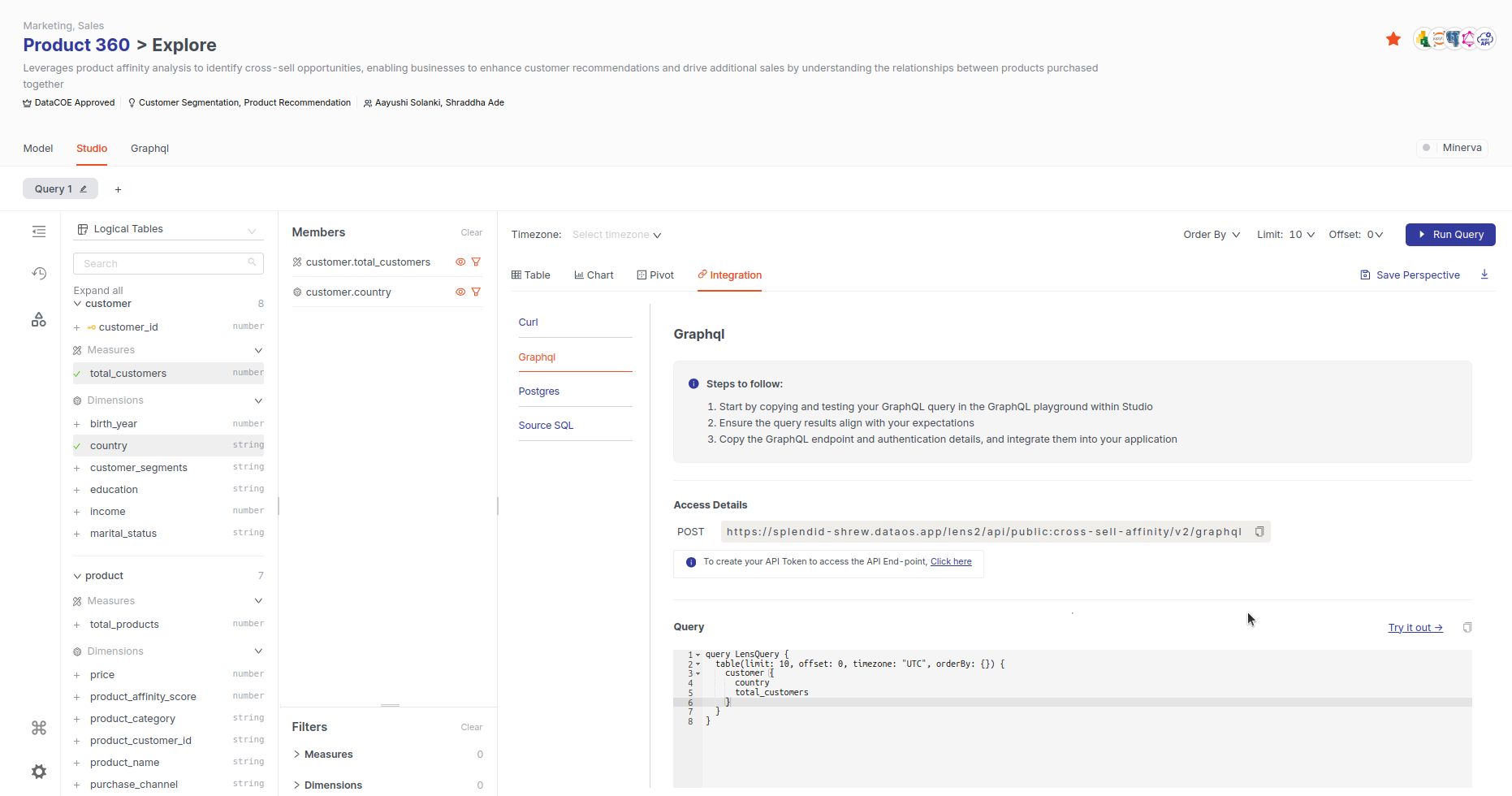
Using GraphQL¶
GraphQL is another option for querying data over HTTP.
To use GraphQL:
- Select 'GraphQL' in integration options.
-
Click on 'GraphQL' and copy the query provided.
-
Test the Query
You can either paste the query into your terminal or click 'Try it out' to test it in the GraphQL playground.
-
View Data in GraphQL Interface
After testing, you can view the results in the GraphQL interface alongside the Studio tab.
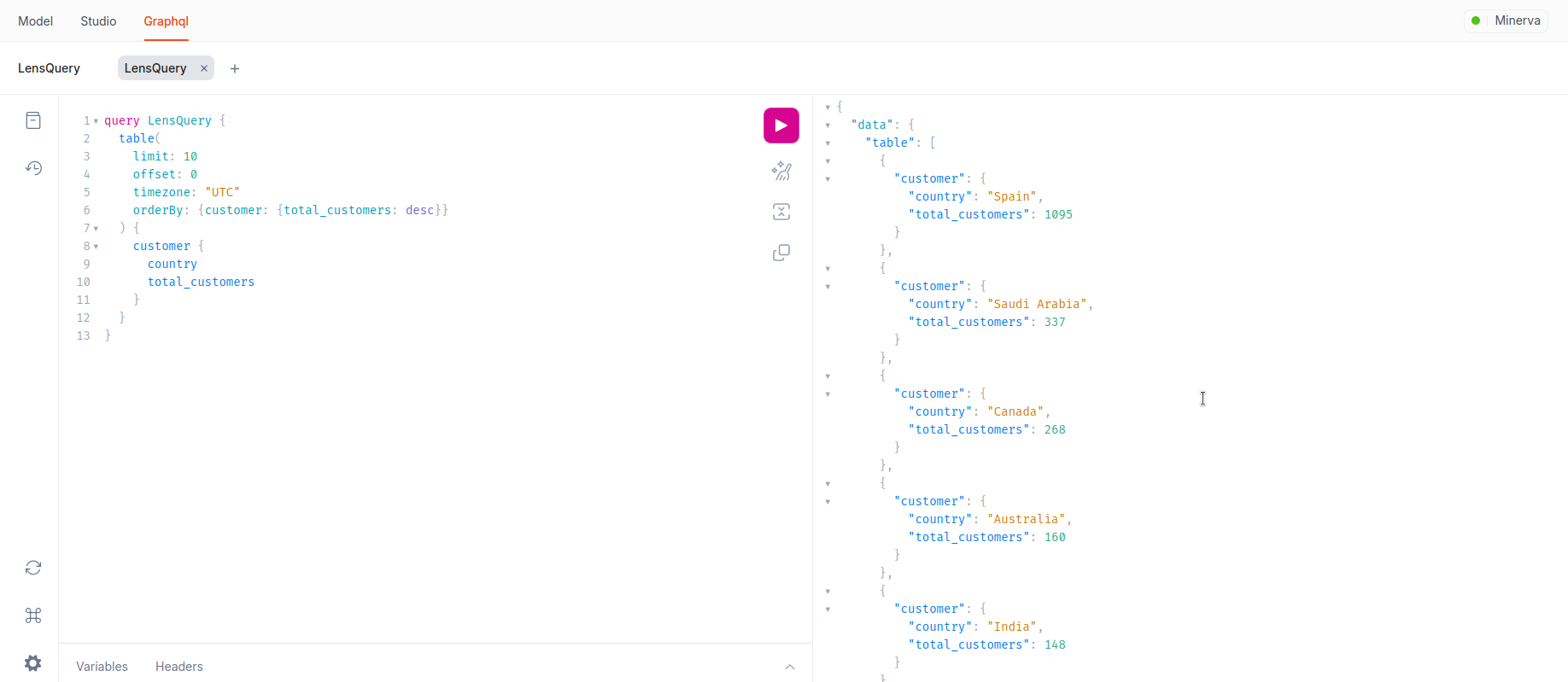
You can now successfully integrate the query code into your application.
Using Postgres¶
For those who prefer using the Postgres database, follow these steps:
-
Copy Postgres Command
To interact with the Postgres database, copy the given PSQL client command and paste it into your terminal. When prompted for a password, enter your API key.
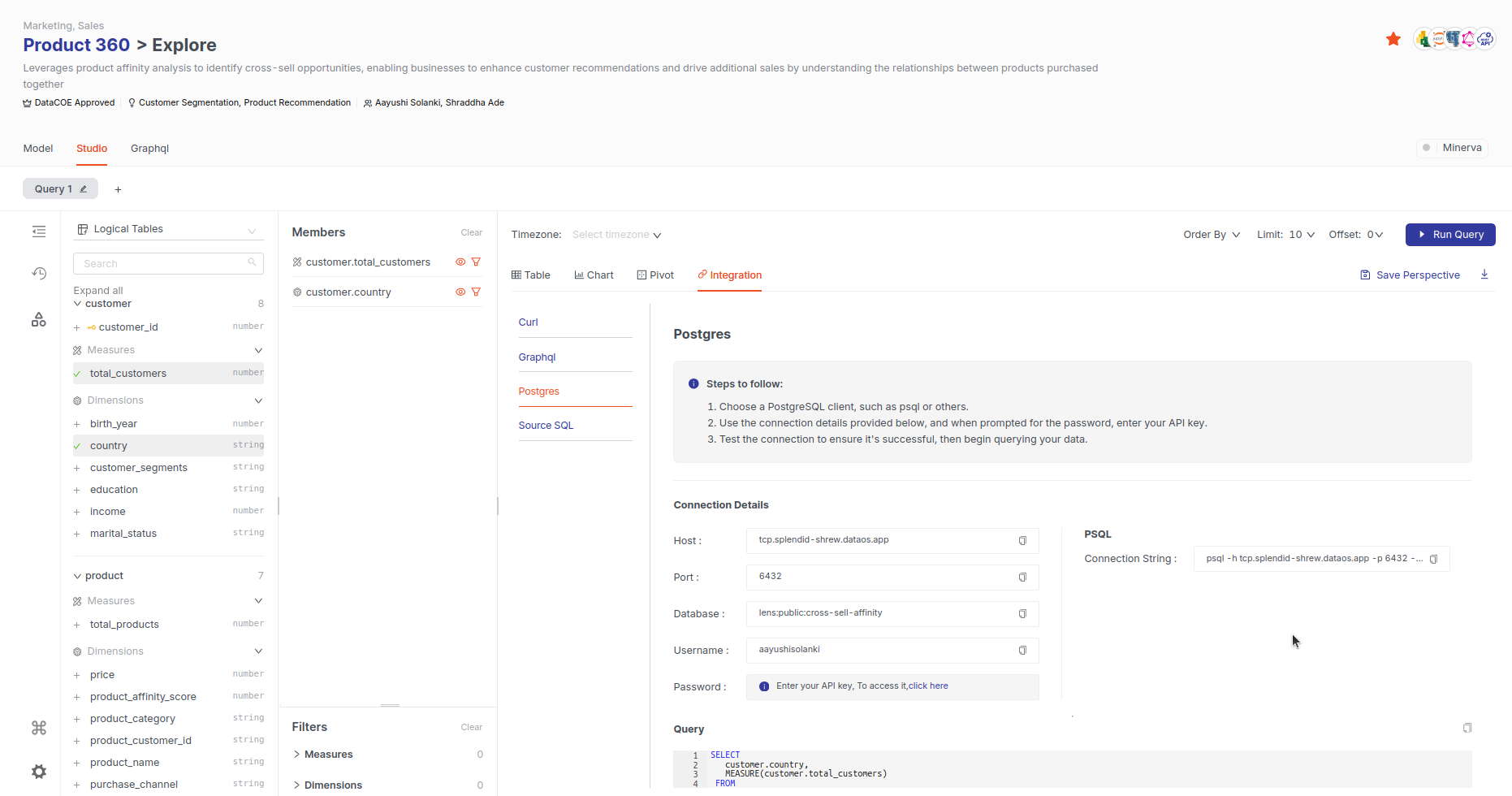
-
Retrieve the API Key
To get the API key, click on the link in the password section of your connection details.
-
Expected Output
Once you enter the command in the terminal, the following output confirms that the Postgres database connection was successful:
psql (16.4 (Ubuntu 16.4-0ubuntu0.24.04.2), server 14.2 (Lens2/public:cross-sell-affinity v0.35.60-9)) lens:public:cross-sell-affinity=>You can now interact with the Lens or semantic model using Postgres commands. For example, to list all tables in the connected database, use:
Expected Output:
List of relations Schema | Name | Type | Owner --------+------------------------------+-------+---------------- public | cross_sell_opportunity_score | table | iamgroot public | customer | table | iamgroot public | product | table | iamgroot public | purchase_data | table | iamgroot public | purchase_frequency | table | iamgroot public | total_spending | table | iamgrootAdditional PostgreSQL Commands¶
Here are some useful commands to interact with the Postgres database:
Command Description Example \d [table_name]Show the schema and details of a specific table. \d customers\lList all databases in the PostgreSQL server. \l\duList all roles and users in the PostgreSQL server. \du\dnList all schemas in the database. \dn\dvList all views in the connected database. \dv\qExit the PostgreSQL prompt. \q