Exploration of Lens using REST APIs¶
REST API enables Lens to deliver data over the HTTP protocol. It is enabled by default and secured using API scopes. It consists of a base path and API scopes:
-
Base Path: All REST API endpoints are prefixed with
/lens2/api. For example,/v2/metais accessed at/lens2/api/<lens_name>/v2/meta. -
API Scopes: Endpoints are secured by API scopes, restricting access based on user permissions. It follows the principle of least privilege, granting only the necessary access.
API Endpoint Request Methods and Body Types
When accessing different API endpoints, the request method and the format of the request body vary. Below is a breakdown of how to interact with each endpoint.
| Endpoint | Method | Request Body Type | Body Format Example |
|---|---|---|---|
meta |
GET | N/A | N/A |
graphql |
POST | GraphQL query | graphql format query LensQuery { table(limit: 10, offset: 0) { products { productcategory average_price average_margin }} } |
load |
POST | Raw or JSON | json format { "query": { "dimensions": ["products.productcategory"], "measures": ["products.average_price", "products.average_margin"]} } |
sql |
POST | Raw or JSON | json format { "query": { "dimensions": ["products.productcategory"], "measures": ["products.average_price", "products.average_margin"] } } |
Authentication and Authorization¶
To securely interact with the Lens REST API, you must authenticate your requests using a DataOS API key and ensure proper user group configurations. This section explains how to generate an API key and configure user groups for accessing the API.
Generating a DataOS API Key¶
To authenticate API requests, you need a DataOS API key. This key validates your identity and ensures only authorized users can access and query the data.
Steps to Generate an API Key:
- Open your terminal and run the following command to create a new API key:
- To view existing API keys, use:
- Note down your API key and keep it secure. You will use this key to authenticate your API requests.
API key tokens can also be fetched from the DataOS GUI, for more details refer to the documentation here.
Configuring User Groups¶
To access and query data via the RESTAPI endpoint, users must be part of a user group with the required permissions. The necessary permissions are defined using the api_scopes attribute within the user group configuration located in the Lens directory. To know more about user groups and data policy click here
Example User Group Configuration
The following YAML configuration demonstrates how to set up Lens user groups with different access levels:
user_groups:
# User group with full access to GRAPHQL API and data querying capabilities
- name: engineer
description: Data Analyst
api_scopes:
- meta # For accessing metadata
- graphql # For accessing the GraphQL API
- data # For querying the data
includes:
- users:id:exampleuser
# User group with access to GRAPHQL API but no data querying capabilities
- name: analyst
description: Data Engineer
api_scopes:
- meta
- graphql
includes:
- users:id:testuser
# User group without access to GRAPHQL API or data querying capabilities
- name: testuser
description: Data Engineer
api_scopes:
- meta
includes:
- users:id:testuser
Explanation of the Configuration:
engineerGroup: This group can access the REST API and query data because it includes both thegraphqlanddataapi_scopes.analystGroup: This group can access the REST API but cannot query the data because thedatascope is missing.testuserGroup: This group cannot access the REST API or query data because both thegraphqlanddatascopes are missing.
Note
The user groups configured above only manage access permissions at the consumption level within DataOS. However, source-level permissions set by the source administrator (e.g., in Snowflake or BigQuery) still apply. For sources accessible through the DataOS Query Engine (Minerva/Themis), you can define source-level permissions using the Bifrost application in the DataOS GUI or using the Policy and Grant Resource using DataOS CLI.
How to access the RESTAPIs?¶
Explore lens using REST APIs using the following methods:
- Postman: A API Testing tool for data application developers
- Curl: A command-line tool for transferring data with URLs, useful for automated scripts.
- Python: Use Python's
requestslibrary for more complex interactions with the API.
Using Postman¶
Use Postman to interact with Lens via REST APIs. Start by importing the following Postman collection.
When working with a Postman collection to test APIs, you typically need to configure authorization, set request methods, and provide the request body. Below are the steps to get started:
-
Open Postman and import the Postman collection:
- Open Postman and click on the Import button located at the top-left corner.
-
Import the Postman Collection file you’ve been given. For example, if you import the Lens API collection from the provided link, you will see a collection of API requests neatly organized into folders.
Postman
-
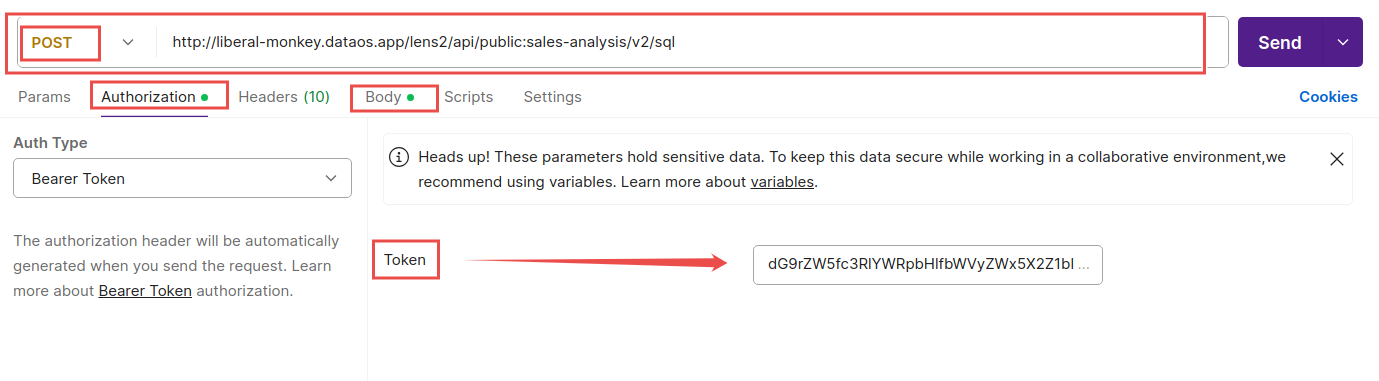
Set up Authorization (bearer token):
- Once the collection is imported, click on the specific API request you want to test.
- Go to the Authorization tab.
- From the Auth Type dropdown, select Bearer Token.
- In the Token field, paste your Bearer token, which you have received from your authentication process.
- This token grants you access to the meta and data scopes.
-
Set the Request type:
- Select the API method you want to use (e.g.,
GET,POST) from the dropdown next to the API URL.
- Select the API method you want to use (e.g.,
-
Prepare the URL and Query the API:
- Prepare the URL according to what data you want to fetch.
-
Replace
<URL>with the appropriate endpoint based on your environment:- For local development, use:
- For a deployed Lens model, use:
-
Replace
<DATAOS_API_KEY>with your actual DataOS API key. Refer to the Generating an API Key section for more information on obtaining an API key. -
Replace
<DATAOS_FQDN>with the fully qualified domain name of your DataOS instance. For example:alpha-omega.dataos.apporhappy-kangaroo.dataos.app. -
Replace
<WORKSPACE>with the workspace name associated with your Lens model. This is typically the name of the DataOS Workspace where the Lens is deployed. For example:public,sandbox, etc. -
Replace
<NAME_OF_LENS>with the name of your deployed Lens model. This corresponds to the specific Lens model you want to query. For e.g.sales360. -
Replace
<ENDPOINT>with the specific endpoint you wish to access. For e.g.meta,load,graphql. -
Replace
<QUERY>with the specific fields you want to query from schema. Make sure to format the query string as valid JSON.
-
Set the Request Body in Postman (for POST Methods):
- If your request is a POST (e.g., for
graphql,load, orsqlendpoints), you will need to configure the Body tab in Postman according to the endpoints.
- Refer to the below image for subsequent steps.
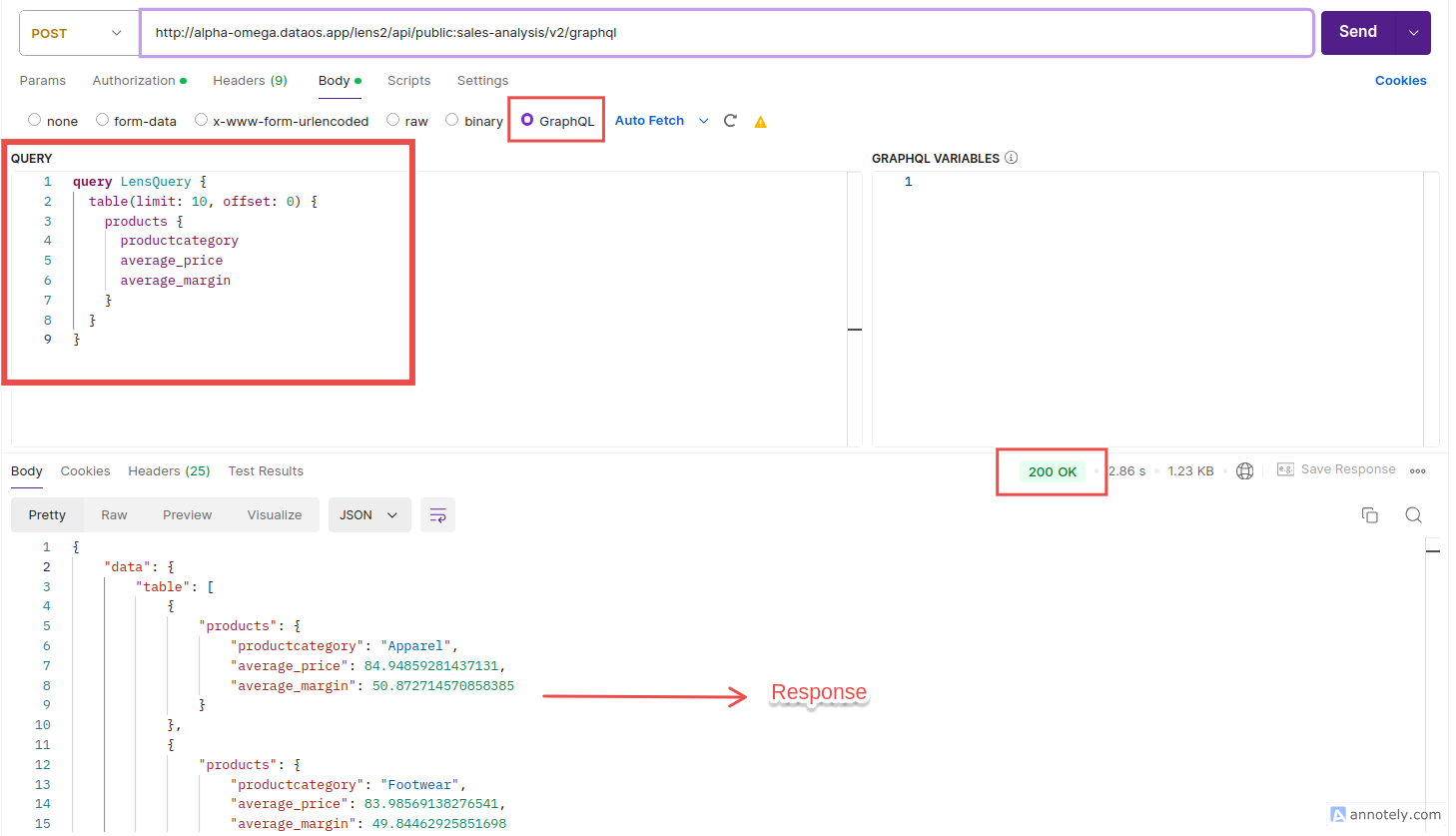
Postman Request - In the
Bodytab, selectGraphQLfrom the format options. - Enter the GraphQL query in the provided field in the following format.
query LensQuery { table(limit: 10, offset: 0) { <TABLENAME> { <DIMENSION> <MEASURE_1> <MEASURE_2> } } }-
Replace table name and choose required dimensions and measures.
-
For Example: If you want to compare the average price and average margin of two major categories: Apparel and Footwear. The request body will be:
- Refer to the below image for subsequent steps.
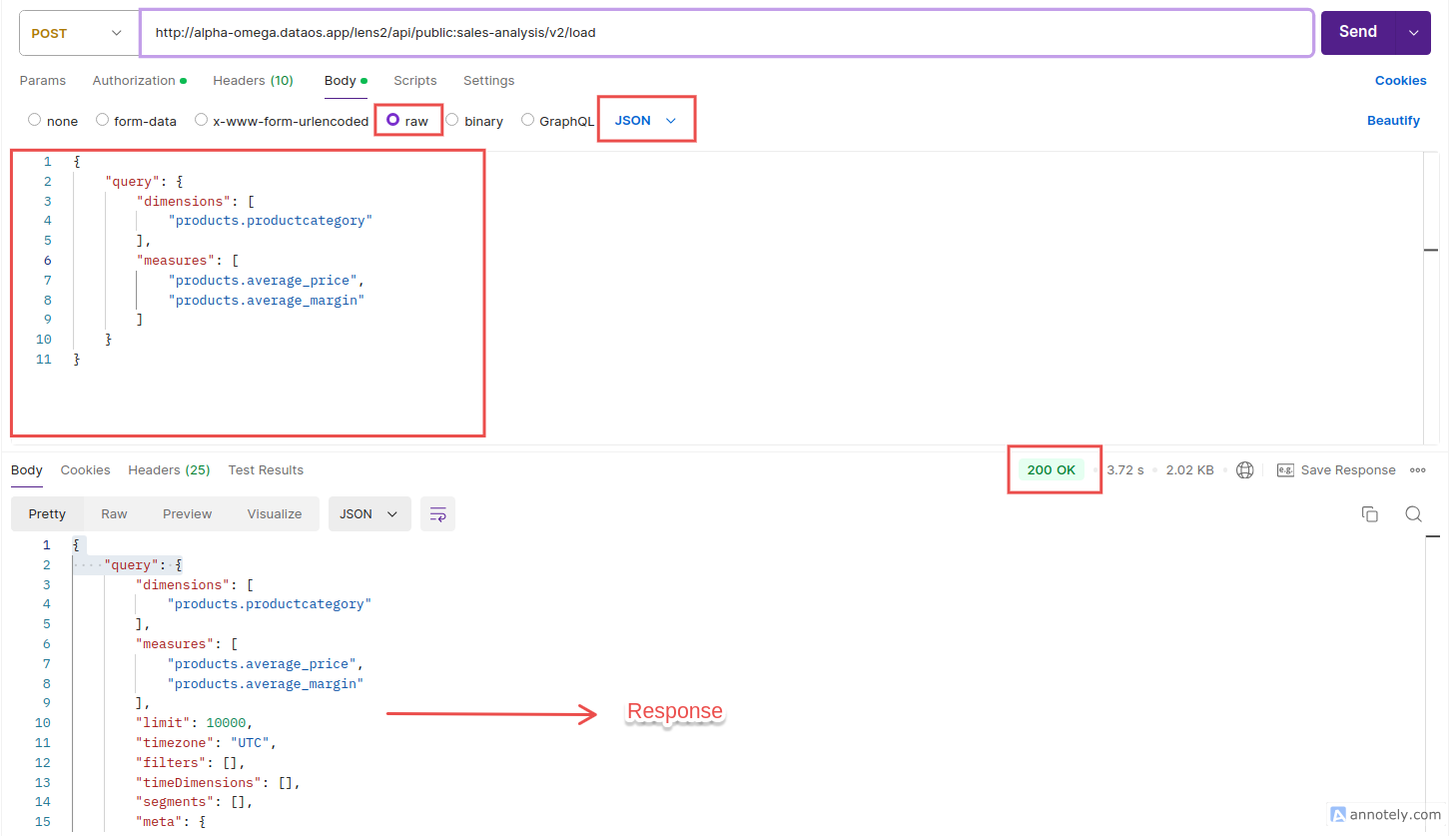
Postman Request - In the
Bodytab, selectraw. - From the dropdown next to
raw, selectJSON. - Enter the
JSONquery in the request body in the following format.
{ "query": { "dimensions": [ "TABLE_NAME.DIMENSIONNAME" ], "measures": [ "TABLE_NAME.MEASURE_1", "TABLE_NAME.MEASURE_2" ] } }-
Replace table name and choose required dimensions and measures.
-
For Example: If you want to compare the average price and average margin of two major categories: Apparel and Footwear. The request body for load endpoint will be:
{"query":{"dimensions":["products.productcategory"],"measures":["products.average_price","products.average_margin"],"limit":10000,"timezone":"UTC","filters":[],"timeDimensions":[],"segments":[],"meta":{"secured":{"segments":[],"dimensions":[]}},"rowLimit":10000},"data":[{"products.productcategory":"Apparel","products.average_price":84.94859281437131,"products.average_margin":50.872714570858385},{"products.productcategory":"Footwear","products.average_price":83.98569138276541,"products.average_margin":49.84462925851698}],"lastRefreshTime":"2024-09-26T06:44:34.180Z","refreshKeyValues":[[{"refresh_key":"14394441"}]],"usedPreAggregations":{},"transformedQuery":{"sortedDimensions":["products.productcategory"],"sortedTimeDimensions":[],"timeDimensions":[],"measures":["products.average_price","products.average_margin"],"leafMeasureAdditive":false,"leafMeasures":["products.average_price","products.average_margin"],"measureToLeafMeasures":{"products.average_price":[{"measure":"products.average_price","additive":false,"type":"avg"}],"products.average_margin":[{"measure":"products.average_margin","additive":false,"type":"number"}]},"hasNoTimeDimensionsWithoutGranularity":true,"allFiltersWithinSelectedDimensions":true,"isAdditive":false,"granularityHierarchies":{"year":["year","quarter","month","month","day","hour","minute","second"],"quarter":["quarter","month","day","hour","minute","second"],"month":["month","day","hour","minute","second"],"week":["week","day","hour","minute","second"],"day":["day","hour","minute","second"],"hour":["hour","minute","second"],"minute":["minute","second"],"second":["second"]},"hasMultipliedMeasures":false,"hasCumulativeMeasures":false,"windowGranularity":null,"filterDimensionsSingleValueEqual":{},"ownedDimensions":["products.productcategory"],"ownedTimeDimensionsWithRollupGranularity":[],"ownedTimeDimensionsAsIs":[],"allBackAliasMembers":{},"hasPostAggregate":false},"annotation":{"measures":{"products.average_price":{"title":"Products Average Price","shortTitle":"Average Price","description":"Average price of the products","type":"number","drillMembers":[],"drillMembersGrouped":{"measures":[],"dimensions":[]}},"products.average_margin":{"title":"Products Average Margin","shortTitle":"Average Margin","description":"Average profit margin per product","type":"number","drillMembers":[],"drillMembersGrouped":{"measures":[],"dimensions":[]}}},"dimensions":{"products.productcategory":{"title":"Products Productcategory","shortTitle":"Productcategory","description":"Category to which the product belongs.","type":"string","meta":{"__secured":false,"secured":false}}},"segments":{},"timeDimensions":{}},"dataSource":"default","dbType":"trino","extDbType":"cubestore","external":false,"slowQuery":false,"total":null,"requestId":"1b38b4b6-9cab-4c45-8759-dbfc34759ff3-span-1"}- You can prettify this JSON Structure.
- If your request is a POST (e.g., for
-
Click Send
- Once the body is set up for the specific endpoint, click 'Send' to execute the request.
Possible Responses¶
Continue wait
If the request takes too long to be processed, Lens Backend responds with { "error": "Continue wait" } and 200 status code. This is how the long polling mechanism in Lens is implemented. Clients should continuously retry the same query in a loop until they get a successful result. Subsequent calls to the Lens endpoints are idempotent and don't lead to scheduling new database queries if not required by the refresh_key. Also, receiving Continue wait doesn't mean the database query has been canceled, and it's actually still being processed by the Lens. Database queries that weren't started and are no longer waited by the client's long polling loop will be marked as orphaned and removed from the querying queue.
Possible reasons of Continue wait:
-
The query requested is heavy, and it takes some time for the database to process it. Clients should wait for its completion, continuously sending the same REST API request. continueWaitTimeout can be adjusted in order to change the time Lens waits before returning Continue wait message.
-
There are many queries requested and Lens backend queues them to save database from overloading.
Error Response¶
Lens REST API has basic errors and HTTP Error codes for all requests.
| Status | Error response | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 400 | Error message | General error. It may be a database error, timeout, or other issue. Check error message for details. |
| 403 | Authorization header isn't set | You didn't provide an auth token. Provide a valid API Token or disable authorization. |
| 403 | Invalid token | The auth token provided is not valid. It may be expired or have an invalid signature. |
| 500 | Error message | Lens internal server error. Check error message for details. |
Using Curl¶
Curl is a command-line tool used for transferring data with URLs, making it a convenient choice for interacting with APIs directly from the terminal. Ensure that curl is installed on your system before proceeding.
-
Prepare the Request: To send a GraphQL query using Curl, construct your request with the following template:
curl -X POST <URL> \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -H "apikey: <DATAOS_API_KEY>" \ -d '{"query": "<QUERY>"}'-
Replace
<URL>with the appropriate endpoint based on your environment:- For local development, use:
- For a deployed Lens model, use:
-
Replace
<DATAOS_API_KEY>with your actual DataOS API key. Refer to the Generating an API Key section for more information on obtaining an API key. -
Replace
<DATAOS_FQDN>with the fully qualified domain name of your DataOS instance. For example:alpha-omega.dataos.apporhappy-kangaroo.dataos.app. -
Replace
<WORKSPACE>with the DataOS Workspace name where the Lens is deployed. -
Replace
<NAME_OF_LENS>with the name of your deployed Lens model. This corresponds to the specific Lens model you want to query. -
Replace
<QUERY>with your query. Make sure to format the query as a valid JSON string. Make sure you paste the query body as per the endpoint.
Sample Request:
curl -X POST 'http://liberal-donkey.dataos.app/lens2/api/public:sales-analysis/v2/load' \ --header 'Content-Type: application/json' \ --header 'Authorization: Bearer dG9rZW5fc3RlYWRpbHlfbWVyZWx5X2Z1bl9veXN0ZXIuMjNjYTdkYzktOGU2Zi00MmIzLTgxMjktM2MxNDY5MTNlYzdl' \ --data '{ "query": { "dimensions": [ "products.productcategory" ], "measures": [ "products.average_price", "products.average_margin" ] } }' -
-
Execute the Command: Run the command in your terminal to execute the query and view the response.
Ensure you replace the placeholders with the actual values specific to your environment. Properly formatted queries and valid API keys are essential for successful API interactions.
Using Python¶
Python provides a flexible and powerful way to interact with the Lens REST API. It is especially useful for building automation scripts or for use in data analysis workflows. Ensure that Python and the requests library are installed on your system before proceeding.
-
Install the
requestsLibrary:If you haven’t already installed the
requestslibrary, you can do so by running the following command: -
Prepare the Python Script:
Use the following template to create a Python script for querying the Lens REST API:
import requests # Define the URL of the Lens RESTAPI endpoint url = "<URL>" # Define the headers including the API key headers = { "Content-Type": "application/json", "apikey": "<DATAOS_API_KEY>" } # Define your RESTAPI query query = """ <QUERY> """ # Send the POST request response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json={'query': query}) # Print the response print(response.json())- Replace
<URL>with the appropriate endpoint based on your environment: - For local development, use:
-
For a deployed Lens model, use:
-
Replace
<DATAOS_API_KEY>with your actual DataOS API key. Refer to the Generating an API Key section for more information on obtaining an API key. -
Replace
<DATAOS_FQDN>with the fully qualified domain name of your DataOS instance. For example:alpha-omega.dataos.apporhappy-kangaroo.dataos.app. -
Replace
<WORKSPACE>with the workspace name associated with your Lens model. This is typically the name of the DataOS Workspace where the Lens is deployed. For example:public,sandbox, etc. -
Replace
<NAME_OF_LENS>with the name of your deployed Lens model. This corresponds to the specific Lens model you want to query. -
Replace
<QUERY>with the specific fields you want to query from your schema. Make sure to format the query string as valid JSON.
Sample Script:
import requests # Define the URL of the Lens RESTAPI endpoint url = "https://alpha-omega.dataos.app/lens2/api/public:sales-analysis/v2/load" # Define the headers including the API key headers = { "Content-Type": "application/json", "apikey": "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz" } # Define your RESTAPI query query = """ query LensQuery { table { products { categories average_margin } } } """ # Send the POST request response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json={'query': query}) # Print the response print(response.json())In the above sample: -
<URL>ishttps://alpha-omega.dataos.app/lens2/api/public:sales-analysis/v2/load-<DATAOS_API_KEY>isabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz(replace with your actual API key) -<WORKSPACE>ispublic-<NAME_OF_LENS>issales-analysis- The query fetchesproductcategoryandaverage_pricefields from theproductstable. - Replace
-
Run the Script:
Save the script as a
.pyfile and execute it using the following command in your terminal:This will send the query to the Lens API and print the response to your terminal.
Note: Ensure you replace the placeholders with the actual values specific to your environment. Properly formatted queries and valid API keys are essential for successful API interactions.